Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 23. An object whose mass is 15.0 kg is pushed with a horizontal force of 20.0 N so that the object moves at a constant velocity. A. Draw the free body diagram, identifying the forces. B. Determine the size of all the forces and label them on the drawing. C. Determine the net force on the object. D. ...
... 23. An object whose mass is 15.0 kg is pushed with a horizontal force of 20.0 N so that the object moves at a constant velocity. A. Draw the free body diagram, identifying the forces. B. Determine the size of all the forces and label them on the drawing. C. Determine the net force on the object. D. ...
Forces: Newton`s Laws
... • If two surfaces are in contact, welding or sticking occurs where the bumps touch each other. These microwelds cause friction. • The larger the force pushing the two surfaces together is, the stronger these microwelds will be, because more of the surface bumps will come into contact. • To move one ...
... • If two surfaces are in contact, welding or sticking occurs where the bumps touch each other. These microwelds cause friction. • The larger the force pushing the two surfaces together is, the stronger these microwelds will be, because more of the surface bumps will come into contact. • To move one ...
Section 1 Powerpoint
... when a force acts on it? • 2. List the four types of friction. • 3. How does air resistance affect the acceleration of a falling object? • 4. Earth’s gravitational force acts in what direction? • 5. Describe why a projectile follows a ...
... when a force acts on it? • 2. List the four types of friction. • 3. How does air resistance affect the acceleration of a falling object? • 4. Earth’s gravitational force acts in what direction? • 5. Describe why a projectile follows a ...
Newton`s Laws
... When an object moves to a different planet. What is the weight of an 85.3-kg person on earth? On Mars (g=3.2 m/s/s)? ...
... When an object moves to a different planet. What is the weight of an 85.3-kg person on earth? On Mars (g=3.2 m/s/s)? ...
Dynamics Part 2
... N.T.L This figure shows the force during a collision between a truck and a train. You can clearly see the forces are EQUAL and OPPOSITE. To help you understand the law better, look at this situation from the point of view of Newton’s Second Law. ...
... N.T.L This figure shows the force during a collision between a truck and a train. You can clearly see the forces are EQUAL and OPPOSITE. To help you understand the law better, look at this situation from the point of view of Newton’s Second Law. ...
Student Notes
... Notice that once you get an object moving it takes less force to keep it moving When the object is moving you are pushing against the kinetic friction ...
... Notice that once you get an object moving it takes less force to keep it moving When the object is moving you are pushing against the kinetic friction ...
Name - Net Start Class
... Newton’s first law of motion states that the motion of an object, such as a baseball changes only if an unbalanced force acts on it. Force and motion are connected. Force and Acceleration What is the difference when throwing a ball as hard and you can or tossing it gently? The harder you throw somet ...
... Newton’s first law of motion states that the motion of an object, such as a baseball changes only if an unbalanced force acts on it. Force and motion are connected. Force and Acceleration What is the difference when throwing a ball as hard and you can or tossing it gently? The harder you throw somet ...
Chapter 4
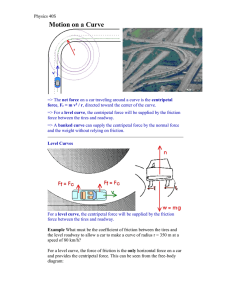
... • Direction of friction – opposite to the direction of attempted sliding (along the surface) • The origin of friction – bonding between the sliding surfaces (microscopic cold-welding) ...
... • Direction of friction – opposite to the direction of attempted sliding (along the surface) • The origin of friction – bonding between the sliding surfaces (microscopic cold-welding) ...
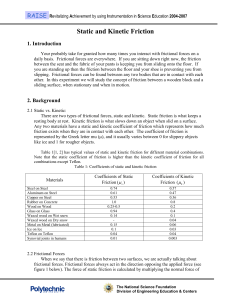
Static and Kinetic Friction
... 2.1 Static vs. Kinetic: There are two types of frictional forces, static and kinetic. Static friction is what keeps a resting body at rest. Kinetic friction is what slows down an object when slid on a surface. Any two materials have a static and kinetic coefficient of friction which represents how m ...
... 2.1 Static vs. Kinetic: There are two types of frictional forces, static and kinetic. Static friction is what keeps a resting body at rest. Kinetic friction is what slows down an object when slid on a surface. Any two materials have a static and kinetic coefficient of friction which represents how m ...
Mechanics
... where µs is the static friction coefficient, and µk is the kinetic friction coefficient. Normally µs ≥ µk . It is important to note that, under static conditions, unless the impending slippage condition is imperative at a contact, the friction force and its direction may be unknown. They can be asce ...
... where µs is the static friction coefficient, and µk is the kinetic friction coefficient. Normally µs ≥ µk . It is important to note that, under static conditions, unless the impending slippage condition is imperative at a contact, the friction force and its direction may be unknown. They can be asce ...
Chapter 5 Lectures
... Mass is one of the single most misunderstood concepts in chemistry and physics. It is not the same as “weight,” although the two measurements are related. Mass is a measure of the amount of inertia that a body has—it’s a measure of how hard it is to change an object’s motion. The more mass you have, ...
... Mass is one of the single most misunderstood concepts in chemistry and physics. It is not the same as “weight,” although the two measurements are related. Mass is a measure of the amount of inertia that a body has—it’s a measure of how hard it is to change an object’s motion. The more mass you have, ...
icq06-07(7)
... Due to air friction, the ball is continuously losing mechanical energy. Therefore it has less KE (and consequently a lower speed) on the way down. This means it will take more time on the way down !! Follow-up: How does the force of air resistance compare to gravity when the ball reaches terminal ve ...
... Due to air friction, the ball is continuously losing mechanical energy. Therefore it has less KE (and consequently a lower speed) on the way down. This means it will take more time on the way down !! Follow-up: How does the force of air resistance compare to gravity when the ball reaches terminal ve ...
friction force
... Friction is overcome, the Force of Kinetic Friction is what slows down a moving object! ...
... Friction is overcome, the Force of Kinetic Friction is what slows down a moving object! ...
Newton`s First Law
... When an object moves to a different planet. What is the weight of an 85.3-kg person on earth? On Mars (g=3.2 m/s/s)? ...
... When an object moves to a different planet. What is the weight of an 85.3-kg person on earth? On Mars (g=3.2 m/s/s)? ...
Static and Kinetic Friction Lab
... will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the weight of the block and any masses it carries. Fill in the Normal Force entries for both Part I data tables. 2. Plot a graph of the maximum static friction force (vertical axis) vs. the normal force (horizontal axis). Use either Logger Pro ...
... will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the weight of the block and any masses it carries. Fill in the Normal Force entries for both Part I data tables. 2. Plot a graph of the maximum static friction force (vertical axis) vs. the normal force (horizontal axis). Use either Logger Pro ...