Combined field trip guide/program with abstracts
... Okanagan Valley is broadly a north-south trending tectonic lineament that is over 300 km in length located in south-central BC and northern Washington (Fig. 2). It separates the Okanagan Highlands plateau to the east, from areas of generally lower elevation, but greater relief, to the west (see cove ...
... Okanagan Valley is broadly a north-south trending tectonic lineament that is over 300 km in length located in south-central BC and northern Washington (Fig. 2). It separates the Okanagan Highlands plateau to the east, from areas of generally lower elevation, but greater relief, to the west (see cove ...
Facets of the Late Paleozoic Strata in Southwestern New Mexico
... conglomerates, red silts, gypsum, and andesite breccia (Oligocene in age?) overlie the Hueco Formation. In this area, both the post-Hueco Paleozoic strata and the Cretaceous beds were removed by erosion during early Tertiary time. Near Emory Pass and Kingston in the Black Range, Tertiary andesites a ...
... conglomerates, red silts, gypsum, and andesite breccia (Oligocene in age?) overlie the Hueco Formation. In this area, both the post-Hueco Paleozoic strata and the Cretaceous beds were removed by erosion during early Tertiary time. Near Emory Pass and Kingston in the Black Range, Tertiary andesites a ...
Mesozoic fill-sequences in Hefei Basin: Implication for Dabie
... surfaces frequently occur at the bottom of this unit. The upward-fining depositional processes are developed in the Zhangqiao Formation, which represents deposition of sandy braided river and alluvial plain. However one complete reverse-grading unit occurs from the K2z1 to the K2z2, with increasing ...
... surfaces frequently occur at the bottom of this unit. The upward-fining depositional processes are developed in the Zhangqiao Formation, which represents deposition of sandy braided river and alluvial plain. However one complete reverse-grading unit occurs from the K2z1 to the K2z2, with increasing ...
5. Nooksack Valley
... Uplift of the modern Cascade and Olympic Mountains commenced about 5 million years ago, developing as a set of north-south trending folds which have resulted from compression of the continental margin. The Puget -Georgia Basin is the trough between those two folds. Over the last two million years, t ...
... Uplift of the modern Cascade and Olympic Mountains commenced about 5 million years ago, developing as a set of north-south trending folds which have resulted from compression of the continental margin. The Puget -Georgia Basin is the trough between those two folds. Over the last two million years, t ...
Chapter 2: Rocks of the Southeastern US
... What happens to a rock when it is metamorphosed? When rocks are subjected to high enough temperatures or pressures, their characteristics begin to change. The weight of overlying rock can cause minerals to realign perpendicularly to the direction of pressure, layering them in a pattern called foliat ...
... What happens to a rock when it is metamorphosed? When rocks are subjected to high enough temperatures or pressures, their characteristics begin to change. The weight of overlying rock can cause minerals to realign perpendicularly to the direction of pressure, layering them in a pattern called foliat ...
A R T I C L E S - Geoscience Research Institute
... of sediment to the ocean of 20,000 million tons/yr, it would still take only 178 Ma to fill these ocean basins with sediment. In other words, the present rate of transport of sediment by rivers could fill the oceans 19× in 3500 Ma. Of course, the oceans, which average 3.8 km in depth of water, are n ...
... of sediment to the ocean of 20,000 million tons/yr, it would still take only 178 Ma to fill these ocean basins with sediment. In other words, the present rate of transport of sediment by rivers could fill the oceans 19× in 3500 Ma. Of course, the oceans, which average 3.8 km in depth of water, are n ...
Himalayan Granite
... using geophysical methods, notably seismology. Earthquakes occur when rocks deep in the crust move along faults and spontaneously release energy. Earthquakes release shock waves, which travel along the surface of the earth (surface waves) and cause the ground to vibrate. Shorter period vibrations mo ...
... using geophysical methods, notably seismology. Earthquakes occur when rocks deep in the crust move along faults and spontaneously release energy. Earthquakes release shock waves, which travel along the surface of the earth (surface waves) and cause the ground to vibrate. Shorter period vibrations mo ...
Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch10
... 3. Stress is closely related to force although the two are technically not the same. Force refers to any action that tends to put stationary objects into motion or change the motion of moving objects. Stress refers to the amount of force applied to a given area. Therefore, stress is force that is sp ...
... 3. Stress is closely related to force although the two are technically not the same. Force refers to any action that tends to put stationary objects into motion or change the motion of moving objects. Stress refers to the amount of force applied to a given area. Therefore, stress is force that is sp ...
Part 3: Normal faults and extensional tectonics
... depth, fabrics reflecting progressively colder and more brittle deformational envi ronments are superimposed upon one another. So, walking from the interior of the core complex out towards the lowgrade upper plate rocks ductile fabrics and my lonites will be overprinted by brittleductile transiti ...
... depth, fabrics reflecting progressively colder and more brittle deformational envi ronments are superimposed upon one another. So, walking from the interior of the core complex out towards the lowgrade upper plate rocks ductile fabrics and my lonites will be overprinted by brittleductile transiti ...
Nipigon GeoTour
... These rocks underlie the entire lake, but only to the west and south are they well exposed on land. The history of these ancient rift rocks began 1.1 billion years ago when forces in the Earth’s mantle stretched the North American continent, breaking it along geological faults. The land sagged betwe ...
... These rocks underlie the entire lake, but only to the west and south are they well exposed on land. The history of these ancient rift rocks began 1.1 billion years ago when forces in the Earth’s mantle stretched the North American continent, breaking it along geological faults. The land sagged betwe ...
Balestro et al., 2011
... The Pellice Valley is part of the Cottian Alps, the central sector of the Italian Western Alps. It is about 20 km in length and borders with the French Queyras region to the west, the Germanasca Valley to the north and the Po Valley to the south. The Pellice Valley is characterized by a composite st ...
... The Pellice Valley is part of the Cottian Alps, the central sector of the Italian Western Alps. It is about 20 km in length and borders with the French Queyras region to the west, the Germanasca Valley to the north and the Po Valley to the south. The Pellice Valley is characterized by a composite st ...
`) Structural evolution of the Raft River Basin, Idaho
... region, timing of events in the Albion and Raft River Mountains is still open to question. It is generally agreed, however, that: (I) the crystalline basement is 2.5 b.y. old; (2) regional west to east thrusting occurred during the early Tertiary; (3) an early metamorphic event ended in late Cre ta ...
... region, timing of events in the Albion and Raft River Mountains is still open to question. It is generally agreed, however, that: (I) the crystalline basement is 2.5 b.y. old; (2) regional west to east thrusting occurred during the early Tertiary; (3) an early metamorphic event ended in late Cre ta ...
Frimmel_Chameis subterrane_Gariep
... typically concentrated in continental detrital phases, such as Zr and Nb, indicate an open marine environment with little continental clastic influence, as these trace element concentrations are all in the range of normal marine carbonate rocks. However, the evaporitederived dolomite is almost devoi ...
... typically concentrated in continental detrital phases, such as Zr and Nb, indicate an open marine environment with little continental clastic influence, as these trace element concentrations are all in the range of normal marine carbonate rocks. However, the evaporitederived dolomite is almost devoi ...
Rock Your World
... high)in)the)Sierra)down)to)the)Central)Valley.)))This)accounts)for)the)rich) agricultural)soils)of)the)valley)made)up)of)sands,)clays,)silts,)and)minerals) from)the)surrounding)mountains.))Heavier)rocks)and)boulders)settle)out)on) stream)bottoms)in)the)mountains.))As)they)continue)to)be)weathered)an ...
... high)in)the)Sierra)down)to)the)Central)Valley.)))This)accounts)for)the)rich) agricultural)soils)of)the)valley)made)up)of)sands,)clays,)silts,)and)minerals) from)the)surrounding)mountains.))Heavier)rocks)and)boulders)settle)out)on) stream)bottoms)in)the)mountains.))As)they)continue)to)be)weathered)an ...
b hulen - University of Nevada, Reno
... northwestern margin of the Basin and Range province. To the west, high volcanic plateaus, (including McGee Mountain) of northwestern Nevada and south-central Oregon form a transition zone between the Basin and Range and the Columbia Plateau (Bonham, 1969). A generalized stratigraphic column for the ...
... northwestern margin of the Basin and Range province. To the west, high volcanic plateaus, (including McGee Mountain) of northwestern Nevada and south-central Oregon form a transition zone between the Basin and Range and the Columbia Plateau (Bonham, 1969). A generalized stratigraphic column for the ...
ft - Colorado Geological Survey
... 'depression that is referred to in this paper as the Rio Grande depression. The basins differ from one another in their physical characters, their present social and economic standards, the order in which they have been successively occupied by different races of men, and the completeness of their o ...
... 'depression that is referred to in this paper as the Rio Grande depression. The basins differ from one another in their physical characters, their present social and economic standards, the order in which they have been successively occupied by different races of men, and the completeness of their o ...
Structures, Mountains and Continents
... that have moved Folds, fractures and faults can occur at any spatial scale, from very small to very big The spatial orientation of planes such as rock layers is described using Strike and Dip Types of faults include normal (extensional), reverse (compressional) and strike-slip (side to side) Folds p ...
... that have moved Folds, fractures and faults can occur at any spatial scale, from very small to very big The spatial orientation of planes such as rock layers is described using Strike and Dip Types of faults include normal (extensional), reverse (compressional) and strike-slip (side to side) Folds p ...
4. Kittitas Valley
... The flows of the Grand Ronde member of the Columbia River Basalts are basalt. Locally, flows include a pillow-palagonite complex at their base, a reflection of the wet landscape which persisted between eruptive events. Elsewhere these flows display classic columnar structure, a reflection of the cooling ...
... The flows of the Grand Ronde member of the Columbia River Basalts are basalt. Locally, flows include a pillow-palagonite complex at their base, a reflection of the wet landscape which persisted between eruptive events. Elsewhere these flows display classic columnar structure, a reflection of the cooling ...
Magneto stratigraphy of Plio-Pleistocene Lake
... sensitive recorders of climate variations; consequently, a local climatic record related to fluctuating depositional environments can be pieced together if suitable age constraints are obtained. In the Confidence Hills of southern Death Valley, late Pliocene to early Pleistocene sediments have been ...
... sensitive recorders of climate variations; consequently, a local climatic record related to fluctuating depositional environments can be pieced together if suitable age constraints are obtained. In the Confidence Hills of southern Death Valley, late Pliocene to early Pleistocene sediments have been ...
Geographic Location of the basin Mumbai Offshore basin
... Shelf Margin block, though under deep marine realm seem to have received lesser quantities of sediments which were either derived from the Diu Arch (?) or from localized provenances. The facies developed in this block are mainly claystone, argillaceous and carbonates with some amount of pelagic faun ...
... Shelf Margin block, though under deep marine realm seem to have received lesser quantities of sediments which were either derived from the Diu Arch (?) or from localized provenances. The facies developed in this block are mainly claystone, argillaceous and carbonates with some amount of pelagic faun ...
Mesozoic Stratigraphy of South
... Andres Mountains, and Lower Cretaceous rocks are known near El Paso, Texas and in the East Potrillo Mountains in southern Dona Ana County. Outcrops are also present near Silver City in western New Mexico where they were called the Sarten sandstone by Darton (1916) . Not enough work has yet been done ...
... Andres Mountains, and Lower Cretaceous rocks are known near El Paso, Texas and in the East Potrillo Mountains in southern Dona Ana County. Outcrops are also present near Silver City in western New Mexico where they were called the Sarten sandstone by Darton (1916) . Not enough work has yet been done ...
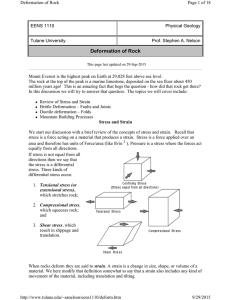
Deformation of Rock
... Horsts & Grabens - Due to the tensional stress responsible for normal faults, they often occur in a series, with adjacent faults dipping in opposite directions. In such a case the down-dropped blocks form grabens and the uplifted blocks form horsts. In areas where tensional stress has recently affec ...
... Horsts & Grabens - Due to the tensional stress responsible for normal faults, they often occur in a series, with adjacent faults dipping in opposite directions. In such a case the down-dropped blocks form grabens and the uplifted blocks form horsts. In areas where tensional stress has recently affec ...
Vertical Contacts - Cal State LA
... accumulated at rates of about 0.3 mm/ka to 2.5 mm/ka (Murchey and Jones, 1984; Hagstrum and Murchey, 1993). In contrast, turbidites on the modern Madeira Abyssal Plain can accumulate at rates of about 1.7-250 mm/ka (Stow et al., 1996). Even the fastest rate of chert sedimentation would require 60 ka ...
... accumulated at rates of about 0.3 mm/ka to 2.5 mm/ka (Murchey and Jones, 1984; Hagstrum and Murchey, 1993). In contrast, turbidites on the modern Madeira Abyssal Plain can accumulate at rates of about 1.7-250 mm/ka (Stow et al., 1996). Even the fastest rate of chert sedimentation would require 60 ka ...
0_primary_structures
... The sinking is triggered by the disturbance during earthquake, storm, or slump At greater depths, partially consolidated mud breaks into pieces and sink into underlying sand, forming disrupted bedding ...
... The sinking is triggered by the disturbance during earthquake, storm, or slump At greater depths, partially consolidated mud breaks into pieces and sink into underlying sand, forming disrupted bedding ...
Geology of the Death Valley area
The exposed geology of the Death Valley area presents a diverse and complex set of at least 23 formations of sedimentary units, two major gaps in the geologic record called unconformities, and at least one distinct set of related formations geologists call a group. The oldest rocks in the area that now includes Death Valley National Park are extensively metamorphosed by intense heat and pressure and are at least 1700 million years old. These rocks were intruded by a mass of granite 1400 Ma (million years ago) and later uplifted and exposed to nearly 500 million years of erosion.Marine deposition occurred 1200 to 800 Ma, creating thick sequences of conglomerate, mudstone, and carbonate rock topped by stromatolites, and possibly glacial deposits from the hypothesized Snowball Earth event. Rifting thinned huge roughly linear parts of the supercontinent Rodinia enough to allow sea water to invade and divide its landmass into component continents separated by narrow straits. A passive margin developed on the edges of these new seas in the Death Valley region. Carbonate banks formed on this part of the two margins only to be subsided as the continental crust thinned until it broke, giving birth to a new ocean basin. An accretion wedge of clastic sediment then started to accumulate at the base of the submerged precipice, entombing the region's first known fossils of complex life. These sandy mudflats gave way about 550 Ma to a carbonate platform which lasted for the next 300 million years of Paleozoic time.The passive margin switched to active margin in the early-to-mid Mesozoic when the Farallon Plate under the Pacific Ocean started to dive below the North American Plate, creating a subduction zone; volcanoes and uplifting mountains were created as a result. Erosion over many millions of years created a relatively featureless plain. Stretching of the crust under western North America started around 16 Ma and is thought to be caused by upwelling from the subducted spreading-zone of the Farallon Plate. This process continues into the present and is thought to be responsible for creating the Basin and Range province. By 2 to 3 million years ago this province had spread to the Death Valley area, ripping it apart and creating Death Valley, Panamint Valley and surrounding ranges. These valleys partially filled with sediment and, during colder periods during the current ice age, with lakes. Lake Manly was the largest of these lakes; it filled Death Valley during each glacial period from 240,000 years ago to 10,000 years ago. By 10,500 years ago these lakes were increasingly cut off from glacial melt from the Sierra Nevada, starving them of water and concentrating salts and minerals. The desert environment seen today developed after these lakes dried up.