Metrics - Cobb Learning
... 9. The law of conservation of energy says energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed (converted). Give an example of mechanical being converted into thermal. Give an example of chemical being converted into electrical. 10. Einstein suggested that energy can be created under certain cond ...
... 9. The law of conservation of energy says energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed (converted). Give an example of mechanical being converted into thermal. Give an example of chemical being converted into electrical. 10. Einstein suggested that energy can be created under certain cond ...
12.2 Speed
... same.) A car going around a bend at a constant 30 mph has a constant speed, but its velocity is not constant. (Note the change in direction.) ...
... same.) A car going around a bend at a constant 30 mph has a constant speed, but its velocity is not constant. (Note the change in direction.) ...
Chapter 1 - asmasaid
... You stand on a scale that rests on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upward. What is the relationship between the force due to gravity and the normal force exerted by the scale? A. N > mg B. N = mg C. N
... You stand on a scale that rests on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upward. What is the relationship between the force due to gravity and the normal force exerted by the scale? A. N > mg B. N = mg C. N
inelastic collision
... Ex. 6 - Starting from rest, two skaters “push off” against each other on smooth level ice. One is a woman (m1 = 54 kg), and one is a man (m2 = 88 kg). The woman recoils with a velocity of vf1 = +2.5 m/s. Find the recoil velocity vf2 of the man. ...
... Ex. 6 - Starting from rest, two skaters “push off” against each other on smooth level ice. One is a woman (m1 = 54 kg), and one is a man (m2 = 88 kg). The woman recoils with a velocity of vf1 = +2.5 m/s. Find the recoil velocity vf2 of the man. ...
forces - Humble ISD
... Forces: Gravity (a field force) • Weight is a force caused (on Earth) by the gravitational attraction of a mass to the Earth’s center. • The weight of a body, of mass m, is defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to grav ...
... Forces: Gravity (a field force) • Weight is a force caused (on Earth) by the gravitational attraction of a mass to the Earth’s center. • The weight of a body, of mass m, is defined to be the force, W, with which it is attracted to the Earth. On Earth, W = mg, where g is the acceleration due to grav ...
Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion π
... Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion ⇒ An object in uniform circular motion is accelerating because its direction is constantly changing. Period (T): time for one complete revolution Speed: v = ...
... Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion ⇒ An object in uniform circular motion is accelerating because its direction is constantly changing. Period (T): time for one complete revolution Speed: v = ...
∑ = −
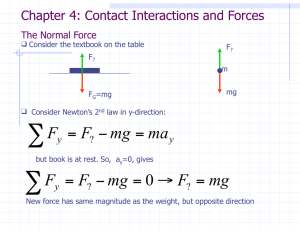
... New force is a result of the contact between the book and the table New force is called the Normal Force, n, N or FN In general it is not equal to mg, - we must usually solve for FN ``Normal’’ means ``perpendicular’’ (to the surface of contact) Now, apply an additional force, FA to the book FA ...
... New force is a result of the contact between the book and the table New force is called the Normal Force, n, N or FN In general it is not equal to mg, - we must usually solve for FN ``Normal’’ means ``perpendicular’’ (to the surface of contact) Now, apply an additional force, FA to the book FA ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... force it is only perceived as one) – is the perceived response of the object’s inertia resisting the circular motion (& its rotating environment) – has a magnitude equal to the centripetal force acting on the body ...
... force it is only perceived as one) – is the perceived response of the object’s inertia resisting the circular motion (& its rotating environment) – has a magnitude equal to the centripetal force acting on the body ...
Content Literacy
... It is a skill you are not born with. It can be taught/learned. It is a skill that should be taught/learned. It should be taught in math/science classes. It plays a bigger role than you think in learning technical subjects. ...
... It is a skill you are not born with. It can be taught/learned. It is a skill that should be taught/learned. It should be taught in math/science classes. It plays a bigger role than you think in learning technical subjects. ...
2 Isaac Newton (1642-1727) - Michigan State University
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
... “In the beginning of 1665 I found the…rule for reducing any dignity of binomial to a series. The same year in May I found the method of tangents and in November the method of fluxions and in the next year in January had the Theory of Colours and in May following I had the entrance into the inverse m ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.