1 CHAPTER 21 CENTRAL FORCES AND EQUIVALENT
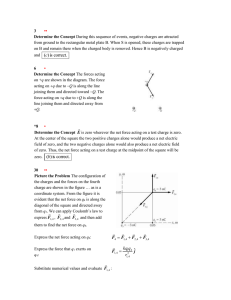
... [As ever, check the dimensions.] This equation, which does not contain the time, when integrated will give us the (r , θ) equation to the path. With these remarks in mind, let us try a few problems. For example: 21.7 Inverse cube attractive force A particle moves in a field such that the attractive ...
... [As ever, check the dimensions.] This equation, which does not contain the time, when integrated will give us the (r , θ) equation to the path. With these remarks in mind, let us try a few problems. For example: 21.7 Inverse cube attractive force A particle moves in a field such that the attractive ...
How and Why Inertial Mass and Gravitational Mass
... result of that matter “curving” or “warping” space and time according to the matter’s presence through a mechanism not yet discovered nor defined. Present physics recognizes that inertial mass and gravitational mass are equal as an empirical fact based on highly precise experiments. But, for example ...
... result of that matter “curving” or “warping” space and time according to the matter’s presence through a mechanism not yet discovered nor defined. Present physics recognizes that inertial mass and gravitational mass are equal as an empirical fact based on highly precise experiments. But, for example ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.