Uniform Motion - Virtual Homeschool Group
... You are moving at the same speed as the car when you jump out so you will roll forward. ...
... You are moving at the same speed as the car when you jump out so you will roll forward. ...
Acceleration - Weber Online
... force, mass, and acceleration of an object. • 1.Determine the relationship between the net force on an object and the object’s acceleration. • 2.Relate the effect of an object’s mass to its acceleration when an unbalanced force is applied. • 3.Determine the relationship between force, mass, and acce ...
... force, mass, and acceleration of an object. • 1.Determine the relationship between the net force on an object and the object’s acceleration. • 2.Relate the effect of an object’s mass to its acceleration when an unbalanced force is applied. • 3.Determine the relationship between force, mass, and acce ...
Inclined Planes, and Pulleys
... Machines are used to make work more convenient by multiplying force at the expense of speed, or vice versa. A machine does not multiply work, however. The work output of a machine is never greater than the work input; thus the law of conservation of energy is not contradicted. In fact, the useful wo ...
... Machines are used to make work more convenient by multiplying force at the expense of speed, or vice versa. A machine does not multiply work, however. The work output of a machine is never greater than the work input; thus the law of conservation of energy is not contradicted. In fact, the useful wo ...
Chapter 1 Matter in Motion
... The “LAW” Part 2 Gravitational force decreases as distance increases. Here’s a fact for thought. The sun is 300,000 times more massive than the Earth. So why aren’t we attracted to the sun? It is because of the distance from the sun. We are so far that the suns gravity is cancel out by the Eart ...
... The “LAW” Part 2 Gravitational force decreases as distance increases. Here’s a fact for thought. The sun is 300,000 times more massive than the Earth. So why aren’t we attracted to the sun? It is because of the distance from the sun. We are so far that the suns gravity is cancel out by the Eart ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • The gravitational force is always attractive • Every mass attracts every other mass • The gravitational force is symmetric • The magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by mass 1 on mass 2 is equal in magnitude to the force exerted by mass 2 on mass 1 • The two forces form an action-reaction ...
... • The gravitational force is always attractive • Every mass attracts every other mass • The gravitational force is symmetric • The magnitude of the gravitational force exerted by mass 1 on mass 2 is equal in magnitude to the force exerted by mass 2 on mass 1 • The two forces form an action-reaction ...
Force
... Other definition: when the net external force on an object is zero the net acceleration of the object is zero External forces-single forces acting on the object and they result from the interacting between an object and its ...
... Other definition: when the net external force on an object is zero the net acceleration of the object is zero External forces-single forces acting on the object and they result from the interacting between an object and its ...
AOS2 KK1 & KK2 Motion & Levers ppt.
... vertically eg. – Transverse (horizontal) taken from hip to hip eg. – Medial (also a horizontal) axis taken from the navel to the small of the back eg. cartwheel ...
... vertically eg. – Transverse (horizontal) taken from hip to hip eg. – Medial (also a horizontal) axis taken from the navel to the small of the back eg. cartwheel ...
12.3 Newton`s 3rd Law of Motion
... According to Newton’s 2nd law, if mass increases and force stays the same, acceleration decreases. The same force acts on both Earth and your pen but Earth has such a large mass that its acceleration is so small you don’t notice it. ...
... According to Newton’s 2nd law, if mass increases and force stays the same, acceleration decreases. The same force acts on both Earth and your pen but Earth has such a large mass that its acceleration is so small you don’t notice it. ...
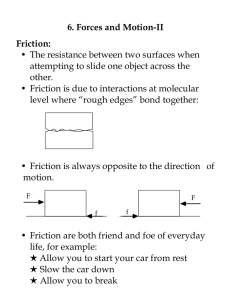
6. Forces and Motion-II Friction: • The resistance between two surfaces when
... level where “rough edges” bond together: ...
... level where “rough edges” bond together: ...
centripetal force and centrifugal force
... consider all the details that are most significant. Read the passage again and students should jot down notes on a 3 x 5 card. They should fill the card with their notes (remind them to pay close attention to the size of their writing). Students should study the notes on their large card and elimina ...
... consider all the details that are most significant. Read the passage again and students should jot down notes on a 3 x 5 card. They should fill the card with their notes (remind them to pay close attention to the size of their writing). Students should study the notes on their large card and elimina ...
Gravity: a force of attraction between objects that is due to their mass
... combination of all forces acting on an object is the net force. ...
... combination of all forces acting on an object is the net force. ...