fast pyrolysis characteristics of sugarcane bagasse hemicellulose
... (on a dry base) were loaded and the reactor was purged by nitrogen gas for 10 min, at a flow rate of 300 mL/min, to remove the air from inside. The sample was pushed to the center of the furnace and pyrolysis began when the tubular furnace was heated to the desired pyrolysis ...
... (on a dry base) were loaded and the reactor was purged by nitrogen gas for 10 min, at a flow rate of 300 mL/min, to remove the air from inside. The sample was pushed to the center of the furnace and pyrolysis began when the tubular furnace was heated to the desired pyrolysis ...
10934_2017_374_MOESM1_ESM
... crystalline sample. As-synthesized UiO-66 particles were refluxed in MeOH for 6 hours, whereas MOF-801 particles were refluxed in water for 2 hours. We evaluated our results of TG profiles before and after the post-treatment in order to investigate residual solvents. It is difficult to tell whether ...
... crystalline sample. As-synthesized UiO-66 particles were refluxed in MeOH for 6 hours, whereas MOF-801 particles were refluxed in water for 2 hours. We evaluated our results of TG profiles before and after the post-treatment in order to investigate residual solvents. It is difficult to tell whether ...
Unit 6 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations
... Balance the following chemical equations using coefficients 1 1Al(OH)3(s) + 3HCl (aq) → 1AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2O (l) 2. 3Fe2O3 (s) + 1CO (g) → 2Fe3O4(s) + 1CO2 (g) 3. 4FeO (s) + 1O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) 4. 2C6H6 (l) + 15O2 (g) → 12CO2 (g) + 6H2O (g) 5. 3Ca(OH)2 (aq) + 2H3PO4 (aq) → 6H2O (l) + 1Ca3(PO4)2 (s) 6 ...
... Balance the following chemical equations using coefficients 1 1Al(OH)3(s) + 3HCl (aq) → 1AlCl3 (aq) + 3H2O (l) 2. 3Fe2O3 (s) + 1CO (g) → 2Fe3O4(s) + 1CO2 (g) 3. 4FeO (s) + 1O2 (g) → 2Fe2O3 (s) 4. 2C6H6 (l) + 15O2 (g) → 12CO2 (g) + 6H2O (g) 5. 3Ca(OH)2 (aq) + 2H3PO4 (aq) → 6H2O (l) + 1Ca3(PO4)2 (s) 6 ...
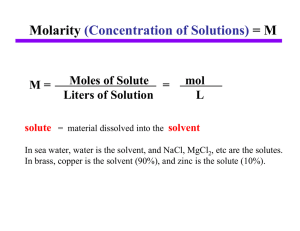
Molarity = M (Concentration of Solutions)
... Later R = 8.314 J / (mol K) = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 An ideal gas is one for which both the volume of molecules and forces between the molecules are so small that they have insignificant effect on its P-V-T behavior. Independent of substance, in the limit that n/V →0, all gases behave ideally. Usually tr ...
... Later R = 8.314 J / (mol K) = 8.314 J mol-1 K-1 An ideal gas is one for which both the volume of molecules and forces between the molecules are so small that they have insignificant effect on its P-V-T behavior. Independent of substance, in the limit that n/V →0, all gases behave ideally. Usually tr ...
Density, Viscosity, Solubility, and Diffusivity of N2O in Aqueous
... encountered in the treatment of flue gases, resulting in very toxic degradation products.2 Amino acid salts can be a possible alternative to alkanolamines in certain areas of gas treating, although they are more expensive than alkanolamines. The ionic nature of these salt solutions makes them more s ...
... encountered in the treatment of flue gases, resulting in very toxic degradation products.2 Amino acid salts can be a possible alternative to alkanolamines in certain areas of gas treating, although they are more expensive than alkanolamines. The ionic nature of these salt solutions makes them more s ...
Lab Manual
... Although no gas has these properties, the behavior of real gases is described quite closely by the ideal gas law at sufficiently high temperatures and low pressures, when relatively large distances between molecules and their high speeds overcome any interaction. A gas does not obey the equation whe ...
... Although no gas has these properties, the behavior of real gases is described quite closely by the ideal gas law at sufficiently high temperatures and low pressures, when relatively large distances between molecules and their high speeds overcome any interaction. A gas does not obey the equation whe ...
1994 AP Chemistry Multiple Choice
... following it. Select the one lettered choice that best answers each question or best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 (A) Heisenberg uncertainty principle (B) Pauli exc ...
... following it. Select the one lettered choice that best answers each question or best fits each statement and then fill in the corresponding oval on the answer sheet. A choice may be used once, more than once, or not at all in each set. Questions 1–4 (A) Heisenberg uncertainty principle (B) Pauli exc ...
1984 Advanced Placement Exam
... 25. What is the order of the reaction with respect to I–? (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 5 (E) 6 26. According to the rate law for the reaction, an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion has what effect on this reaction? (A) The rate of reaction increases. (B) The rate of reaction decreases. (C) The ...
... 25. What is the order of the reaction with respect to I–? (A) 1 (B) 2 (C) 3 (D) 5 (E) 6 26. According to the rate law for the reaction, an increase in the concentration of hydronium ion has what effect on this reaction? (A) The rate of reaction increases. (B) The rate of reaction decreases. (C) The ...
Chapter III: Matter - Norwell Public Schools
... Sublimation Solid changes to vapor without going through liquid ...
... Sublimation Solid changes to vapor without going through liquid ...
Chp 5 Circle the correct answer Consider three 1
... c) The force in which the Ar atoms collide with their container is the same in both containers. d) The frequency with which the Ar atoms collide with their container is the same in both containers. Chp 6 1. One mole of an ideal gas is expanded from a volume of 1.00 liter to a volume of 10.00 liters ...
... c) The force in which the Ar atoms collide with their container is the same in both containers. d) The frequency with which the Ar atoms collide with their container is the same in both containers. Chp 6 1. One mole of an ideal gas is expanded from a volume of 1.00 liter to a volume of 10.00 liters ...
Honors Chemistry Unit 4 Student Packet: Honors Chemistry Problem
... Honors Chemistry: Problem Set Chapter 11 Classify each of these statements as always true (AT); sometimes true (ST); or never true (NT) 1. In an equation, a substance is shown to be in the gaseous state by placing an upwardpointing arrow after its formula. 2. The symbol ∆ placed over the arrow in a ...
... Honors Chemistry: Problem Set Chapter 11 Classify each of these statements as always true (AT); sometimes true (ST); or never true (NT) 1. In an equation, a substance is shown to be in the gaseous state by placing an upwardpointing arrow after its formula. 2. The symbol ∆ placed over the arrow in a ...
Gases Properties of Gases Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
... The internal energy, U, of a system is a function of the state of the system. Although we cannot measure the absolute state of a system, we can measure changes in the state of the system in a relative way, by measuring the work and the heat that takes place during a chemical change. As U is a functi ...
... The internal energy, U, of a system is a function of the state of the system. Although we cannot measure the absolute state of a system, we can measure changes in the state of the system in a relative way, by measuring the work and the heat that takes place during a chemical change. As U is a functi ...
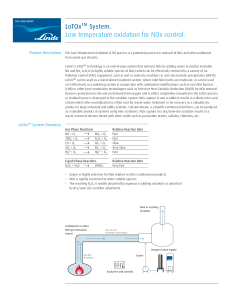
LoTOx™ System. Low temperature oxidation for NOx
... Linde modular ozone and oxygen supply systems enable quick and easy retrofit of the LoTOx process into customer’s existing APC systems without significant changes or additional major process equipment. The small, modular system footprint allows flexibility of the equipment layout to meet unique spat ...
... Linde modular ozone and oxygen supply systems enable quick and easy retrofit of the LoTOx process into customer’s existing APC systems without significant changes or additional major process equipment. The small, modular system footprint allows flexibility of the equipment layout to meet unique spat ...
Chemistry II Exams and Keys 2014 Season
... Use the letters in parentheses for your answers. Choose the letter that best completes or answers the item. Be certain that erasures are complete. Please PRINT your name, school area code, and which test you are taking on the scan-tron. 1. Potassium perchlorate is prepared by three successive chemic ...
... Use the letters in parentheses for your answers. Choose the letter that best completes or answers the item. Be certain that erasures are complete. Please PRINT your name, school area code, and which test you are taking on the scan-tron. 1. Potassium perchlorate is prepared by three successive chemic ...
C - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... A. Atoms contain electrons. B. Practically all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. C. Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. T ...
... A. Atoms contain electrons. B. Practically all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. C. Atoms contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. D. Atoms have a positively charged nucleus surrounded by an electron cloud. E. No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 65. T ...
Chemistry Exam 2 Specifications and Sample Exam
... SECTION B – Short answer questions Instructions for Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided. To obtain full marks for your responses you should • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given ful ...
... SECTION B – Short answer questions Instructions for Section B Answer all questions in the spaces provided. To obtain full marks for your responses you should • give simpliÞed answers with an appropriate number of signiÞcant Þgures to all numerical questions; unsimpliÞed answers will not be given ful ...
AP `94 Multiple Choice
... 38. Concentrations of colored substances are 41. A strip of metallic scandium, Sc, is placed in a beaker containing concentrated nitric acid. A commonly measured by means of a brown gas rapidly forms, the scandium spectrophotometer. Which of the following would disappears, and the resulting liquid i ...
... 38. Concentrations of colored substances are 41. A strip of metallic scandium, Sc, is placed in a beaker containing concentrated nitric acid. A commonly measured by means of a brown gas rapidly forms, the scandium spectrophotometer. Which of the following would disappears, and the resulting liquid i ...
12 The Gaseous State of Matter Chapter Outline Properties of Gases
... Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
... Copyright © 2014 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved. ...
Entropy geometric construction of a pure substance with normal
... volume e = E/V = constant, a negative sign of the chemical potential implies that the number of states increases as the particle density n = N/V also increases, see Eq. (2). Conversely, a positive µ signals that the number of states decreases when particle density n increases. The first behavior is ...
... volume e = E/V = constant, a negative sign of the chemical potential implies that the number of states increases as the particle density n = N/V also increases, see Eq. (2). Conversely, a positive µ signals that the number of states decreases when particle density n increases. The first behavior is ...
Test3_sp2012with answers
... _D__13. Which of the following influence the vapor pressure of liquids? A) polarity of liquid molecules B) mass of liquid molecules C) temperature of liquid D) more than one response is correct __B_14. Which of the following is not a standard condition (STP) for gas measurements? A) 0OC B) 100 oC C) ...
... _D__13. Which of the following influence the vapor pressure of liquids? A) polarity of liquid molecules B) mass of liquid molecules C) temperature of liquid D) more than one response is correct __B_14. Which of the following is not a standard condition (STP) for gas measurements? A) 0OC B) 100 oC C) ...
Fall 2008 Blank Final Exam
... Select the best multiple-choice answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions during the exam, please ask the proctor. Open and start this exam when instructed. When finished, place ...
... Select the best multiple-choice answer by filling in the corresponding circle on the rear page of the answer sheet. If you have any questions before the exam, please ask. If you have any questions during the exam, please ask the proctor. Open and start this exam when instructed. When finished, place ...
A) 0% B) 20% C) 50% D) 80% E) 100% 1. Naturally occurring boron
... Low pressure and low temperature Low pressure and high temperature High pressure and high temperature High pressure and low density Low temperature and high density ...
... Low pressure and low temperature Low pressure and high temperature High pressure and high temperature High pressure and low density Low temperature and high density ...
Document
... The initial state is 1 mol of either ethane or ethanol and enough oxygen to complete the combustion. Because ∆Hf°[O2(g)] = 0, the enthalpy of the initial state is simply the standard enthalpy of formation of 1 mol of ethane in one case and 1 mol of ethanol in the other. The combustion reaction that ...
... The initial state is 1 mol of either ethane or ethanol and enough oxygen to complete the combustion. Because ∆Hf°[O2(g)] = 0, the enthalpy of the initial state is simply the standard enthalpy of formation of 1 mol of ethane in one case and 1 mol of ethanol in the other. The combustion reaction that ...
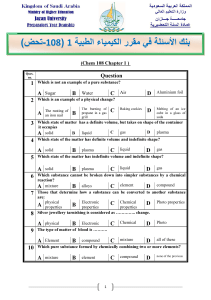
ض ( ا ء ا ط ك ا رر 108 1) -
... Which state of the matter has definite volume and indefinite shape? solid B plasma C liquid D gas Which state of the matter has indefinite volume and indefinite shape? ...
... Which state of the matter has definite volume and indefinite shape? solid B plasma C liquid D gas Which state of the matter has indefinite volume and indefinite shape? ...
Gas chromatography

Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture (the relative amounts of such components can also be determined). In some situations, GC may help in identifying a compound. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture.In gas chromatography, the mobile phase (or ""moving phase"") is a carrier gas, usually an inert gas such as helium or an unreactive gas such as nitrogen. The stationary phase is a microscopic layer of liquid or polymer on an inert solid support, inside a piece of glass or metal tubing called a column (a homage to the fractionating column used in distillation). The instrument used to perform gas chromatography is called a gas chromatograph (or ""aerograph"", ""gas separator"").The gaseous compounds being analyzed interact with the walls of the column, which is coated with a stationary phase. This causes each compound to elute at a different time, known as the retention time of the compound. The comparison of retention times is what gives GC its analytical usefulness.Gas chromatography is in principle similar to column chromatography (as well as other forms of chromatography, such as HPLC, TLC), but has several notable differences. First, the process of separating the compounds in a mixture is carried out between a liquid stationary phase and a gas mobile phase, whereas in column chromatography the stationary phase is a solid and the mobile phase is a liquid. (Hence the full name of the procedure is ""Gas–liquid chromatography"", referring to the mobile and stationary phases, respectively.) Second, the column through which the gas phase passes is located in an oven where the temperature of the gas can be controlled, whereas column chromatography (typically) has no such temperature control. Finally, the concentration of a compound in the gas phase is solely a function of the vapor pressure of the gas.Gas chromatography is also similar to fractional distillation, since both processes separate the components of a mixture primarily based on boiling point (or vapor pressure) differences. However, fractional distillation is typically used to separate components of a mixture on a large scale, whereas GC can be used on a much smaller scale (i.e. microscale).Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Strictly speaking, GLPC is the most correct terminology, and is thus preferred by many authors.