Overview of Geologic Structures
... Generally: as stress is applied to rocks at low temp, and low press, rocks will first deform elastically (with ability to return to original size and shape once stress is removed), once the level of stress exceeds the elastic limit of a given type of rock (i.e. the point or strength of a rock, with ...
... Generally: as stress is applied to rocks at low temp, and low press, rocks will first deform elastically (with ability to return to original size and shape once stress is removed), once the level of stress exceeds the elastic limit of a given type of rock (i.e. the point or strength of a rock, with ...
Crustal-Scale Cross-Section of the US Cordillera
... continental margin collisions, and subduction of a large oceanic plateau. Early Mesozoic subduction along the Pacific margin of North America was modified by a 165–176 Ma collision of a major intraoceanic arc/ophiolite complex. A complex SW Pacific-like set of small plates and their boundaries at va ...
... continental margin collisions, and subduction of a large oceanic plateau. Early Mesozoic subduction along the Pacific margin of North America was modified by a 165–176 Ma collision of a major intraoceanic arc/ophiolite complex. A complex SW Pacific-like set of small plates and their boundaries at va ...
L
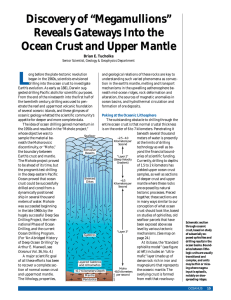
... of opportunity finally to sample the oceanic lithosphere in detail. Marine geologists are now proposing to drill a series of half- to one-kilometer-deep holes, aligned in the direction of fault slip across the surfaces of megamullions. From these cores, we should be able to construct a composite, bu ...
... of opportunity finally to sample the oceanic lithosphere in detail. Marine geologists are now proposing to drill a series of half- to one-kilometer-deep holes, aligned in the direction of fault slip across the surfaces of megamullions. From these cores, we should be able to construct a composite, bu ...
B - Kaufman ISD
... 64. Fast moving water in a river or a stream often carries sediments. As the water slows down, these sediments are left along the banks or the bottom of the river or stream. This process of leaving sediments in a new place is called— A B C D ...
... 64. Fast moving water in a river or a stream often carries sediments. As the water slows down, these sediments are left along the banks or the bottom of the river or stream. This process of leaving sediments in a new place is called— A B C D ...
B - Midland ISD
... 64. Fast moving water in a river or a stream often carries sediments. As the water slows down, these sediments are left along the banks or the bottom of the river or stream. This process of leaving sediments in a new place is called— A B C D ...
... 64. Fast moving water in a river or a stream often carries sediments. As the water slows down, these sediments are left along the banks or the bottom of the river or stream. This process of leaving sediments in a new place is called— A B C D ...
the structure of the sierra maestra near santiago de cuba
... mountain ridges found along the south coast of the Province of Oriente; but, locally, the name is also commonly applied to the most prominent ridge, and this, in some cases, has caused much confusion. In this article the name is used for the entire range and also for the well-defined divide that fol ...
... mountain ridges found along the south coast of the Province of Oriente; but, locally, the name is also commonly applied to the most prominent ridge, and this, in some cases, has caused much confusion. In this article the name is used for the entire range and also for the well-defined divide that fol ...
Faults, Block Rotations and the Origin of the Orava Basin
... (Serravallian). The NNW-SSE strike-slip fault in the Outer Western Carpathian wear reactivated during the late Miocene time of extension as the normal ones. The elevation of the Babia Góra and Pilsko and the present-day morphotectonic depression between these two mountains is probably related to the ...
... (Serravallian). The NNW-SSE strike-slip fault in the Outer Western Carpathian wear reactivated during the late Miocene time of extension as the normal ones. The elevation of the Babia Góra and Pilsko and the present-day morphotectonic depression between these two mountains is probably related to the ...
Chapter 2: Rocks of the Northwest Central US
... sandstones, and iron formations, were deposited between 1.8 and 1.6 billion years ago before being subjected to mild metamorphism. although the Sioux Quartzite is largely overlain by Cretaceous rocks and Pleistocene glacial materials, it appears in small outcrops in southeastern South Dakota and adj ...
... sandstones, and iron formations, were deposited between 1.8 and 1.6 billion years ago before being subjected to mild metamorphism. although the Sioux Quartzite is largely overlain by Cretaceous rocks and Pleistocene glacial materials, it appears in small outcrops in southeastern South Dakota and adj ...
Geologic Map of the Deer Lodge and Conleys Lake 71/2
... lacking major faults on the east side. With the exception of a small remnant of metasedimentary rocks of the Proterozoic Belt Supergroup on the west side of the Deer Lodge Valley, all rocks exposed in these two quadrangles are Mesozoic or Cenozoic. The Swift Formation (Jurassic age) and Cretaceous s ...
... lacking major faults on the east side. With the exception of a small remnant of metasedimentary rocks of the Proterozoic Belt Supergroup on the west side of the Deer Lodge Valley, all rocks exposed in these two quadrangles are Mesozoic or Cenozoic. The Swift Formation (Jurassic age) and Cretaceous s ...
MSU Billings Government Documents Weeding List I 19.3 Numbers 2000’s
... Geochemical Survey of the Craig Study Area – Craig and Dixon Entrance Quadrangles and the Western Edges of the Ketchikan and Prince Rupert Quadrangles, Southeast Alaska I 19.3: 2083-A-K ...
... Geochemical Survey of the Craig Study Area – Craig and Dixon Entrance Quadrangles and the Western Edges of the Ketchikan and Prince Rupert Quadrangles, Southeast Alaska I 19.3: 2083-A-K ...
Bulletin 96: Geology of the Little Hatchet Mountains Hidalgo and
... siltstone, limestone-cobble conglomerate, arkose, and sandy (arkosic) limestone. Limestone conglomerate and red elastic beds are predominant in the lower part. Arkose and gray shale are more common in the upper part. Near the top, limestone is more common. The contact with the overlying U-Bar Format ...
... siltstone, limestone-cobble conglomerate, arkose, and sandy (arkosic) limestone. Limestone conglomerate and red elastic beds are predominant in the lower part. Arkose and gray shale are more common in the upper part. Near the top, limestone is more common. The contact with the overlying U-Bar Format ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... The sinking is triggered by the disturbance during earthquake, storm, or slump At greater depths, partially consolidated mud breaks into pieces and sink into underlying sand, forming disrupted bedding ...
... The sinking is triggered by the disturbance during earthquake, storm, or slump At greater depths, partially consolidated mud breaks into pieces and sink into underlying sand, forming disrupted bedding ...
Field Guide to Tectonic Evolution of Utah`s Central Wasatch
... of stretching of Earth’s crust across the Wasatch Fault is only 1-2 mm/yr. However, the last major earthquake was 1350 years ago. Since this time 1.3 to 2.7 meters of elastic strain energy has accumulated along the Salt Lake City segment of the Wasatch Fault. A fault slip of 1-3 meters over the 40 k ...
... of stretching of Earth’s crust across the Wasatch Fault is only 1-2 mm/yr. However, the last major earthquake was 1350 years ago. Since this time 1.3 to 2.7 meters of elastic strain energy has accumulated along the Salt Lake City segment of the Wasatch Fault. A fault slip of 1-3 meters over the 40 k ...
View PDF - Cengage
... most recent supercontinent, called Pangaea, during the Paleozoic Era (see Figure NY-NJ.2). During the Mesozoic Era (the so-called Age of Reptiles), Pangaea rifted apart and a new ocean basin, the Atlantic, formed along the eastern margin of North America. The Atlantic Ocean basin continued to widen ...
... most recent supercontinent, called Pangaea, during the Paleozoic Era (see Figure NY-NJ.2). During the Mesozoic Era (the so-called Age of Reptiles), Pangaea rifted apart and a new ocean basin, the Atlantic, formed along the eastern margin of North America. The Atlantic Ocean basin continued to widen ...
Record - cloudfront.net
... A whole range of terms may depend on how one views a particular concept, such as geosynclinal evolution, the cause of mountain building, or the cycle of erosion. There are two main ways of tackling this problem: 1. The glossary might attempt to include translations of ...
... A whole range of terms may depend on how one views a particular concept, such as geosynclinal evolution, the cause of mountain building, or the cycle of erosion. There are two main ways of tackling this problem: 1. The glossary might attempt to include translations of ...
Questions for any rock face 8: faults What
... Every effort has been made to locate and contact copyright holders of materials included in this activity in order to obtain their permission. Please contact us if, however, you believe your copyright is being infringed: we welcome any information that will help us to update our records. If you have ...
... Every effort has been made to locate and contact copyright holders of materials included in this activity in order to obtain their permission. Please contact us if, however, you believe your copyright is being infringed: we welcome any information that will help us to update our records. If you have ...
The Ocean Bottom
... produced by the break down of rocks on land Biogenic sediment produced by organisms Authigenic sediment produced in place by chemical reactions in seawater or within the upper sediment Volcanogenic sediment produced from the ejections of volcanic eruptions Cosmogenic sediments produced from ...
... produced by the break down of rocks on land Biogenic sediment produced by organisms Authigenic sediment produced in place by chemical reactions in seawater or within the upper sediment Volcanogenic sediment produced from the ejections of volcanic eruptions Cosmogenic sediments produced from ...
Structure
... layer as it intersects with a horizontal surface • Dip – is measured at right angles to strike and is the amount of tilting of the formation (angle at which the bed is inclined from the horizontal) ...
... layer as it intersects with a horizontal surface • Dip – is measured at right angles to strike and is the amount of tilting of the formation (angle at which the bed is inclined from the horizontal) ...
05c_U7E_PlanetEarth_p396-410
... lighter continental crust of the North American Plate, as you can see in Figure 3.19. At the same time, the pressure of the two plates ramming against each other forced the sediments on the edge of the North American Plate to fold and break. Some of these sediment layers were pushed so hard that the ...
... lighter continental crust of the North American Plate, as you can see in Figure 3.19. At the same time, the pressure of the two plates ramming against each other forced the sediments on the edge of the North American Plate to fold and break. Some of these sediment layers were pushed so hard that the ...
klip river wetlands - Aberystwyth University Users Site
... deposited in the Permian period by large rivers in delta and floodplain settings. Since the time of deposition, these sandstones and shales have been little disturbed by faulting, folding or tilting and retain their original horizontal layering. Good outcrops which reveal this layering can be seen a ...
... deposited in the Permian period by large rivers in delta and floodplain settings. Since the time of deposition, these sandstones and shales have been little disturbed by faulting, folding or tilting and retain their original horizontal layering. Good outcrops which reveal this layering can be seen a ...
Current ripple marks
... • On broad continental margins – with abundant sand, long barrier islands lie offshore – separated from the mainland by a lagoon ...
... • On broad continental margins – with abundant sand, long barrier islands lie offshore – separated from the mainland by a lagoon ...
The Gold Belt of the Blue Mountains of Oregon
... The part of the Blue Mountains represented on the accompanying map consists of several cores of older rocks partly surrounded by floods of Neocene lavas, rhyolites, andesites, and basalts. If the map were extended somewhat farther north it would be seen that the same lavas entirely surround the nort ...
... The part of the Blue Mountains represented on the accompanying map consists of several cores of older rocks partly surrounded by floods of Neocene lavas, rhyolites, andesites, and basalts. If the map were extended somewhat farther north it would be seen that the same lavas entirely surround the nort ...
Three early arguments for deep time— part 3
... and underestimate the depositional potential of the Flood: ...
... and underestimate the depositional potential of the Flood: ...
. ·
... and diagenetically controlled pore geometry are partially or wholly sedimentological features. The TrentonIBlack River play is basin wide in scope, and accurate stratigraphic correlations and analyses are necessary for rigorous petroleum exploration and development (Figure 7). Sequence stratigraphic ...
... and diagenetically controlled pore geometry are partially or wholly sedimentological features. The TrentonIBlack River play is basin wide in scope, and accurate stratigraphic correlations and analyses are necessary for rigorous petroleum exploration and development (Figure 7). Sequence stratigraphic ...
Chapter 6 - Sedimentary Rock
... • Windblown dunes are typically composed – of well-sorted, well-rounded sand – with cross-beds meters to tens of meters high – land-dwelling plants and animals make up any ...
... • Windblown dunes are typically composed – of well-sorted, well-rounded sand – with cross-beds meters to tens of meters high – land-dwelling plants and animals make up any ...
Geology of the Death Valley area
The exposed geology of the Death Valley area presents a diverse and complex set of at least 23 formations of sedimentary units, two major gaps in the geologic record called unconformities, and at least one distinct set of related formations geologists call a group. The oldest rocks in the area that now includes Death Valley National Park are extensively metamorphosed by intense heat and pressure and are at least 1700 million years old. These rocks were intruded by a mass of granite 1400 Ma (million years ago) and later uplifted and exposed to nearly 500 million years of erosion.Marine deposition occurred 1200 to 800 Ma, creating thick sequences of conglomerate, mudstone, and carbonate rock topped by stromatolites, and possibly glacial deposits from the hypothesized Snowball Earth event. Rifting thinned huge roughly linear parts of the supercontinent Rodinia enough to allow sea water to invade and divide its landmass into component continents separated by narrow straits. A passive margin developed on the edges of these new seas in the Death Valley region. Carbonate banks formed on this part of the two margins only to be subsided as the continental crust thinned until it broke, giving birth to a new ocean basin. An accretion wedge of clastic sediment then started to accumulate at the base of the submerged precipice, entombing the region's first known fossils of complex life. These sandy mudflats gave way about 550 Ma to a carbonate platform which lasted for the next 300 million years of Paleozoic time.The passive margin switched to active margin in the early-to-mid Mesozoic when the Farallon Plate under the Pacific Ocean started to dive below the North American Plate, creating a subduction zone; volcanoes and uplifting mountains were created as a result. Erosion over many millions of years created a relatively featureless plain. Stretching of the crust under western North America started around 16 Ma and is thought to be caused by upwelling from the subducted spreading-zone of the Farallon Plate. This process continues into the present and is thought to be responsible for creating the Basin and Range province. By 2 to 3 million years ago this province had spread to the Death Valley area, ripping it apart and creating Death Valley, Panamint Valley and surrounding ranges. These valleys partially filled with sediment and, during colder periods during the current ice age, with lakes. Lake Manly was the largest of these lakes; it filled Death Valley during each glacial period from 240,000 years ago to 10,000 years ago. By 10,500 years ago these lakes were increasingly cut off from glacial melt from the Sierra Nevada, starving them of water and concentrating salts and minerals. The desert environment seen today developed after these lakes dried up.