Physics 101 Fall 02 - Youngstown State University
... Frequency (f) = number of turns a rotating object makes in one second. f = # of turns/time taken to make the turns. Unit: Cycles per second or hertz (Hz) 1 cycle/second = 1 Hz Eg 1. The frequency of the second hand of an analogue clock = 1 turn/60s = 1/60 Hz. ...
... Frequency (f) = number of turns a rotating object makes in one second. f = # of turns/time taken to make the turns. Unit: Cycles per second or hertz (Hz) 1 cycle/second = 1 Hz Eg 1. The frequency of the second hand of an analogue clock = 1 turn/60s = 1/60 Hz. ...
Document
... 7. The only force acting on a 2.0kg body as it moves along a positive x axis has an x component Fx = -6x N, with x in meters. The velocity at x = 3.0 m is 8.0 m/s. (a) What is the velocity of the body at x = 4.0 m? (b) At what positive value of x will the body have a velocity of 5.0 m/s? ANSWER: (a ...
... 7. The only force acting on a 2.0kg body as it moves along a positive x axis has an x component Fx = -6x N, with x in meters. The velocity at x = 3.0 m is 8.0 m/s. (a) What is the velocity of the body at x = 4.0 m? (b) At what positive value of x will the body have a velocity of 5.0 m/s? ANSWER: (a ...
Document
... • Concept of conservation of momentum also applies to the analysis of the mass center motion, ...
... • Concept of conservation of momentum also applies to the analysis of the mass center motion, ...
Forces in 1
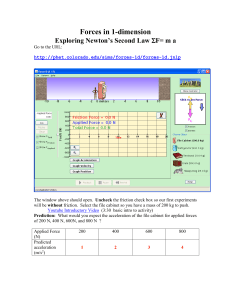
... Friction: Watch the video on 1-D forces Friction to obtain the information required for the questions below. What is the mass of the file cabinet? (include correct units) M= ____200 kg__________ What is the maximum magnitude (ignore +/-) of the static friction force? (include units) Static Friction ...
... Friction: Watch the video on 1-D forces Friction to obtain the information required for the questions below. What is the mass of the file cabinet? (include correct units) M= ____200 kg__________ What is the maximum magnitude (ignore +/-) of the static friction force? (include units) Static Friction ...
R - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... HO = constant We conclude that the angular momentum of a particle moving under a central force is constant, both in magnitude and direction, and that the particle moves in a plane perpendicular to HO . ...
... HO = constant We conclude that the angular momentum of a particle moving under a central force is constant, both in magnitude and direction, and that the particle moves in a plane perpendicular to HO . ...
Ordinary Differential Equations
... where ω 0 k/m is the angular frequency of the un-damped oscillator (b=0). The forced oscillator vibrates at the frequency of the driving force and that the amplitude of the oscillator is constant for a given driving force because it is being driven in steady-state by an external force. For small d ...
... where ω 0 k/m is the angular frequency of the un-damped oscillator (b=0). The forced oscillator vibrates at the frequency of the driving force and that the amplitude of the oscillator is constant for a given driving force because it is being driven in steady-state by an external force. For small d ...
Circular Motion - Garnet Valley School District
... A 0.50 kg box is attached to string on a frictionless horizontal table. The box revolves in a circle of radius 2.8 m. If the box completes 1 revolution every 2.0 seconds, what is the tension in the string? FN r ...
... A 0.50 kg box is attached to string on a frictionless horizontal table. The box revolves in a circle of radius 2.8 m. If the box completes 1 revolution every 2.0 seconds, what is the tension in the string? FN r ...
File
... Whenever an object moves against another object, it is likely to experience frictional forces. These are forces that act in the direction opposite to the direction of movement. Friction can be useful. Friction between our shoes and the floor stop us from slipping, and friction between tyres and the ...
... Whenever an object moves against another object, it is likely to experience frictional forces. These are forces that act in the direction opposite to the direction of movement. Friction can be useful. Friction between our shoes and the floor stop us from slipping, and friction between tyres and the ...
Updated Center of Mass
... The equations above show that the center of mass of a system of particles moves as though all the system's mass were concentrated there, and that the vector sum of all the external forces were applied there. A dramatic example is given in the figure. In a fireworks display a rocket is launched and m ...
... The equations above show that the center of mass of a system of particles moves as though all the system's mass were concentrated there, and that the vector sum of all the external forces were applied there. A dramatic example is given in the figure. In a fireworks display a rocket is launched and m ...
Analyzing a Dual Fan Carts Motion (Low Tech).
... In order to accurately measure the force produced by the fans each lab group will need an electronic lab scale or lab balance, such as a triple beam balance. Typically, each fan with fresh alkaline batteries will have a difference in mass of about 10g = 0.01kg, which is a difference in weight of 0.1 ...
... In order to accurately measure the force produced by the fans each lab group will need an electronic lab scale or lab balance, such as a triple beam balance. Typically, each fan with fresh alkaline batteries will have a difference in mass of about 10g = 0.01kg, which is a difference in weight of 0.1 ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued
... External forces – Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity (and momentum) of a mass. ...
... External forces – Forces exerted on the objects by agents external to the system. Net force changes the velocity (and momentum) of a mass. ...
Forces and the Laws of Motion
... – The resultant vector is the sum of two or more vectors and can be determined trigonometrically or graphically. – A single vector can be resolved into two or more components that have the same effect. Fx = F.cosq F ...
... – The resultant vector is the sum of two or more vectors and can be determined trigonometrically or graphically. – A single vector can be resolved into two or more components that have the same effect. Fx = F.cosq F ...
2.Newtons_Laws
... Applied Force – “pushing/pulling” by hand. Gravitational Force (or “weight”) = mg Tension – applied by a rope or string Frictional force – applied by a surface to an object, acting parallel to the surface. • Normal Force applied by a surface to an object, acting normal to the surface. ...
... Applied Force – “pushing/pulling” by hand. Gravitational Force (or “weight”) = mg Tension – applied by a rope or string Frictional force – applied by a surface to an object, acting parallel to the surface. • Normal Force applied by a surface to an object, acting normal to the surface. ...
Chap. 7 Momentum - Coal City Unit District #1
... The impact force will still react the same. 1. If the impulse is over a long time, then the impact force is small. Example - a circus net 2. If the impulse is over a short time, then the impact force is large. Example - a body dumped from a 10 story window ...
... The impact force will still react the same. 1. If the impulse is over a long time, then the impact force is small. Example - a circus net 2. If the impulse is over a short time, then the impact force is large. Example - a body dumped from a 10 story window ...