on that object
... -Frictional forces -Tension in a string -Gravitational Force (or weight = mg where g is 9.8 m/s2) - “Normal forces” (one object touching another). 2. Draw a “Freebody Diagram” -draw the object, show all forces acting on that object as vectors pointing in the correct direction. Show the direction of ...
... -Frictional forces -Tension in a string -Gravitational Force (or weight = mg where g is 9.8 m/s2) - “Normal forces” (one object touching another). 2. Draw a “Freebody Diagram” -draw the object, show all forces acting on that object as vectors pointing in the correct direction. Show the direction of ...
Lecture 10
... You push on an object and it moves. If you stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law ...
... You push on an object and it moves. If you stop pushing an object, does it stop moving? Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is Newton’s 1st Law, and it is also known as the Law ...
Review - Hingham Schools
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
... Be able to identify and diagram the forces on an object. Know what net force means and understand the direction it points relative to a and v for different types of motion. Know the differences between mass and weight. Be able to calculate weight given the mass and vice versa. Be able to apply Newto ...
Newtons laws
... Mass is directly related to inertia. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to resist change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing with out friction. ...
... Mass is directly related to inertia. • The greater the mass the greater the tendency to resist change of an object’s motion. • objects will continue to do as they are doing with out friction. ...
CircularMotion&Gravitation
... Newton and Satellite Motion Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “ ...
... Newton and Satellite Motion Newton’s Law of Gravitation predicts artificial satellites can orbit the earth with centripetal acceleration. Satellites have acceleration towards the center of Earth, but they also have tangential speed to keep them in orbit! Astronauts in orbit are often described as “ ...
Work
... A man is letting a 300 kg piano slide 4 m at constant velocity down a 30° incline while exerting a 400 N force on the horizontal. What work does he do? • The component of the force is (400 N)(cos 30) = -350 N • Negative since it is opposite the displacement • The work is (-350 N)(4 m) = ...
... A man is letting a 300 kg piano slide 4 m at constant velocity down a 30° incline while exerting a 400 N force on the horizontal. What work does he do? • The component of the force is (400 N)(cos 30) = -350 N • Negative since it is opposite the displacement • The work is (-350 N)(4 m) = ...
Centripetal and Gravitational Forces
... Centrifugal force ("fictitious" force) represents the effects of inertia that arise in connection with rotation It is experienced as an outward force away from the center of rotation. ...
... Centrifugal force ("fictitious" force) represents the effects of inertia that arise in connection with rotation It is experienced as an outward force away from the center of rotation. ...
Class10
... But hang on a minute.... What happens if we remove all resistance to motion, i.e. friction and air resistance? ...
... But hang on a minute.... What happens if we remove all resistance to motion, i.e. friction and air resistance? ...
Net Force
... Newton’s Second Law requires a net force. • One or more forces act on an object • Forces are vectors that can be added ...
... Newton’s Second Law requires a net force. • One or more forces act on an object • Forces are vectors that can be added ...
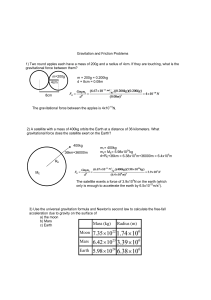
Mass (kg) Radius (m) Moon Mars Earth
... First derive the formula for the freefall acceleration ag on the surface of a body (e.g. a planet) of mass M and radius R. Consider an object of mass m sitting on the surface. Then by Newton's second law the force of gravity on the object is: ...
... First derive the formula for the freefall acceleration ag on the surface of a body (e.g. a planet) of mass M and radius R. Consider an object of mass m sitting on the surface. Then by Newton's second law the force of gravity on the object is: ...
PHY 101 ... ______________________ Take home exam #1 Solution Key
... Name ___Solution Key______________________ ...
... Name ___Solution Key______________________ ...
Forces
... Newton’s Law of Gravity • Gravity is the natural force that pulls one object toward another. The strength of this pull depends on the mass of the objects involved. • The pull is directly proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. ...
... Newton’s Law of Gravity • Gravity is the natural force that pulls one object toward another. The strength of this pull depends on the mass of the objects involved. • The pull is directly proportional to the masses of the objects and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. ...
File
... This is just the weight of the passenger when the elevator is at rest or moving with a constant velocity. (c) When the acceleration is directed upward, Fapp = (72.2 kg) (3.2m/s2 - -9.8m/s2) = 939 N When the acceleration is directed downward, Fapp = (72.2 kg) (-3.2m/s2 - -9.8m/s2) = 477 N ...
... This is just the weight of the passenger when the elevator is at rest or moving with a constant velocity. (c) When the acceleration is directed upward, Fapp = (72.2 kg) (3.2m/s2 - -9.8m/s2) = 939 N When the acceleration is directed downward, Fapp = (72.2 kg) (-3.2m/s2 - -9.8m/s2) = 477 N ...