Force due to gravity: A field force (a vector quantity) that always is
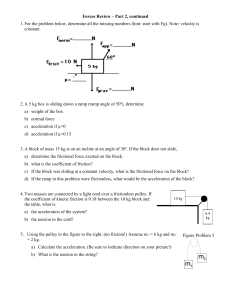
... a) the acceleration of the masses, and b) the magnitude of the tension in the string? c) the force in the bracket (while the blocks are in motion) that attaches the pulley to the ceiling 5) A 50kg box is pushed by a 600N force into a 30 kg box. The coefficient of friction between the boxes is 0.1. F ...
... a) the acceleration of the masses, and b) the magnitude of the tension in the string? c) the force in the bracket (while the blocks are in motion) that attaches the pulley to the ceiling 5) A 50kg box is pushed by a 600N force into a 30 kg box. The coefficient of friction between the boxes is 0.1. F ...
ME2 – MECHANICAL COMPONENTS
... Work can be defined in therm of torque T, acting through a given rotational displacement. ...
... Work can be defined in therm of torque T, acting through a given rotational displacement. ...
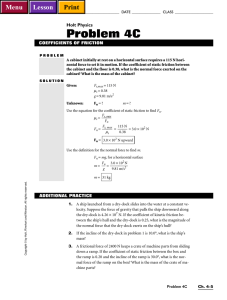
Holt Physics Problem 4C
... 1. A ship launched from a dry-dock slides into the water at a constant velocity. Suppose the force of gravity that pulls the ship downward along the dry-dock is 4.26 × 107 N. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ship’s hull and the dry-dock is 0.25, what is the magnitude of the normal ...
... 1. A ship launched from a dry-dock slides into the water at a constant velocity. Suppose the force of gravity that pulls the ship downward along the dry-dock is 4.26 × 107 N. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ship’s hull and the dry-dock is 0.25, what is the magnitude of the normal ...
Coefficient of Friction Lab
... problem – then you need to show all of your work. 1) Draw a free body diagram of the block being pulled on a flat surface. Label all forces. 2) Draw a free body diagram of the block being pulled on the inclined plane. Label all forces. 3) Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the woo ...
... problem – then you need to show all of your work. 1) Draw a free body diagram of the block being pulled on a flat surface. Label all forces. 2) Draw a free body diagram of the block being pulled on the inclined plane. Label all forces. 3) Calculate the coefficient of kinetic friction between the woo ...
Unit 5 2-D Forces
... Acts in the opposite direction of motion Acts parallel to the surfaces in contact. Is caused by interlocking irregularities All of these ...
... Acts in the opposite direction of motion Acts parallel to the surfaces in contact. Is caused by interlocking irregularities All of these ...
Static and Kinetic Friction
... 2.1 Static vs. Kinetic: There are two types of frictional forces, static and kinetic. Static friction is what keeps a resting body at rest. Kinetic friction is what slows down an object when slid on a surface. Any two materials have a static and kinetic coefficient of friction which represents how m ...
... 2.1 Static vs. Kinetic: There are two types of frictional forces, static and kinetic. Static friction is what keeps a resting body at rest. Kinetic friction is what slows down an object when slid on a surface. Any two materials have a static and kinetic coefficient of friction which represents how m ...
4-8 friction - mrhsluniewskiscience
... • Kinetic friction occurs when force is applied to an object and the object moves. ...
... • Kinetic friction occurs when force is applied to an object and the object moves. ...
1. What is a vector quantity? Give an example?
... When Fnet is zero, the object CANNOT be __________. a) accelerating b) at rest c) moving at a constant speed d) moving at a velocity that is constant 13. An object moving in a straight line increases its speed. What does this mean about the forces acting on the object? a) the forces acting on the ob ...
... When Fnet is zero, the object CANNOT be __________. a) accelerating b) at rest c) moving at a constant speed d) moving at a velocity that is constant 13. An object moving in a straight line increases its speed. What does this mean about the forces acting on the object? a) the forces acting on the ob ...
What are Forces? - Ms. Y`s 5th Grade Class
... from the earth they “lose” weight. Weight is caused by the force of attraction between the earth and objects on its surface. The greater the distance an object has from the earth, the less the force of attraction which would exist. ...
... from the earth they “lose” weight. Weight is caused by the force of attraction between the earth and objects on its surface. The greater the distance an object has from the earth, the less the force of attraction which would exist. ...
Applications of Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Frictional forces depend upon how hard the surfaces are being pressed together -> force perpendicular to the surface = normal force (FN) the types of surfaces that are in contact -> coefficient of friction F f ≤ µ s FN F f = µ k FN Material wood on wood wood on stone steel on steel (smooth) rubber t ...
... Frictional forces depend upon how hard the surfaces are being pressed together -> force perpendicular to the surface = normal force (FN) the types of surfaces that are in contact -> coefficient of friction F f ≤ µ s FN F f = µ k FN Material wood on wood wood on stone steel on steel (smooth) rubber t ...
Physics218_lecture_008
... acceleration and force • 1) Objects moving in a circle always have a component of acceleration, called centripetal, which is toward the center of the circle.* • 2) Centripetal acceleration must be caused by a force: – Friction, gravity – whatever force keeps it moving in a circle. – This force is of ...
... acceleration and force • 1) Objects moving in a circle always have a component of acceleration, called centripetal, which is toward the center of the circle.* • 2) Centripetal acceleration must be caused by a force: – Friction, gravity – whatever force keeps it moving in a circle. – This force is of ...
Chapter 4
... • Direction of friction – opposite to the direction of attempted sliding (along the surface) • The origin of friction – bonding between the sliding surfaces (microscopic cold-welding) ...
... • Direction of friction – opposite to the direction of attempted sliding (along the surface) • The origin of friction – bonding between the sliding surfaces (microscopic cold-welding) ...
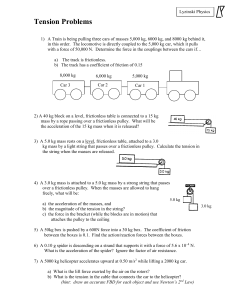
Review Forces Part 2
... c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. b) what is the coefficient of friction? c) If the block was sliding at a constant velocity, what is the ...
... c) acceleration if µ=0 d) acceleration if µ=0.15 3. A block of mass 15 kg is on an incline at an angle of 30º. If the block does not slide, a) determine the frictional force exerted on the block. b) what is the coefficient of friction? c) If the block was sliding at a constant velocity, what is the ...
Motion Along a Straight Line at Constant Acceleration
... required to keep the object moving in a circle. In reality this force is provided by another force, e.g. The tension in a string, friction or the force of gravity. ...
... required to keep the object moving in a circle. In reality this force is provided by another force, e.g. The tension in a string, friction or the force of gravity. ...
Section 1: Measuring Motion
... Friction – Friction between two surfaces that are not moving past each other. ...
... Friction – Friction between two surfaces that are not moving past each other. ...
Physics 151 Week 9 Day 3
... Caused by electron repulsion between two objects - Friction opposes (in opposite direction of) applied force - Direction of Friction force is Opposite of direction of motion / acceleration - Parallel to motion / Resists force of acceleration Friction Force is a contact force that acts on an object b ...
... Caused by electron repulsion between two objects - Friction opposes (in opposite direction of) applied force - Direction of Friction force is Opposite of direction of motion / acceleration - Parallel to motion / Resists force of acceleration Friction Force is a contact force that acts on an object b ...