Gravity, Air Resistence, Terminal Velocity, and Projectile Motion
... The force of gravity is NOT the same as the acceleration DUE to gravity! ...
... The force of gravity is NOT the same as the acceleration DUE to gravity! ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Newton`s second law
... If two particles are connected by a string passing over a smooth pulley or peg, the heavier particle will move downwards and the lighter one upwards. Three modelling assumptions are important here (and often appear in examination questions). • As before, if they are connected by an inextensible stri ...
... If two particles are connected by a string passing over a smooth pulley or peg, the heavier particle will move downwards and the lighter one upwards. Three modelling assumptions are important here (and often appear in examination questions). • As before, if they are connected by an inextensible stri ...
Work Done
... displacement. If the granola bar were moving vertically, such as in an elevator, then they each force would be doing work. Moving up in an elevator the normal force would do positive work, and the weight would do negative work. N Tofu Almond Crunch mg ...
... displacement. If the granola bar were moving vertically, such as in an elevator, then they each force would be doing work. Moving up in an elevator the normal force would do positive work, and the weight would do negative work. N Tofu Almond Crunch mg ...
Powerpoint Slides - Faculty Web Sites
... 1. Newton’s 1st Law: An object at rest, remains at rest, OR if in motion, travels in a straight line at constant velocity, UNLESS acted on by a net force. ...
... 1. Newton’s 1st Law: An object at rest, remains at rest, OR if in motion, travels in a straight line at constant velocity, UNLESS acted on by a net force. ...
posted
... EVALUATE: If in part (b) the pull force is decreased, block B will slow down, with an acceleration directed to the left. In this case the friction force on A would be to the left, to prevent relative motion between the two blocks by giving A an acceleration equal to that of B. ay ...
... EVALUATE: If in part (b) the pull force is decreased, block B will slow down, with an acceleration directed to the left. In this case the friction force on A would be to the left, to prevent relative motion between the two blocks by giving A an acceleration equal to that of B. ay ...
Solutions for HW chapter 18
... Therefore, the +2q charge is located at a position of x 0.71 m . 16- REASONING According to Newton’s second law, the centripetal acceleration experienced by the orbiting electron is equal to the centripetal force divided by the electron’s mass. Recall from Section 5.3 that the centripetal force F ...
... Therefore, the +2q charge is located at a position of x 0.71 m . 16- REASONING According to Newton’s second law, the centripetal acceleration experienced by the orbiting electron is equal to the centripetal force divided by the electron’s mass. Recall from Section 5.3 that the centripetal force F ...
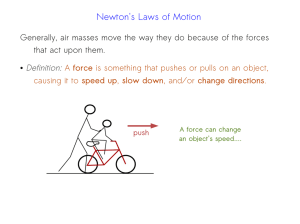
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... In our case, the moving object is any small mass of air as it moves through the atmosphere. And because the Earth is rotating, this air will appear to be deflected by a Coriolis force, much like the example ...
... In our case, the moving object is any small mass of air as it moves through the atmosphere. And because the Earth is rotating, this air will appear to be deflected by a Coriolis force, much like the example ...
Secondary Robot
... Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a ...
... Motion states that the acceleration of an object is produced by a net force in the same direction as the acceleration, is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. This means that the acceleration (a) of an object is dependant on a ...
File - PHYSICS PHUN WITH MS.BEGUM
... 38. The metric unit of force is called the Newton. 39. Objects keep moving, even when there are no forces present due to their inertia. 40. Inertia is the resistance of any material to change its state of motion. 41. A car at rest has more inertia than a mouse moving at 20 m/s, because it has more m ...
... 38. The metric unit of force is called the Newton. 39. Objects keep moving, even when there are no forces present due to their inertia. 40. Inertia is the resistance of any material to change its state of motion. 41. A car at rest has more inertia than a mouse moving at 20 m/s, because it has more m ...
Potoourii of Interia Demos - Otterbein Neutrino Research Group
... eventually slowing an object down. Friction has three types on a surface: sliding, rolling, and static Acceleration – The rte in which velocity (speed together with the direction of the motion) is changing Net force – The combination of all forces acting on an object. For example: if you pull on an ...
... eventually slowing an object down. Friction has three types on a surface: sliding, rolling, and static Acceleration – The rte in which velocity (speed together with the direction of the motion) is changing Net force – The combination of all forces acting on an object. For example: if you pull on an ...
Tuesday, June 3, 2008
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frame Newton’s 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of net external force, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity. What does this statement tell us? ...
... Newton’s First Law and Inertial Frame Newton’s 1st law of motion (Law of Inertia): In the absence of net external force, an object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion continues in motion with a constant velocity. What does this statement tell us? ...