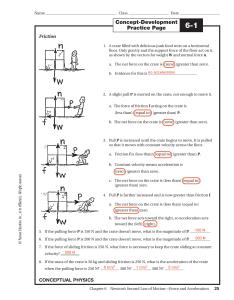
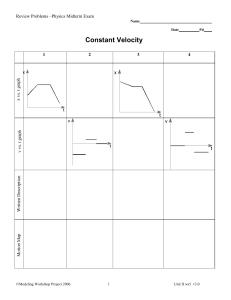
Dynamicssv
... 2. push the cart longer before release 3. push the cart continuously 4. change the mass of the cart 5. it is impossible to do that In order to achieve a non-zero acceleration, it is necessary to maintain the applied force. The only way to do this would be to continue pushing the cart as it moves dow ...
... 2. push the cart longer before release 3. push the cart continuously 4. change the mass of the cart 5. it is impossible to do that In order to achieve a non-zero acceleration, it is necessary to maintain the applied force. The only way to do this would be to continue pushing the cart as it moves dow ...
Unit 4 - Youngstown City Schools
... Using Newton’s Second Law, Fnet = m a. Since weight is a force, F = W. Since the acceleration caused by the force is due to gravity, a = g Since mass never changes, m = m Therefore W = m g Since the ball is traveling at a constant velocity, there is no acceleration; a = 0. According to Newton’s Seco ...
... Using Newton’s Second Law, Fnet = m a. Since weight is a force, F = W. Since the acceleration caused by the force is due to gravity, a = g Since mass never changes, m = m Therefore W = m g Since the ball is traveling at a constant velocity, there is no acceleration; a = 0. According to Newton’s Seco ...
hw6
... kinetic friction is 0.25. Determine the work done on the box by each of the four forces that act on the box. Be sure to include the proper plus or minus sign for the work done by each force. **24 Multiple-Concept Example 5 reviews many of the concepts that play a role in this problem. An extreme ski ...
... kinetic friction is 0.25. Determine the work done on the box by each of the four forces that act on the box. Be sure to include the proper plus or minus sign for the work done by each force. **24 Multiple-Concept Example 5 reviews many of the concepts that play a role in this problem. An extreme ski ...
Chapter 10 Forces
... Newton’s First and Second Laws Standard 8.2.e Students know that when the forces on an object are unbalanced, the object will change its velocity (that is, it will speed up, slow down, or change direction). Standard 8.2.f Students know the greater the mass of an object, the more force is needed to a ...
... Newton’s First and Second Laws Standard 8.2.e Students know that when the forces on an object are unbalanced, the object will change its velocity (that is, it will speed up, slow down, or change direction). Standard 8.2.f Students know the greater the mass of an object, the more force is needed to a ...
conceptual physics ch.4
... Extra: a) What is the acceleration of an object that moves at constant velocity? b) What is the net force on the object in this case? Ans. a) 0 m/s/s, when there is no change in velocity, there can be no acceleration. b) 0 Newtons, an object moving at constant velocity does not have an unbalanced fo ...
... Extra: a) What is the acceleration of an object that moves at constant velocity? b) What is the net force on the object in this case? Ans. a) 0 m/s/s, when there is no change in velocity, there can be no acceleration. b) 0 Newtons, an object moving at constant velocity does not have an unbalanced fo ...
Physics 151 Week 9 Day 3
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
Solutions1
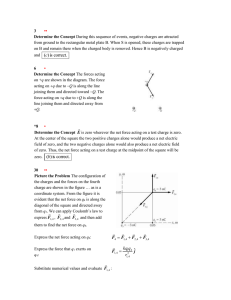
... Determine the Concept E is zero wherever the net force acting on a test charge is zero. At the center of the square the two positive charges alone would produce a net electric field of zero, and the two negative charges alone would also produce a net electric field of zero. Thus, the net force actin ...
... Determine the Concept E is zero wherever the net force acting on a test charge is zero. At the center of the square the two positive charges alone would produce a net electric field of zero, and the two negative charges alone would also produce a net electric field of zero. Thus, the net force actin ...
ANSWERS TO FORCES _ WORKSHEET 1 Question L: Describe the
... so that air travelling over the top of the wing travels a greaterdistancethan air travelling underneaththe bottom of the wing. This resultsin the air travelling over the top occupying a greatervolume in the sametime and so being less dense.While the differencein density would createvery little lift ...
... so that air travelling over the top of the wing travels a greaterdistancethan air travelling underneaththe bottom of the wing. This resultsin the air travelling over the top occupying a greatervolume in the sametime and so being less dense.While the differencein density would createvery little lift ...
Chapter 3: Motion and Forces Goals of Period 3
... velocity, and acceleration. Distance: We use the symbol D to represent the distance between two points. Distances are measured by comparing the length of the path between two points to standard lengths such as meters or feet. We assume that the length of a meter stick held in our hands is constant, ...
... velocity, and acceleration. Distance: We use the symbol D to represent the distance between two points. Distances are measured by comparing the length of the path between two points to standard lengths such as meters or feet. We assume that the length of a meter stick held in our hands is constant, ...
Lecture 2c - Newton`s Laws & Applications
... Summary of Chapter 4 • Newton’s first law: If the net force on an object is zero, it will remain either at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed. • Newton’s second law: • Newton’s third law: • Weight is the gravitational force on an object. • Free-body diagrams are essential for probl ...
... Summary of Chapter 4 • Newton’s first law: If the net force on an object is zero, it will remain either at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed. • Newton’s second law: • Newton’s third law: • Weight is the gravitational force on an object. • Free-body diagrams are essential for probl ...