Episode 209 - Teaching Advanced Physics
... avoid the boredom factor (‘but we've done all this already'!). The task is presented as a fairly open-ended investigation, but with lots of hints. Students drop increasing numbers of cupcake holders through a height of up to 3 metres (the higher the better up to this value). The area presented to th ...
... avoid the boredom factor (‘but we've done all this already'!). The task is presented as a fairly open-ended investigation, but with lots of hints. Students drop increasing numbers of cupcake holders through a height of up to 3 metres (the higher the better up to this value). The area presented to th ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws
... Active Learning: Forces and Newton’s Laws II Newton’s Laws 1. In which of the following scenarios is the net force on the object zero? (circle all that apply) a. car traveling at constant speed in a straight line b. block sliding down a steep incline at constant speed c. parachuter drifting down at ...
... Active Learning: Forces and Newton’s Laws II Newton’s Laws 1. In which of the following scenarios is the net force on the object zero? (circle all that apply) a. car traveling at constant speed in a straight line b. block sliding down a steep incline at constant speed c. parachuter drifting down at ...
Lect-26
... Therefore, the kinematic equations cannot be applied If the block is released from some position x = A, then the initial acceleration is –kA/m When the block passes through the equilibrium position, a = 0 The block continues to x = -A where its acceleration is +kA/m ...
... Therefore, the kinematic equations cannot be applied If the block is released from some position x = A, then the initial acceleration is –kA/m When the block passes through the equilibrium position, a = 0 The block continues to x = -A where its acceleration is +kA/m ...
Exam II Difficult Problems
... • A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance. Momentum changed by Impulse ...
... • A rock is dropped from a high tower and falls freely under the influence of gravity. Which one of the following statements concerning the rock as it falls is true? Neglect the effects of air resistance. Momentum changed by Impulse ...
Projectile Motion
... C. What is the cannonball’s maximum height? D. What is the total time of travel? E. What is the cannonball’s range? ...
... C. What is the cannonball’s maximum height? D. What is the total time of travel? E. What is the cannonball’s range? ...
Example
... velocity varies from point to point. Its magnitude is equal to r where r is the distance of the point from O. Its direction is tangent to the circular orbit (see fig. a). The net velocity is the vector sum of these two terms. For example, the velocity of point P is always zero. The velocity of the ...
... velocity varies from point to point. Its magnitude is equal to r where r is the distance of the point from O. Its direction is tangent to the circular orbit (see fig. a). The net velocity is the vector sum of these two terms. For example, the velocity of point P is always zero. The velocity of the ...
Balanced And Unbalanced Forces We perform different types of
... You must have observed that when a billiard ball is struck by a pool cue, the rod moves slowly whereas the ball moves with a very high speed. Can you relate the velocity of the rod with the velocity of the ball after impact? The velocities of two bodies before and after collision can be related to e ...
... You must have observed that when a billiard ball is struck by a pool cue, the rod moves slowly whereas the ball moves with a very high speed. Can you relate the velocity of the rod with the velocity of the ball after impact? The velocities of two bodies before and after collision can be related to e ...
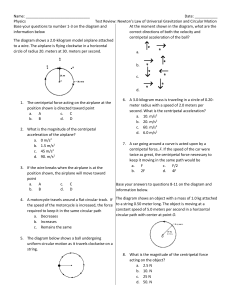
Circular Motion Test Review Name
... 6) A boy and a girl are riding on a merry-go-round which is turning at a constant rate. The boy is near the outer edge, and the girl is closer to the center. Who has the greater angular displacement? A) the boy B) the girl C) Both have the same non-zero angular displacement. D) Both have zero angula ...
... 6) A boy and a girl are riding on a merry-go-round which is turning at a constant rate. The boy is near the outer edge, and the girl is closer to the center. Who has the greater angular displacement? A) the boy B) the girl C) Both have the same non-zero angular displacement. D) Both have zero angula ...
Study Materials - English
... We have learnt that a force is needed to change a speed or the direction of motion of an object. We always observe that an object dropped from a height falls towards the earth. We know that all the planets go around the sun. The moon goes around the earth. In all these cases, there must be some forc ...
... We have learnt that a force is needed to change a speed or the direction of motion of an object. We always observe that an object dropped from a height falls towards the earth. We know that all the planets go around the sun. The moon goes around the earth. In all these cases, there must be some forc ...
Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Gravitation
... • Note that m is the mass of the central object that is being orbited. The mass of the planet or satellite that is in orbit does not affect its speed or period. • The mean radius (r) is the distance between the centers of the two bodies. ...
... • Note that m is the mass of the central object that is being orbited. The mass of the planet or satellite that is in orbit does not affect its speed or period. • The mean radius (r) is the distance between the centers of the two bodies. ...
PHYS 1443 – Section 501 Lecture #1
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
... People have been very curious about the stars in the sky, making observations for a long time. But the data people collected have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proporti ...
Question Bank - India Study Channel
... 2. Consider a planet whose radius and mass were half that of earth. What will be the value of acceleration due to gravity at its surface? 3. Write the S.I. units of (i) pressure (ii) relative density 4. The earth attracts the moon. Does moon attract the earth? If so, why does earth does not move tow ...
... 2. Consider a planet whose radius and mass were half that of earth. What will be the value of acceleration due to gravity at its surface? 3. Write the S.I. units of (i) pressure (ii) relative density 4. The earth attracts the moon. Does moon attract the earth? If so, why does earth does not move tow ...
What Was THAT Again?
... Two objects side by side must have the same speed. Acceleration and velocity are always in the same direction. Velocity is a force. If velocity is zero, then acceleration must be zero too. FALLING BODIES Heavier objects fall faster than light ones. Acceleration is the same as velocity. ...
... Two objects side by side must have the same speed. Acceleration and velocity are always in the same direction. Velocity is a force. If velocity is zero, then acceleration must be zero too. FALLING BODIES Heavier objects fall faster than light ones. Acceleration is the same as velocity. ...
Total Time
... particular direction. Examples: An airplane moving North at 500 mph A missile moving towards you at 200 m/s ...
... particular direction. Examples: An airplane moving North at 500 mph A missile moving towards you at 200 m/s ...
Document
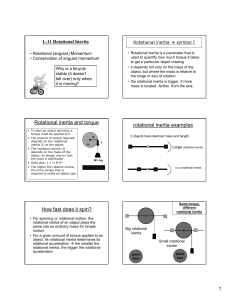
... The direction of is along the zaxis, perpendicular to the wheel, and is given by the right hand rule. To remind you that angular velocity has a direction, I’ll write z,avg=/t and z=d/dt. Our rules for vectors apply. You get to choose the direction of the z-axis. Whether z is positive or neg ...
... The direction of is along the zaxis, perpendicular to the wheel, and is given by the right hand rule. To remind you that angular velocity has a direction, I’ll write z,avg=/t and z=d/dt. Our rules for vectors apply. You get to choose the direction of the z-axis. Whether z is positive or neg ...