Stacey Carpenter
... mph, and they run into you. It makes a huge difference which direction they’re going! They could hit you at 61 mph from in front or 1 mph from behind (or anything in between from another direction). If they're in front of you, you'll never hit. acceleration (a change in velocity)– Are you accelera ...
... mph, and they run into you. It makes a huge difference which direction they’re going! They could hit you at 61 mph from in front or 1 mph from behind (or anything in between from another direction). If they're in front of you, you'll never hit. acceleration (a change in velocity)– Are you accelera ...
Ph211_CH6_worksheet-f06
... FNet = fs + FN + mg = fs ˆi + FN - mg ˆj = 15,185 N ˆi =ma c ˆi e. What is the maximum centripetal force exerted on this car just before the tires lose traction with the road? (Assume μmax is 0.88 for dry pavement). Explain the discrepancy s between your answer and the answer in (c). Ans ...
... FNet = fs + FN + mg = fs ˆi + FN - mg ˆj = 15,185 N ˆi =ma c ˆi e. What is the maximum centripetal force exerted on this car just before the tires lose traction with the road? (Assume μmax is 0.88 for dry pavement). Explain the discrepancy s between your answer and the answer in (c). Ans ...
Free Body Diagrams
... (ii) Calculate frictional force (iii) Find net force down the slope => acceleration (iv) Use vf = vi + at => vf ...
... (ii) Calculate frictional force (iii) Find net force down the slope => acceleration (iv) Use vf = vi + at => vf ...
chapter7
... If the angular acceleration and the angular velocity are in the same direction, the angular speed will increase with time. If the angular acceleration and the angular velocity are in opposite directions, the angular speed will decrease with time. ...
... If the angular acceleration and the angular velocity are in the same direction, the angular speed will increase with time. If the angular acceleration and the angular velocity are in opposite directions, the angular speed will decrease with time. ...
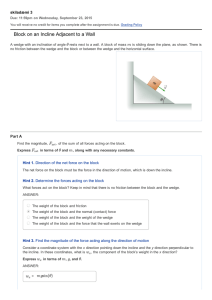
Block on an Incline Adjacent to a Wall
... Your answer to Part B could be expressed as either mg sin(θ) cos(θ) or mg sin(2θ)/2. In either form, we see that as θ gets very small or as θ approaches 90 degrees (π/2 radians), the contact force between the wall and the wedge goes to zero. This is what we should expect; in the first limit ( θ smal ...
... Your answer to Part B could be expressed as either mg sin(θ) cos(θ) or mg sin(2θ)/2. In either form, we see that as θ gets very small or as θ approaches 90 degrees (π/2 radians), the contact force between the wall and the wedge goes to zero. This is what we should expect; in the first limit ( θ smal ...
Dynamics Notes
... revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), revolutionized not just our understanding of the solar system, but our understanding of nature in general, as future attempts to understand the universe - which were before the domain of God and religion - instead switche ...
... revolutionibus orbium coelestium (On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres), revolutionized not just our understanding of the solar system, but our understanding of nature in general, as future attempts to understand the universe - which were before the domain of God and religion - instead switche ...
Lesson 2 - Choteau Schools
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion (cont.) • In a force pair, one force is called the action force and the other force is called the reaction force. – When you push against an object, the force you apply is called the action force. – The force applied by the object back against you is called the reaction ...
... Newton’s Third Law of Motion (cont.) • In a force pair, one force is called the action force and the other force is called the reaction force. – When you push against an object, the force you apply is called the action force. – The force applied by the object back against you is called the reaction ...
Torque
... Torque is a twist or turn that tends to produce rotation. * * * Applications are found in many common tools around the home or industry where it is necessary to turn, tighten or loosen devices. ...
... Torque is a twist or turn that tends to produce rotation. * * * Applications are found in many common tools around the home or industry where it is necessary to turn, tighten or loosen devices. ...
Petar-Bosnic-Intervi..
... AAG: Now the "moment of truth" in building this device is the materials-science: since this is a mass-based effect, and not an electrodynamic one, the rubber would tend to meet the road in terms of finding a strong enough material to withstand the rapid rotation. You've talked about using Carbon Fib ...
... AAG: Now the "moment of truth" in building this device is the materials-science: since this is a mass-based effect, and not an electrodynamic one, the rubber would tend to meet the road in terms of finding a strong enough material to withstand the rapid rotation. You've talked about using Carbon Fib ...