Isolated elliptical galaxies in the local Universe
... fraction of ellipticals with younger stellar populations is predicted than in clusters (Kauffmann 1996; Niemi et al. 2010). This may indicate different formation histories. Theoretical models suggest that ellipticals in clusters form through dissipative infall of gas and numerous mergers that took pla ...
... fraction of ellipticals with younger stellar populations is predicted than in clusters (Kauffmann 1996; Niemi et al. 2010). This may indicate different formation histories. Theoretical models suggest that ellipticals in clusters form through dissipative infall of gas and numerous mergers that took pla ...
Galaxy Morphology - The University of Alabama
... interior to a sharp edge. They are commonly seen in Hubble’s disk-shaped S0 class (section 5.2). If a bar is present, the bar may fill a lens in one dimension. Lenses may be round or slightly elliptical in shape (Kormendy 1979). If elliptical in shape they would also be considered ovals. Nuclear bar ...
... interior to a sharp edge. They are commonly seen in Hubble’s disk-shaped S0 class (section 5.2). If a bar is present, the bar may fill a lens in one dimension. Lenses may be round or slightly elliptical in shape (Kormendy 1979). If elliptical in shape they would also be considered ovals. Nuclear bar ...
Spectro-Morphology of Galaxies.
... values in UV are expected to be lower than in optical, for the same galaxy (Kuchinski at al. 2000). Indeed, some early spiral galaxies NGC 1317, M81, and M94 present a ring of young stars in UV (Reichen et al. 1994, Waller et al. 2001), with a faint or nonexistent central bulge that trends to decrea ...
... values in UV are expected to be lower than in optical, for the same galaxy (Kuchinski at al. 2000). Indeed, some early spiral galaxies NGC 1317, M81, and M94 present a ring of young stars in UV (Reichen et al. 1994, Waller et al. 2001), with a faint or nonexistent central bulge that trends to decrea ...
The SAMI Galaxy Survey: extraplanar gas, galactic winds, and their
... Strong supernova feedback drives multiphase gas consisting of hot 107−8 K X-ray emitting gas, warm 104 K ionized gas, and cold neutral atomic and molecular gas, to a speed of a few hundred kilometres per second (see Veilleux et al. 2005 for a review). The optical line-emitting gas usually presents w ...
... Strong supernova feedback drives multiphase gas consisting of hot 107−8 K X-ray emitting gas, warm 104 K ionized gas, and cold neutral atomic and molecular gas, to a speed of a few hundred kilometres per second (see Veilleux et al. 2005 for a review). The optical line-emitting gas usually presents w ...
Where are the Fossils of the First Galaxies? I. Local Volume Maps
... the GK06 simulations with the observed distributions of the ultra faints: (1) Due to the resolution of their N-body simulations, GK06 cannot resolve dwarfs with circular velocity, vmax , < 13 km s−1 which roughly corresponds to a simulated dwarf with LV < 105 L⊙ . With two exceptions, no ultra faint ...
... the GK06 simulations with the observed distributions of the ultra faints: (1) Due to the resolution of their N-body simulations, GK06 cannot resolve dwarfs with circular velocity, vmax , < 13 km s−1 which roughly corresponds to a simulated dwarf with LV < 105 L⊙ . With two exceptions, no ultra faint ...
Galaxy properties
... such a relation is found, it can be used to calibrate cosmic distances and turn a specific class of galaxies into standard candles. On the other hand, relations between different galaxy properties and their evolution with time is crucial to understanding galaxy origins, formation and the relationshi ...
... such a relation is found, it can be used to calibrate cosmic distances and turn a specific class of galaxies into standard candles. On the other hand, relations between different galaxy properties and their evolution with time is crucial to understanding galaxy origins, formation and the relationshi ...
Galactic planar tides on the comets of Oort Cloud and analogs in
... A comet cloud analog of Oort Cloud, is probably a common feature around extra solar planetary systems spread out across the Galaxy. Several external perturbations are able to change the comet orbits. The most important of them is the Galactic tide which may re-inject the comets towards the inner par ...
... A comet cloud analog of Oort Cloud, is probably a common feature around extra solar planetary systems spread out across the Galaxy. Several external perturbations are able to change the comet orbits. The most important of them is the Galactic tide which may re-inject the comets towards the inner par ...
Catalogue of observed tangents to the spiral
... from different tracers. We recorded the complete published reference of each tracer (journal, table, figure, section), and thus were able to delete or replace erroneous or misplaced references. Also, newer instrumentation allows the detection of the arm tangents as inferred from the recent 6.7 GHz m ...
... from different tracers. We recorded the complete published reference of each tracer (journal, table, figure, section), and thus were able to delete or replace erroneous or misplaced references. Also, newer instrumentation allows the detection of the arm tangents as inferred from the recent 6.7 GHz m ...
AST 346, Galaxies, Part 6
... Bulge stars share rotation, larger random motions than disk, σ ∼ Vc . Bulge’s extent is Re , the half-light radius. Studies show Re ' 0.1hR , ranging from 100 pc to several kpc. Origin of bulges is not clear; their high densities could be a result of being older than the disk. Alternatively, they co ...
... Bulge stars share rotation, larger random motions than disk, σ ∼ Vc . Bulge’s extent is Re , the half-light radius. Studies show Re ' 0.1hR , ranging from 100 pc to several kpc. Origin of bulges is not clear; their high densities could be a result of being older than the disk. Alternatively, they co ...
The Diverse Galaxies
... Look-back time is the time light from a distant object has traveled to reach us. Objects have been detected that may be as far away as 13 billion light-years. Look-back time complicates our interpretation of galaxies because the farther out we look, the earlier in time we are seeing them. Ho ...
... Look-back time is the time light from a distant object has traveled to reach us. Objects have been detected that may be as far away as 13 billion light-years. Look-back time complicates our interpretation of galaxies because the farther out we look, the earlier in time we are seeing them. Ho ...
PH607lec10-3gal1
... decline smoothly with radius. When a smooth luminosity profile is subtracted from the actual surface brightness, `shells' or `ripples', centered on the galaxy, are seen. • The fraction of field E galaxies with shell-like features is at least 17% and possibly more than 44%. • The colours of shells in ...
... decline smoothly with radius. When a smooth luminosity profile is subtracted from the actual surface brightness, `shells' or `ripples', centered on the galaxy, are seen. • The fraction of field E galaxies with shell-like features is at least 17% and possibly more than 44%. • The colours of shells in ...
PH607lec09-3gal1
... decline smoothly with radius. When a smooth luminosity profile is subtracted from the actual surface brightness, `shells' or `ripples', centered on the galaxy, are seen. • The fraction of field E galaxies with shell-like features is at least 17% and possibly more than 44%. • The colours of shells in ...
... decline smoothly with radius. When a smooth luminosity profile is subtracted from the actual surface brightness, `shells' or `ripples', centered on the galaxy, are seen. • The fraction of field E galaxies with shell-like features is at least 17% and possibly more than 44%. • The colours of shells in ...
M31`s Heavy Element Distribution and Outer Disk
... metal rich placed at [M/H] = −1.0, Milky Way metal rich globular clusters are concentrated toward the center of the galaxy. M31 has a larger number of metal-rich globular clusters than the Milky Way. As in the Milky Way, the metal rich M31 globular clusters lie preferentially toward the center of th ...
... metal rich placed at [M/H] = −1.0, Milky Way metal rich globular clusters are concentrated toward the center of the galaxy. M31 has a larger number of metal-rich globular clusters than the Milky Way. As in the Milky Way, the metal rich M31 globular clusters lie preferentially toward the center of th ...
LET`S MAKE A PORTRAIT OF A GALAXY Abstract
... Lenticular galaxies look like spiral ones, thus their abbreviation is S0. However, their structure is quite different: stellar formation stopped long ago, because the interstellar matter was used up. Therefore, they consist of old population II stars only, or at least chiefly. From their appearance ...
... Lenticular galaxies look like spiral ones, thus their abbreviation is S0. However, their structure is quite different: stellar formation stopped long ago, because the interstellar matter was used up. Therefore, they consist of old population II stars only, or at least chiefly. From their appearance ...
Hwihyun Kim
... – Small galaxies form first and later assemble into larger objects – Denser environment affects galaxy evolution – Complicated than the pure monolithic collapse model – Kaviraj et al. (2005) : Optical CMR of early-type galaxies only if monolithic => we are not probing the entire star formation histo ...
... – Small galaxies form first and later assemble into larger objects – Denser environment affects galaxy evolution – Complicated than the pure monolithic collapse model – Kaviraj et al. (2005) : Optical CMR of early-type galaxies only if monolithic => we are not probing the entire star formation histo ...
Chapter 16
... From the measurement of stellar velocities near the center of a galaxy: Infer mass in the very center central black holes! Several million, up to more than a billion solar masses! Supermassive ...
... From the measurement of stellar velocities near the center of a galaxy: Infer mass in the very center central black holes! Several million, up to more than a billion solar masses! Supermassive ...
Galaxies, Cosmology and Dark Matter - IA
... The Galaxy was built in two phases: 1. In the beginning the gas collapsed within a few hundred million years from a large volume: → metal poor stars (and GCs) with negligible rotation → halo 2. After that a slower, dissipative phase followed: → because of its angular momentum, the gas concentrated m ...
... The Galaxy was built in two phases: 1. In the beginning the gas collapsed within a few hundred million years from a large volume: → metal poor stars (and GCs) with negligible rotation → halo 2. After that a slower, dissipative phase followed: → because of its angular momentum, the gas concentrated m ...
Galactic Disk Populations
... Evolution of Abundance Ratios in the Galaxy Overwhelming majority of Galactic field stars have [X/Fe] with very little scatter over a range of 4 dex in [Fe/H]. the star forming gas must be well mixed Rate of star formation must be low enough to allow time for element creation followed by large scal ...
... Evolution of Abundance Ratios in the Galaxy Overwhelming majority of Galactic field stars have [X/Fe] with very little scatter over a range of 4 dex in [Fe/H]. the star forming gas must be well mixed Rate of star formation must be low enough to allow time for element creation followed by large scal ...
Module 5: To the Galaxies and Beyond!
... Galaxies come in many different shapes and sizes, not just barred spirals like our Milky Way galaxy. Astronomers find it useful to divide galaxies into groups based on how they look in visible light, much like one would see if looking through a telescope. The Hubble sequence is a way of classifying ...
... Galaxies come in many different shapes and sizes, not just barred spirals like our Milky Way galaxy. Astronomers find it useful to divide galaxies into groups based on how they look in visible light, much like one would see if looking through a telescope. The Hubble sequence is a way of classifying ...
Velocity Field in the Local Volume
... of the Local Group (~1 Mpc) and their random motions are surprisingly small. Before 2000 year, the precise Cepheid distances were known only for members of Local Group and for small sample of giant galaxies. Most of Local Volume galaxies had rough distance estimates from luminosity of brightest star ...
... of the Local Group (~1 Mpc) and their random motions are surprisingly small. Before 2000 year, the precise Cepheid distances were known only for members of Local Group and for small sample of giant galaxies. Most of Local Volume galaxies had rough distance estimates from luminosity of brightest star ...
Family Space Day Overview – Galaxies
... stars, like those in the Pleiades, are continually being born. The Pleiades stars are only about 80 million years old. Which is older, the Sun or the Hubble galaxies? It depends on what you mean by “age.” The Sun is about 4.5 billion years old. But the Hubble “deep-field” galaxies are among the most ...
... stars, like those in the Pleiades, are continually being born. The Pleiades stars are only about 80 million years old. Which is older, the Sun or the Hubble galaxies? It depends on what you mean by “age.” The Sun is about 4.5 billion years old. But the Hubble “deep-field” galaxies are among the most ...
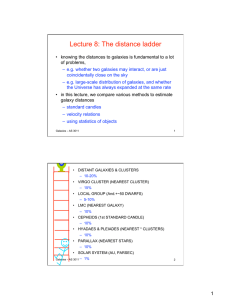
Lecture 8: The distance ladder
... Hubble’s law and distances • the most fundamental method is to use the redshift to estimate the distances to faint galaxies: • Hubble’s law is v = H0 d – so measure v and use H0 is ≈ 70 km s-1 Mpc-1 – NB this only works if the motion is cosmological, not within the Local Group, for example! • ...
... Hubble’s law and distances • the most fundamental method is to use the redshift to estimate the distances to faint galaxies: • Hubble’s law is v = H0 d – so measure v and use H0 is ≈ 70 km s-1 Mpc-1 – NB this only works if the motion is cosmological, not within the Local Group, for example! • ...
Galaxies
... galaxy looks like in the UV (it would probably not be classified as an Sb). If M81 would have been at z=1, it would look like in the right image. ...
... galaxy looks like in the UV (it would probably not be classified as an Sb). If M81 would have been at z=1, it would look like in the right image. ...
Milky Way

The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains our Solar System. Its name ""milky"" is derived from its appearance as a dim glowing band arching across the night sky whose individual stars cannot be distinguished by the naked eye. The term ""Milky Way"" is a translation of the Latin via lactea, from the Greek γαλαξίας κύκλος (galaxías kýklos, ""milky circle""). From Earth the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies—now known to number in the billions.The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy that has a diameter usually considered to be roughly 100,000–120,000 light-years but may be 150,000–180,000 light-years. The Milky Way is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars, although this number may be as high as one trillion. There are probably at least 100 billion planets in the Milky Way. The Solar System is located within the disk, about 27,000 light-years from the Galactic Center, on the inner edge of one of the spiral-shaped concentrations of gas and dust called the Orion Arm. The stars in the inner ≈10,000 light-years form a bulge and one or more bars that radiate from the bulge. The very center is marked by an intense radio source, named Sagittarius A*, which is likely to be a supermassive black hole.Stars and gases at a wide range of distances from the Galactic Center orbit at approximately 220 kilometers per second. The constant rotation speed contradicts the laws of Keplerian dynamics and suggests that much of the mass of the Milky Way does not emit or absorb electromagnetic radiation. This mass has been given the name ""dark matter"". The rotational period is about 240 million years at the position of the Sun. The Milky Way as a whole is moving at a velocity of approximately 600 km per second with respect to extragalactic frames of reference. The oldest stars in the Milky Way are nearly as old as the Universe itself and thus must have formed shortly after the Big Bang.The Milky Way has several satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, which is a component of the Virgo Supercluster, which again is a component of the Laniakea Supercluster.