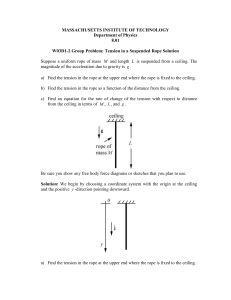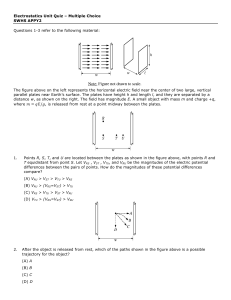
Topic 2 Problem Set 2016
... A ballistic pendulum consists of a 1.75-kg block of wood that is hanging from the ceiling in such a way that when a bullet enters it, the block’s change in height can be recorded as it swings. A bullet having a mass of 4.50-grams and unknown velocity strikes the block and becomes imbedded in it. The ...
... A ballistic pendulum consists of a 1.75-kg block of wood that is hanging from the ceiling in such a way that when a bullet enters it, the block’s change in height can be recorded as it swings. A bullet having a mass of 4.50-grams and unknown velocity strikes the block and becomes imbedded in it. The ...
Electric field = force per charge
... Lines indicate the strength and direction of the electric field. The more dense the lines, the stronger the field. ...
... Lines indicate the strength and direction of the electric field. The more dense the lines, the stronger the field. ...
Physics - Separate Science
... Be able to use the equations to calculate speed and acceleration Understand the difference between speed and velocity Be able to construct and interpret distance-time graphs for an object moving in a straight line when the object is stationary or moving with a constant speed Understand that the grad ...
... Be able to use the equations to calculate speed and acceleration Understand the difference between speed and velocity Be able to construct and interpret distance-time graphs for an object moving in a straight line when the object is stationary or moving with a constant speed Understand that the grad ...
Midterm 1
... The astronaut does have weight – this being the force of attraction between them and the earth. It is this force that keeps them in orbit – otherwise they would continue in a straight line. The astronaut does have mass – since this is the case of all bodies. The astronaut does not have the perceptio ...
... The astronaut does have weight – this being the force of attraction between them and the earth. It is this force that keeps them in orbit – otherwise they would continue in a straight line. The astronaut does have mass – since this is the case of all bodies. The astronaut does not have the perceptio ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.