Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... Newton’s 3rd law: Whatever magnitude of force the bat applies to the ball, the ball applies the same magnitude of force back (opposite direction) onto the bat. The bat is slowed by the force of the ball on the bat, and the ball is accelerated by the force of the bat A gun firing a bullet Newton’s 3r ...
... Newton’s 3rd law: Whatever magnitude of force the bat applies to the ball, the ball applies the same magnitude of force back (opposite direction) onto the bat. The bat is slowed by the force of the ball on the bat, and the ball is accelerated by the force of the bat A gun firing a bullet Newton’s 3r ...
5 N
... Notice that when the forces are balanced, the object might still be moving, but the objects are not accelerating, instead they have a constant velocity. Hence, once in motion – it’s always in motion unless acted upon by what? Another Force. ...
... Notice that when the forces are balanced, the object might still be moving, but the objects are not accelerating, instead they have a constant velocity. Hence, once in motion – it’s always in motion unless acted upon by what? Another Force. ...
Free Body Diagrams - Mr. Romero
... This is a free-body diagram of the Statue of Liberty. She is represented by a simple box. The forces acting on her are labeled with a magnitude and the arrow shows direction. Notice the surrounding objects are stripped away and the forces acting on the object are shown. ...
... This is a free-body diagram of the Statue of Liberty. She is represented by a simple box. The forces acting on her are labeled with a magnitude and the arrow shows direction. Notice the surrounding objects are stripped away and the forces acting on the object are shown. ...
Walker Chapter 5 (Newton`s Laws)
... • In order to change the velocity of an object— magnitude or direction—a net force is required. • An inertial reference frame is one in which the first law is true. The surface of the earth is a good approximation to an inertial frame of reference. Accelerating reference frames are not inertial. ...
... • In order to change the velocity of an object— magnitude or direction—a net force is required. • An inertial reference frame is one in which the first law is true. The surface of the earth is a good approximation to an inertial frame of reference. Accelerating reference frames are not inertial. ...
Relativity1
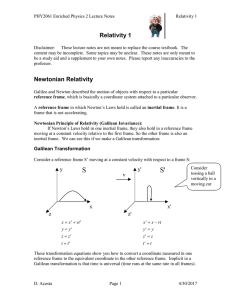
... Newtonian Relativity Galileo and Newton described the motion of objects with respect to a particular reference frame, which is basically a coordinate system attached to a particular observer. A reference frame in which Newton’s Laws hold is called an inertial frame. It is a frame that is not acceler ...
... Newtonian Relativity Galileo and Newton described the motion of objects with respect to a particular reference frame, which is basically a coordinate system attached to a particular observer. A reference frame in which Newton’s Laws hold is called an inertial frame. It is a frame that is not acceler ...
Tutorial_03_Newton2 - UMD Physics
... rope, the other end of which is then reeled in by a machine. The rope pulls the child straight upward at steady speed. The child weighs 250 newtons, which means gravity pulls him downward with 250 newtons of force. A. (Work together) In the box at the right, draw a diagram of this situation that you ...
... rope, the other end of which is then reeled in by a machine. The rope pulls the child straight upward at steady speed. The child weighs 250 newtons, which means gravity pulls him downward with 250 newtons of force. A. (Work together) In the box at the right, draw a diagram of this situation that you ...
Central Net Force Particle Model:
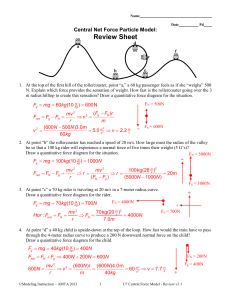
... 8. Here is the data for the space shuttle in its orbit around earth: Shuttle mass in orbit = 94,802 kg mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg shuttle orbital height above the earth = 2.76 x 105m radius of the earth = 6.38 x106 m shuttle tangential velocity when in orbit = 7823 m/sec a. Use the principles ...
... 8. Here is the data for the space shuttle in its orbit around earth: Shuttle mass in orbit = 94,802 kg mass of the earth = 6 x 1024 kg shuttle orbital height above the earth = 2.76 x 105m radius of the earth = 6.38 x106 m shuttle tangential velocity when in orbit = 7823 m/sec a. Use the principles ...
Exam I - Physics
... pages for scratch work. PARTIAL CREDIT POSSIBLE: Select one (1), two (2), or three (3) answers 6 points if you mark the single correct answer 4 points if the correct answer is among your two choices 2 points if the correct answer is among your three choices 10 problems, 6 pts each =60 pts = 50% of e ...
... pages for scratch work. PARTIAL CREDIT POSSIBLE: Select one (1), two (2), or three (3) answers 6 points if you mark the single correct answer 4 points if the correct answer is among your two choices 2 points if the correct answer is among your three choices 10 problems, 6 pts each =60 pts = 50% of e ...
Unbalanced Forces & Acceleration
... Unbalanced Forces and Velocity (cont.) • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the same direction as the motion speeds the object up. • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the opposite direction as the motion slows the object down. • Friction is applied in the opposite dire ...
... Unbalanced Forces and Velocity (cont.) • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the same direction as the motion speeds the object up. • An unbalanced force applied to a moving object in the opposite direction as the motion slows the object down. • Friction is applied in the opposite dire ...
Newton`s Laws PPT for HTML
... constant velocity, unless acted upon by a net external force.” The property of an object that causes it to resist changes in its motion is called inertia. Inertia is proportional to an object’s mass. Inertia causes motion at a constant velocity. ...
... constant velocity, unless acted upon by a net external force.” The property of an object that causes it to resist changes in its motion is called inertia. Inertia is proportional to an object’s mass. Inertia causes motion at a constant velocity. ...