Physics Review
... 94. The watt and the horsepower are both units of ____________________. 95. A machine is a device that changes a(an) ____________________. 96. The force that is exerted on a machine is called the ____________________ force. 97. The _________________________ of a machine is the number of times that t ...
... 94. The watt and the horsepower are both units of ____________________. 95. A machine is a device that changes a(an) ____________________. 96. The force that is exerted on a machine is called the ____________________ force. 97. The _________________________ of a machine is the number of times that t ...
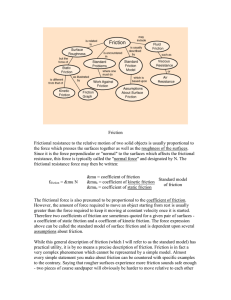
Static Friction
... kinetic friction. Typical results for the woods I have used are 0.4 for the static coefficient and 0.3 for the kinetic coefficient. When carefully standardized surfaces are used to measure the friction coefficients, the difference between static and kinetic coefficients tends to disappear, indicatin ...
... kinetic friction. Typical results for the woods I have used are 0.4 for the static coefficient and 0.3 for the kinetic coefficient. When carefully standardized surfaces are used to measure the friction coefficients, the difference between static and kinetic coefficients tends to disappear, indicatin ...
UserManual4Modules
... horizontally at the same time. Assume negligible air friction 2. Draw the path ( position versus time) of simultaneous fall of both balls 3. At each position show the direction of velocities of both balls 4. From the paths that you have drawn, is it possible for Ball A and ball B to hit 5. the groun ...
... horizontally at the same time. Assume negligible air friction 2. Draw the path ( position versus time) of simultaneous fall of both balls 3. At each position show the direction of velocities of both balls 4. From the paths that you have drawn, is it possible for Ball A and ball B to hit 5. the groun ...
Units and Dimensions - RIT
... Vectors: We will for the moment deal with 1D and 2D cases. A scalar is a quantity that has a value, but no direction. A scalar can be positive or negative. Scalar arithmetic is the usual stuff you learned through grade school: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising to a power. ...
... Vectors: We will for the moment deal with 1D and 2D cases. A scalar is a quantity that has a value, but no direction. A scalar can be positive or negative. Scalar arithmetic is the usual stuff you learned through grade school: addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and raising to a power. ...
PP Chapter 2 Text
... the same when direction is not a factor. the same for free-fall situations. Explanation: Velocity is the rate at which distance changes with time; acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes with time. ...
... the same when direction is not a factor. the same for free-fall situations. Explanation: Velocity is the rate at which distance changes with time; acceleration is the rate at which velocity changes with time. ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.