Force - TeacherWeb
... 3rd Main Idea… Types of Friction Types of friction when there is contact between surfaces: _______ friction, a book ____________. ______ friction, a book _____________. ______ friction, contact between bike ________. ___ __________ (Fluid friction) pushes _______ _______________ as it falls. ...
... 3rd Main Idea… Types of Friction Types of friction when there is contact between surfaces: _______ friction, a book ____________. ______ friction, a book _____________. ______ friction, contact between bike ________. ___ __________ (Fluid friction) pushes _______ _______________ as it falls. ...
Concepts and Skills
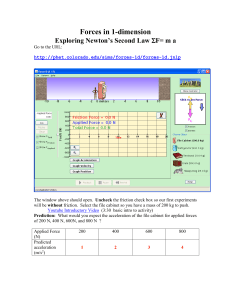
... “when an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object will experience acceleration proportional to the size of the unbalanced force”. The direction of the acceleration will be the same as the direction of the force. In this equation F is the net force (FNET), the unbalanced force that causes the a ...
... “when an unbalanced force acts on an object, the object will experience acceleration proportional to the size of the unbalanced force”. The direction of the acceleration will be the same as the direction of the force. In this equation F is the net force (FNET), the unbalanced force that causes the a ...
Static and Kinetic Friction
... Once the box starts to slide, you must continue to exert a force to keep the object moving, or friction will slow it to a stop. The friction acting on the box while it is moving is called kinetic friction. In order to slide the box with a constant velocity, a force equivalent to the force of kinetic ...
... Once the box starts to slide, you must continue to exert a force to keep the object moving, or friction will slow it to a stop. The friction acting on the box while it is moving is called kinetic friction. In order to slide the box with a constant velocity, a force equivalent to the force of kinetic ...
Matter in Motion
... • Example: A car was driving 35 mph, North. • Resulting velocity: Combining more than one velocity. • Example: a person walking backwards in a bus which is traveling ...
... • Example: A car was driving 35 mph, North. • Resulting velocity: Combining more than one velocity. • Example: a person walking backwards in a bus which is traveling ...
Fundamentals of mechanics and strength of materials
... I. Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform rectilinear motion, except if it is compelled by forces acting on it to change that state. The principle of inertia II. The change of motion is proportional to the applied force and takes place in the direction of the straight line along whi ...
... I. Every body continues in its state of rest or of uniform rectilinear motion, except if it is compelled by forces acting on it to change that state. The principle of inertia II. The change of motion is proportional to the applied force and takes place in the direction of the straight line along whi ...
Answers to the Problems on May the Force Be With You
... (b) The doors open. In the elevator is a bathroom scale calibrated in newtons. She steps on the scale. What does the scale read? The elevator is not accelerating, so the force on her is just due to gravity Scale reads 470 N ...
... (b) The doors open. In the elevator is a bathroom scale calibrated in newtons. She steps on the scale. What does the scale read? The elevator is not accelerating, so the force on her is just due to gravity Scale reads 470 N ...
Thursday, June 9, 2005
... Resistive force exerted on a moving object due to viscosity or other types of frictional properties of the medium in, or surface on, which the object moves. These forces are either proportional to the velocity or the normal force. Force of static friction, fs: The resistive force exerted on the obje ...
... Resistive force exerted on a moving object due to viscosity or other types of frictional properties of the medium in, or surface on, which the object moves. These forces are either proportional to the velocity or the normal force. Force of static friction, fs: The resistive force exerted on the obje ...
1.0 Newtons laws
... – An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an external force ...
... – An object at rest will stay at rest and an object in motion stays in motion unless acted on by an external force ...
Name
... 14. ___Net Force____ is the overall force on an object after all the forces are added together. 15. ___Force____ is a push or a pull. 16. ___Weight____ is the force of gravity on a person or object at the surface of a planet. 17. ___Mass____ is the amount of matter in an object. 18. ___Inertia____ i ...
... 14. ___Net Force____ is the overall force on an object after all the forces are added together. 15. ___Force____ is a push or a pull. 16. ___Weight____ is the force of gravity on a person or object at the surface of a planet. 17. ___Mass____ is the amount of matter in an object. 18. ___Inertia____ i ...