simple harmonic motion
... Figure 2: Five key points of a mass oscillating on a spring. The mass completes an entire cycle as it goes from position A to position E. A description of each position is as follows: Position A: The spring is compressed; the mass is above the equilibrium point at y = A and is about to be released. ...
... Figure 2: Five key points of a mass oscillating on a spring. The mass completes an entire cycle as it goes from position A to position E. A description of each position is as follows: Position A: The spring is compressed; the mass is above the equilibrium point at y = A and is about to be released. ...
Lab Report - Activity P08: Newton`s Second Law – Constant Force
... The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object: F a net m a is acceleration, Fnet is net force, and m is mass. Applying Newton’s Second Law to the static setup used in this activity for an o ...
... The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to and in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object: F a net m a is acceleration, Fnet is net force, and m is mass. Applying Newton’s Second Law to the static setup used in this activity for an o ...
t - UW Canvas
... When the direction of velocity and acceleration are the same, the object is speeding up. When the direction of velocity and acceleration are opposite, the object is slowing down. When an object slows down, its acceleration is opposite to the direction of its motion. This is known as deceleration. ...
... When the direction of velocity and acceleration are the same, the object is speeding up. When the direction of velocity and acceleration are opposite, the object is slowing down. When an object slows down, its acceleration is opposite to the direction of its motion. This is known as deceleration. ...
Chapters 4&5
... • The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle believed that forces - pushes and pulls - caused motion • The Aristotelian view prevailed for some 2000 years • Galileo first discovered the correct relation between force and motion • Force causes not motion itself but change in motion ...
... • The ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle believed that forces - pushes and pulls - caused motion • The Aristotelian view prevailed for some 2000 years • Galileo first discovered the correct relation between force and motion • Force causes not motion itself but change in motion ...
This laboratory investigation was modified from a Verneir Probe Lab
... Start the mass moving up and down by lifting it 10 cm and then releasing it. Take care that the mass is not swinging from side to side. Click to record position and velocity data. Print your graphs and compare to your predictions. Comment on any differences. To calculate the spring potential energy, ...
... Start the mass moving up and down by lifting it 10 cm and then releasing it. Take care that the mass is not swinging from side to side. Click to record position and velocity data. Print your graphs and compare to your predictions. Comment on any differences. To calculate the spring potential energy, ...
Acceleration Due to Gravity
... gravity is the net force that is responsible for downward motion of free falling objects. It accelerates all objects at the same rate, that is, two objects of roughly the same size ...
... gravity is the net force that is responsible for downward motion of free falling objects. It accelerates all objects at the same rate, that is, two objects of roughly the same size ...
experimenting with forces
... understand how the force of gravity works. This is sort of a science fairytale. The true story seems to be that Newton was walking through an apple orchard one day, when he started thinking about how things fall. He especially wondered why apples always fall straight down and why they speed up as th ...
... understand how the force of gravity works. This is sort of a science fairytale. The true story seems to be that Newton was walking through an apple orchard one day, when he started thinking about how things fall. He especially wondered why apples always fall straight down and why they speed up as th ...
Radial (Centripetal) Acceleration – ar or ac
... Radial (Centripetal) Acceleration – ar or ac I. Uniform Circular Motion ‘uniform’ means ‘constant’ - In this case, it refers to constant speed (v) or constant angular speed ( , omega). A particle moves in circular motion with constant speed. dv Recall that in one dimension, (linear) acceleration w ...
... Radial (Centripetal) Acceleration – ar or ac I. Uniform Circular Motion ‘uniform’ means ‘constant’ - In this case, it refers to constant speed (v) or constant angular speed ( , omega). A particle moves in circular motion with constant speed. dv Recall that in one dimension, (linear) acceleration w ...
File - Thomas Tallis Science
... If there is no resultant force on an object, can it be moving? Aristotle thought that all objects tend to move towards their natural place in the universe, and that their velocity was determined by the strength of this force. For instance, heavier objects would move towards the ground more quickly t ...
... If there is no resultant force on an object, can it be moving? Aristotle thought that all objects tend to move towards their natural place in the universe, and that their velocity was determined by the strength of this force. For instance, heavier objects would move towards the ground more quickly t ...
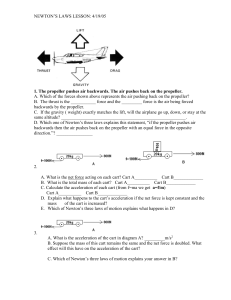
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
Rotational Kinematics (Part I from chapter 10)
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
... Every particle on the disc undergoes circular motion about the origin, O Polar coordinates are convenient to use to represent the position of P (or any other point) P is located at (r, q) where r is the distance from the origin to P and q is the measured counterclockwise from the reference line ...
Force and Motion
... 2. If Lightning travels 1000m in 10 seconds, how far will he travel in 1 minute? 3. If it takes Doc Hudson 120 seconds to travel 3600 m, how long will it take him to travel 10,000 m? 4. Football player “A” has a mass of 100 kg and creates a force of 250 N, while football player “B” has a mass of 90 ...
... 2. If Lightning travels 1000m in 10 seconds, how far will he travel in 1 minute? 3. If it takes Doc Hudson 120 seconds to travel 3600 m, how long will it take him to travel 10,000 m? 4. Football player “A” has a mass of 100 kg and creates a force of 250 N, while football player “B” has a mass of 90 ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
... the force just change the velocity? Also, what does the mass of the cart have to do with how the motion changes? We know that it takes a much harder push to get a heavy cart moving than a lighter one. A Force Sensor and an Accelerometer will let you measure the force on a cart simultaneously with th ...
ALL PHYSICS REVIEW SHEET NAME: 1. Change .0005 m to milli
... 25. If a truck 5000kg moving 45m/s collides head on with a car 3444kg moving 34m/s in the other direction, what will their speed be? 26. If a crate 344kg slides 4m down a 46º ramp at a constant speed because of a man pushing back on it, find a) force exerted by man b) work done by man on crate, c) w ...
... 25. If a truck 5000kg moving 45m/s collides head on with a car 3444kg moving 34m/s in the other direction, what will their speed be? 26. If a crate 344kg slides 4m down a 46º ramp at a constant speed because of a man pushing back on it, find a) force exerted by man b) work done by man on crate, c) w ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... This law relates to the sum total of the forces on the body ( F ) the body's mass (m) and the acceleration produced (a) Note F must have the same F = ma. direction as 'a'. Newtons 3rd law of motion For every action force acting on one object, there is an equal but opposite reaction force acting o ...
... This law relates to the sum total of the forces on the body ( F ) the body's mass (m) and the acceleration produced (a) Note F must have the same F = ma. direction as 'a'. Newtons 3rd law of motion For every action force acting on one object, there is an equal but opposite reaction force acting o ...
Study Guide for GLO Conceptual Physics
... (frictionless) surface will continue to roll forever unless an external force acts on it. A zookeeper has to lift a lion on a stretcher at certain acceleration so the force must be equal to the mass of the stretcher and the lion times the acceleration needed. Example of Newton’s third law: Two ice s ...
... (frictionless) surface will continue to roll forever unless an external force acts on it. A zookeeper has to lift a lion on a stretcher at certain acceleration so the force must be equal to the mass of the stretcher and the lion times the acceleration needed. Example of Newton’s third law: Two ice s ...
Systems of Particles
... initially at rest (Figure below). The person slides on the cart’s top surface and finally comes to rest relative to the cart. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the person and the cart is 0.400. Friction between the cart and ground can be neglected. (a) Find the final velocity of the person ...
... initially at rest (Figure below). The person slides on the cart’s top surface and finally comes to rest relative to the cart. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the person and the cart is 0.400. Friction between the cart and ground can be neglected. (a) Find the final velocity of the person ...