PHYSICAL SCIENCE
... • As an object falls faster, the upward force of air resistance increases. • Eventually, the upward air resistance force becomes large enough to balance the downward force of gravity – making the net force on the object 0. • As a result, the object falls with a constant speed – terminal velocity. • ...
... • As an object falls faster, the upward force of air resistance increases. • Eventually, the upward air resistance force becomes large enough to balance the downward force of gravity – making the net force on the object 0. • As a result, the object falls with a constant speed – terminal velocity. • ...
30 Physics
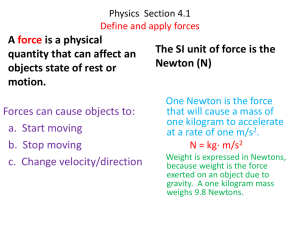
... (measured in Newtons). So why do so many people confuse the two and/or not differentiate the two? It just so happens that the more mass an object has the more it weighs and in fact mass and weight are proportional. So if an objects mass is doubled so is its weight....but they are NOT THE SAME!! Grav ...
... (measured in Newtons). So why do so many people confuse the two and/or not differentiate the two? It just so happens that the more mass an object has the more it weighs and in fact mass and weight are proportional. So if an objects mass is doubled so is its weight....but they are NOT THE SAME!! Grav ...
Investigating g On Other Planets Virtual Lab
... Discussion: A __________is any push or pull on an object and is measured in Newtons. ______________ forces are forces that are equal and opposite. ________________forces can cause a change in motion. According to Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, if a net force is applied to an object, the object will ___ ...
... Discussion: A __________is any push or pull on an object and is measured in Newtons. ______________ forces are forces that are equal and opposite. ________________forces can cause a change in motion. According to Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion, if a net force is applied to an object, the object will ___ ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... her box a greater distance? The student who_________________. a. pushed with less force b. who had lesser body mass c. pushed with more force d. who had greater body mass ...
... her box a greater distance? The student who_________________. a. pushed with less force b. who had lesser body mass c. pushed with more force d. who had greater body mass ...
Unit B, Chapter 3, Lesson 4
... should hit the ground at the same time. • Mass has no control over the rate at which objects fall. Gravity pulls harder on the object with more mass, but inertia overpowers gravity. – The objects have the same amount of acceleration. ...
... should hit the ground at the same time. • Mass has no control over the rate at which objects fall. Gravity pulls harder on the object with more mass, but inertia overpowers gravity. – The objects have the same amount of acceleration. ...
Newton`s third law of motion
... When the forces applied to an object produces a net force greater than zero the forces are unbalanced Unbalanced forces acting on an object do not cancel each other out. The object will accelerate in the direction of the strongest force. Motion occurs when forces are unbalanced Unbalanced forces htt ...
... When the forces applied to an object produces a net force greater than zero the forces are unbalanced Unbalanced forces acting on an object do not cancel each other out. The object will accelerate in the direction of the strongest force. Motion occurs when forces are unbalanced Unbalanced forces htt ...
Slide 1
... 6. Newton’s first law of motion: Objects in motion will stay in motion and objects at rest will stay at rest, an unbalanced force unless acted on by __________________. ...
... 6. Newton’s first law of motion: Objects in motion will stay in motion and objects at rest will stay at rest, an unbalanced force unless acted on by __________________. ...
Projectile motion and drag
... This section shows the use of a spreadsheet to calculate the properties of the motion of an object projected vertically upwards and affected by air resistance. Velocity at any point = v Drag force is proportional to v2 Drag force = Cv2 where C is the drag coefficient [= 0.00077 in this case] Acceler ...
... This section shows the use of a spreadsheet to calculate the properties of the motion of an object projected vertically upwards and affected by air resistance. Velocity at any point = v Drag force is proportional to v2 Drag force = Cv2 where C is the drag coefficient [= 0.00077 in this case] Acceler ...
Free fall

In Newtonian physics, free fall is any motion of a body where its weight is the only force acting upon it. In the context of general relativity, where gravitation is reduced to a space-time curvature, a body in free fall has no force acting on it and it moves along a geodesic. The present article only concerns itself with free fall in the Newtonian domain.An object in the technical sense of free fall may not necessarily be falling down in the usual sense of the term. An object moving upwards would not normally be considered to be falling, but if it is subject to the force of gravity only, it is said to be in free fall. The moon is thus in free fall.In a uniform gravitational field, in the absence of any other forces, gravitation acts on each part of the body equally and this is weightlessness, a condition that also occurs when the gravitational field is zero (such as when far away from any gravitating body). A body in free fall experiences ""0 g"".The term ""free fall"" is often used more loosely than in the strict sense defined above. Thus, falling through an atmosphere without a deployed parachute, or lifting device, is also often referred to as free fall. The aerodynamic drag forces in such situations prevent them from producing full weightlessness, and thus a skydiver's ""free fall"" after reaching terminal velocity produces the sensation of the body's weight being supported on a cushion of air.