Tajika and Matsui - Rice Department of Earth Science
... The effect of volatde exchange between surface reservoirs and the mantle on the evolution of proto-CO 2 atmosphere on the Earth is investigated using a global carbon cycle model coupled with thermal evolution of the mantle. Carbon is assumed to circulate among five reservoirs (atmosphere, ocean, con ...
... The effect of volatde exchange between surface reservoirs and the mantle on the evolution of proto-CO 2 atmosphere on the Earth is investigated using a global carbon cycle model coupled with thermal evolution of the mantle. Carbon is assumed to circulate among five reservoirs (atmosphere, ocean, con ...
Atmospheric oxygen regulation at low Proterozoic levels by
... the Great Oxidation Event should therefore have been stabilized by the oxygen sensitivity of oxidative weathering. The resulting oxygen level and negative feedback strength would have depended on the kinetics of oxidative weathering at low pO2, which are determined by oxygen transport and reaction i ...
... the Great Oxidation Event should therefore have been stabilized by the oxygen sensitivity of oxidative weathering. The resulting oxygen level and negative feedback strength would have depended on the kinetics of oxidative weathering at low pO2, which are determined by oxygen transport and reaction i ...
TOTAL EMISSIVITY OF CARBON DIOXIDE AND ITS
... standard concentration of the absorbent gas, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.6697 x 10 W/m K ), and T is the standard temperature (290 K). Although this formula has been widely used, several factors are missing that have a definitive influence on the results. Exempli gratia, it fails to accoun ...
... standard concentration of the absorbent gas, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.6697 x 10 W/m K ), and T is the standard temperature (290 K). Although this formula has been widely used, several factors are missing that have a definitive influence on the results. Exempli gratia, it fails to accoun ...
Q1. The Earth is made up of several layers. (a) Draw one straight
... Draw one straight line from each substance to an environmental effect that it causes. One has been done for you. ...
... Draw one straight line from each substance to an environmental effect that it causes. One has been done for you. ...
Changes to the Atmosphere
... were synthesised. After a long time, these molecules and structures became living organisms. Two scientists, Miller and Urey, used the apparatus below to investigate the development of life on Earth. The gases in the reaction chamber were water vapour, methane and ...
... were synthesised. After a long time, these molecules and structures became living organisms. Two scientists, Miller and Urey, used the apparatus below to investigate the development of life on Earth. The gases in the reaction chamber were water vapour, methane and ...
Slide 1
... the living material and soil is released, causing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to increase. When agricultural land is abandoned and forests are allowed to re-grow, carbon is stored in the accumulating living biomass and soils, causing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to decreas ...
... the living material and soil is released, causing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to increase. When agricultural land is abandoned and forests are allowed to re-grow, carbon is stored in the accumulating living biomass and soils, causing atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations to decreas ...
C1b Foundation 1
... This meteorite heated limestone in the Earth’s crust causing the release of large amounts of carbon dioxide. Explain how carbon dioxide is released from limestone. ...
... This meteorite heated limestone in the Earth’s crust causing the release of large amounts of carbon dioxide. Explain how carbon dioxide is released from limestone. ...
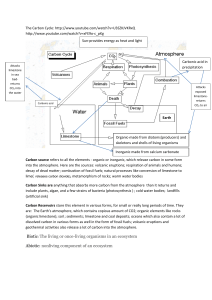
What is carbon cycle?
... surface ocean and release the gas back to the atmosphere. Ocean plants and animals also contribute to the exchange of CO2 through photosynthesis and respiration. Some of the carbonrich dead organisms will sink to the bottom of the ocean and form layers of limestone sediment on the ocean floor, re ...
... surface ocean and release the gas back to the atmosphere. Ocean plants and animals also contribute to the exchange of CO2 through photosynthesis and respiration. Some of the carbonrich dead organisms will sink to the bottom of the ocean and form layers of limestone sediment on the ocean floor, re ...
The boundless carbon cycle - Stroud Water Research Center
... Since 1750, continuously increasing anthropogenic CO2 emissions and land-use change have perturbed the natural carbon cycle. Of the 9.1 Pg C yr–1 (1 Pg C = 1 petagram or 109 metric tons of carbon) emitted in this way between 2000 and 2006, 4.1 Pg C yr–1 have accumulated in the atmosphere, 2.2 Pg C y ...
... Since 1750, continuously increasing anthropogenic CO2 emissions and land-use change have perturbed the natural carbon cycle. Of the 9.1 Pg C yr–1 (1 Pg C = 1 petagram or 109 metric tons of carbon) emitted in this way between 2000 and 2006, 4.1 Pg C yr–1 have accumulated in the atmosphere, 2.2 Pg C y ...
carbon dioxide - Life Learning Cloud
... • When they are burned it releases sulfur dioxide • This is a poisonous gas that causes acid rain • High temperatures inside car engines can cause nitrogen and oxygen to react forming nitrogen oxides • These are poisonous and can trigger asthma and cause acid rain • Diesel engines can release partic ...
... • When they are burned it releases sulfur dioxide • This is a poisonous gas that causes acid rain • High temperatures inside car engines can cause nitrogen and oxygen to react forming nitrogen oxides • These are poisonous and can trigger asthma and cause acid rain • Diesel engines can release partic ...
IAN MILLER: Longterm_Role_carbon
... are relatively constant leading to an equilibrium in atmospheric CO2—there are negligible changes in fluxes during the Pleistocene. • In geologic time, negative feedbacks serve to regulate the equilibrium. – High CO2, more warming, more plant growth, less CO2, less warming… ...
... are relatively constant leading to an equilibrium in atmospheric CO2—there are negligible changes in fluxes during the Pleistocene. • In geologic time, negative feedbacks serve to regulate the equilibrium. – High CO2, more warming, more plant growth, less CO2, less warming… ...
1. dia
... This carbon cycle has of primary importance because two of the greenhouse gases, the CO2 and methane are included. The carbon cycle is more sophisticated than that of the water cycle, due to the presence of chemical transformation. It means that not only the path of gases from sources to sinks has t ...
... This carbon cycle has of primary importance because two of the greenhouse gases, the CO2 and methane are included. The carbon cycle is more sophisticated than that of the water cycle, due to the presence of chemical transformation. It means that not only the path of gases from sources to sinks has t ...
Document
... This carbon cycle has of primary importance because two of the greenhouse gases, the CO2 and methane are included. The carbon cycle is more sophisticated than that of the water cycle, due to the presence of chemical transformation. It means that not only the path of gases from sources to sinks has t ...
... This carbon cycle has of primary importance because two of the greenhouse gases, the CO2 and methane are included. The carbon cycle is more sophisticated than that of the water cycle, due to the presence of chemical transformation. It means that not only the path of gases from sources to sinks has t ...
Biogeochemical assessments
... 7. How has the CO2 concentration changed over time? a. no change b. it decreased c. it increased d. it cannot be determined 8. What process is responsible for the change in question 7? a. photosynthesis b. nitrogen fixation c. oxidation d. reduction 9. Which reservoir on Earth contains the most carb ...
... 7. How has the CO2 concentration changed over time? a. no change b. it decreased c. it increased d. it cannot be determined 8. What process is responsible for the change in question 7? a. photosynthesis b. nitrogen fixation c. oxidation d. reduction 9. Which reservoir on Earth contains the most carb ...
The Biogeochemical Carbon Cycle
... Simple Planetary Energy Balance •Likely solution to FYSP requires understanding of Earth’s energy balance (& C cycle) ...
... Simple Planetary Energy Balance •Likely solution to FYSP requires understanding of Earth’s energy balance (& C cycle) ...
WELIM Solar Energy
... equilibrium. This is called the solubility pump. But the solubility pump is slowing down. Unfortunately, the solubility of carbon dioxide in water is temperature dependent. So, as global warming causes the ocean’s temperature to increase, less carbon dioxide can be dissolved into the ocean. And the ...
... equilibrium. This is called the solubility pump. But the solubility pump is slowing down. Unfortunately, the solubility of carbon dioxide in water is temperature dependent. So, as global warming causes the ocean’s temperature to increase, less carbon dioxide can be dissolved into the ocean. And the ...
Biotic: The living or once-living organisms in an ecosystem Abiotic
... Carbon source refers to all the elements - organic or inorganic, which release carbon in some form into the atmosphere. Here are the sources: volcanic eruptions; respiration of animals and humans; decay of dead matter; combustion of fossil fuels; natural processes like conversion of limestone to lim ...
... Carbon source refers to all the elements - organic or inorganic, which release carbon in some form into the atmosphere. Here are the sources: volcanic eruptions; respiration of animals and humans; decay of dead matter; combustion of fossil fuels; natural processes like conversion of limestone to lim ...
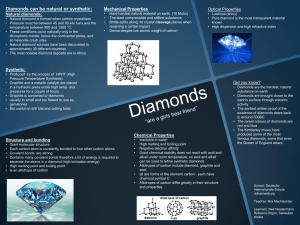
Organisation Deutsche Internationale Schule Diamonds
... in a hydraulic press under high temp. and pressures for a couple of hours • Graphite is converted to diamonds • usually to small and too flawed to use as ...
... in a hydraulic press under high temp. and pressures for a couple of hours • Graphite is converted to diamonds • usually to small and too flawed to use as ...
Review II for Making a Habitable Earth and Plate Tectonics Units
... boundaries, hazard(s) associated with the boundary, and give at least one example of such a boundary at the Earth’s surface. a.) Diverging (constructive) What it is? ...
... boundaries, hazard(s) associated with the boundary, and give at least one example of such a boundary at the Earth’s surface. a.) Diverging (constructive) What it is? ...
The Carbon Cycle
... 13. What role does fire play in the cycle? 14. What role does deforestation play? 15. What controls carbon dioxide exchange in the oceans? 16. What temperature water favors the uptake of carbon dioxide? 17. What type of currents favor the uptake of carbon dioxide? 18. How does the carbon cycle diffe ...
... 13. What role does fire play in the cycle? 14. What role does deforestation play? 15. What controls carbon dioxide exchange in the oceans? 16. What temperature water favors the uptake of carbon dioxide? 17. What type of currents favor the uptake of carbon dioxide? 18. How does the carbon cycle diffe ...
reducing black carbon emissions
... Because black carbon remains in the atmosphere for only days or weeks, reducing emissions can be an effective rapid response to slow warming in the near term, buying critical time to realize reductions in longlived greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide.v Each region of the world has a unique mix of n ...
... Because black carbon remains in the atmosphere for only days or weeks, reducing emissions can be an effective rapid response to slow warming in the near term, buying critical time to realize reductions in longlived greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide.v Each region of the world has a unique mix of n ...
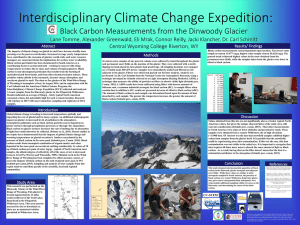
(ICCE): Black Carbon Measurements from the Dinwoody Glacier
... impacting the rate of glacial melt in many regions. An additional anthropogenic impact on glaciers is increased levels of pollution in the atmosphere. Atmospheric pollutants such as black carbon particles can be deposited on glacier surfaces through precipitation processes or through ‘dry deposition ...
... impacting the rate of glacial melt in many regions. An additional anthropogenic impact on glaciers is increased levels of pollution in the atmosphere. Atmospheric pollutants such as black carbon particles can be deposited on glacier surfaces through precipitation processes or through ‘dry deposition ...
Aerosol concentrations and hurricanes over the
... Discuss recent studies that suggest aerosols such as black carbon are changing atmospheric stability and sea surface temperatures (SSTs). ...
... Discuss recent studies that suggest aerosols such as black carbon are changing atmospheric stability and sea surface temperatures (SSTs). ...
Link - www7
... lungs where it may enter the bloodstream. Exposure to these particles is associated with respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as premature death and is particularly hazardous for people with heart or lung diseases, as well as children and elderly adults. Environmental Effects Once emitte ...
... lungs where it may enter the bloodstream. Exposure to these particles is associated with respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, as well as premature death and is particularly hazardous for people with heart or lung diseases, as well as children and elderly adults. Environmental Effects Once emitte ...
Black carbon

Chemically, black carbon or BC is a component of fine particulate matter (PM ≤ 2.5 µm in aerodynamic diameter). Black Carbon consists of pure carbon in several linked forms. It is formed through the incomplete combustion of fossil fuels, biofuel, and biomass, and is emitted in both anthropogenic and naturally occurring soot.Black carbon causes human morbidity and premature mortality.In climatology black carbon is a climate forcing agent. Black carbon warms the Earth by absorbing heat in the atmosphere and by reducing albedo when deposited on snow and ice. Black carbon stays in the atmosphere for only several days to weeks, whereas carbon dioxide (CO2) has an atmospheric lifetime of more than 100 years.The term black carbon is also used in soil sciences and geology, referring either to deposited atmospheric black carbon or to directly incorporated black carbon from vegetation fires. Especially in the tropics, black carbon in soils significantly contributes to fertility as it is able to absorb important plant nutrients.