Academic Vocabulary for Social Studies Grade 2
... 8. limited resources- having only a certain amount of something 9. natural resources/raw materials- materials used to make a product; trees 10. human resources- people that work in factories and make things 11. capital resources- all of the tools used to make a good 12. occupation- a job a person wo ...
... 8. limited resources- having only a certain amount of something 9. natural resources/raw materials- materials used to make a product; trees 10. human resources- people that work in factories and make things 11. capital resources- all of the tools used to make a good 12. occupation- a job a person wo ...
Folded Mountain Range
... Folded mountain ranges are the largest and most complex type of mountains found on continents. Most of these mountains consist of roughly parallel ridges of sedimentary rock. The energy needed to shape thousands of meters of sedimentary rock layers into folded mountains comes from the movements of E ...
... Folded mountain ranges are the largest and most complex type of mountains found on continents. Most of these mountains consist of roughly parallel ridges of sedimentary rock. The energy needed to shape thousands of meters of sedimentary rock layers into folded mountains comes from the movements of E ...
Chapter 1 Geography, History, and the
... earth from place to place? The answer is that the Earth rotates on its axis. As the Earth moves, the sun appears to rise in some places and set in other places. Throughout the world people use the rising and setting of the sun to set their clocks. ...
... earth from place to place? The answer is that the Earth rotates on its axis. As the Earth moves, the sun appears to rise in some places and set in other places. Throughout the world people use the rising and setting of the sun to set their clocks. ...
Chapter 1
... lines measure distance east and west of the PRIME MERIDIAN The PRIME MERIDIAN is an imaginary line that runs thru Greenwich, England from the North Pole to the South Pole. ...
... lines measure distance east and west of the PRIME MERIDIAN The PRIME MERIDIAN is an imaginary line that runs thru Greenwich, England from the North Pole to the South Pole. ...
Fall Semester Review Questions 1. What is the disadvantage of a
... B. weathering C. earthquakes D. erosion 15. An example of an external force of change is A. weathering B. subduction C. accretion D. faulting 16. Which of the following examples illustrates the difference between physical weathering and chemical weathering? A. Beaches form from the sediments washed ...
... B. weathering C. earthquakes D. erosion 15. An example of an external force of change is A. weathering B. subduction C. accretion D. faulting 16. Which of the following examples illustrates the difference between physical weathering and chemical weathering? A. Beaches form from the sediments washed ...
IntroBasics
... – Mapmakers wanted to present this information correctly. – The best way was to put it on a globe, a ...
... – Mapmakers wanted to present this information correctly. – The best way was to put it on a globe, a ...
Reading an Elevation Map
... above sea level the land in a region is. Land that is at sea level is at the same height, or level, as the sea. Land rises from that point. (In some inland areas, however, the land is actually below sea level.) The highest point above sea level on Earth is the peak of Mount Everest. It stands 29,028 ...
... above sea level the land in a region is. Land that is at sea level is at the same height, or level, as the sea. Land rises from that point. (In some inland areas, however, the land is actually below sea level.) The highest point above sea level on Earth is the peak of Mount Everest. It stands 29,028 ...
document
... What is Human Geography? The study of how people make places, how we organize space and society, how we interact with each other in places and across space, and how we make sense of others and ourselves in our locality, region, and world. ...
... What is Human Geography? The study of how people make places, how we organize space and society, how we interact with each other in places and across space, and how we make sense of others and ourselves in our locality, region, and world. ...
A revised map of Australia`s Physiographic Regions: a hierarchical
... Soil Resources Information System (ASRIS). The revision was carried out by digitising the original map and then overlaying it on the Shuttle Radar Terrain Model (SRTM), which has a resolution of 90 m. The first step was to adjust the original boundaries to more closely reflect the landforms as depic ...
... Soil Resources Information System (ASRIS). The revision was carried out by digitising the original map and then overlaying it on the Shuttle Radar Terrain Model (SRTM), which has a resolution of 90 m. The first step was to adjust the original boundaries to more closely reflect the landforms as depic ...
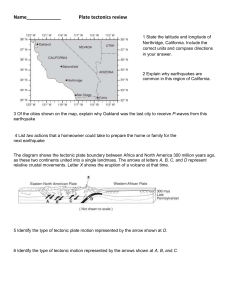
Name_____________ Plate tectonics review 1 State the latitude
... bedrock geology of Iceland, an island located on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on surface bedrock which is igneous in origin. Glaciers cover some surface bedrock. ...
... bedrock geology of Iceland, an island located on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. Points A, B, C, and D are locations on surface bedrock which is igneous in origin. Glaciers cover some surface bedrock. ...
Ocean Landforms - Net Start Class
... A deep-sea trench is a narrow, elongate, v-shaped depression in the ocean floor. ...
... A deep-sea trench is a narrow, elongate, v-shaped depression in the ocean floor. ...
File - Crook County School District #1
... central place and the surrounding places affected by it, Perceptual regions defined by people’s feelings and attitudes about the areas) Movement (How people, goods, ideas move from on place to another) Human-Environment Interaction (HEI) (How people use their environment) How have they changed it? ...
... central place and the surrounding places affected by it, Perceptual regions defined by people’s feelings and attitudes about the areas) Movement (How people, goods, ideas move from on place to another) Human-Environment Interaction (HEI) (How people use their environment) How have they changed it? ...
GEOREFERENCING
... Equidistant projections Equidistant maps preserve the distances between certain points. Scale is not maintained correctly by any projection throughout an entire map; however, there are, in most cases, one or more lines on a map along which scale is maintained correctly. Most equidistant projections ...
... Equidistant projections Equidistant maps preserve the distances between certain points. Scale is not maintained correctly by any projection throughout an entire map; however, there are, in most cases, one or more lines on a map along which scale is maintained correctly. Most equidistant projections ...
geography
... • Map projections are ways of drawing the Earth on a flat surface – Mercator projection • Shows true shapes of landmasses • Distorts size, especially for places far from Equator ...
... • Map projections are ways of drawing the Earth on a flat surface – Mercator projection • Shows true shapes of landmasses • Distorts size, especially for places far from Equator ...
geography
... • Map projections are ways of drawing the Earth on a flat surface – Mercator projection • Shows true shapes of landmasses • Distorts size, especially for places far from Equator ...
... • Map projections are ways of drawing the Earth on a flat surface – Mercator projection • Shows true shapes of landmasses • Distorts size, especially for places far from Equator ...
Document
... 2. Describe the stages involved in Nebula hypothesis including the abundant elements involved in the early formation of the universe. ...
... 2. Describe the stages involved in Nebula hypothesis including the abundant elements involved in the early formation of the universe. ...
What Grows Here? - Edible Schoolyard Pittsburgh
... sugarcane, thrive under the predictably hot and humid weather conditions found in the Earth’s tropical zones. Tropical Zones are often grouped into more specialized climate categories, such as “humid-‐tropic”, “ ...
... sugarcane, thrive under the predictably hot and humid weather conditions found in the Earth’s tropical zones. Tropical Zones are often grouped into more specialized climate categories, such as “humid-‐tropic”, “ ...
Plate Tectonics
... Give map of the world and have students (in groups) recreate Pangaea from continents, using the map of plate boundaries (would help if they have some knowledge of what is where, divergent and convergent boundaries) Then give map of Pangaea to compare. Using this new map they can mark on the plate ma ...
... Give map of the world and have students (in groups) recreate Pangaea from continents, using the map of plate boundaries (would help if they have some knowledge of what is where, divergent and convergent boundaries) Then give map of Pangaea to compare. Using this new map they can mark on the plate ma ...
Physical Geography of Southeast Asia
... into Myanmar (Burma) and the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR). The precipitous terrain of Lao PDR and Thailand generates interest in the river and its tributaries for hydropower development. The terrain, soils, water, and climate make it one of the world’s most biologically rich regions. T ...
... into Myanmar (Burma) and the Lao People’s Democratic Republic (Lao PDR). The precipitous terrain of Lao PDR and Thailand generates interest in the river and its tributaries for hydropower development. The terrain, soils, water, and climate make it one of the world’s most biologically rich regions. T ...
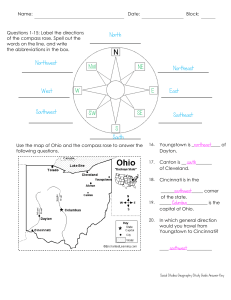
North Northeast East Southeast South Southwest
... Use the scale on the map to answer the distance question below. Draw a line between each pair of cities in each question. Use a different color for each one. ...
... Use the scale on the map to answer the distance question below. Draw a line between each pair of cities in each question. Use a different color for each one. ...
Earth Science Project: Three Dimensional Model of
... hot, convecting mantle; and a dense, metallic core. 6.1.c: Students know lithospheric plates the size of continents and oceans move at rates of centimeters per year in response to movements in the mantle. ...
... hot, convecting mantle; and a dense, metallic core. 6.1.c: Students know lithospheric plates the size of continents and oceans move at rates of centimeters per year in response to movements in the mantle. ...
geogch01
... • degree- a unit of measure used to determine absolute location; on globes and maps, latitude and longitude are measured in degrees • equator- an imaginary line that circles the globe at its widest point (halfway between the North and South poles), dividing the Earth into two halves called hemispher ...
... • degree- a unit of measure used to determine absolute location; on globes and maps, latitude and longitude are measured in degrees • equator- an imaginary line that circles the globe at its widest point (halfway between the North and South poles), dividing the Earth into two halves called hemispher ...
Early world maps
The earliest known world maps date to classical antiquity, the oldest examples of the 6th to 5th centuries BC still based on the flat Earth paradigm.World maps assuming a spherical Earth first appear in the Hellenistic period.The developments of Greek geography during this time, notably by Eratosthenes and Posidonius culminated in the Roman era, with Ptolemy's world map (2nd century AD), which would remain authoritative throughout the Middle Ages.Since Ptolemy, knowledge of the approximate size of the globe allowed cartographers to estimate the extent of their geographical knowledge, and to indicate parts of the globe known to exist but not yet explored as terra incognita.With the Age of Discovery, during the 15th to 18th centuries, world maps became increasingly accurate; exploration of Antarctica and the interior of Africa was left to the 19th and early 20th century.