Electric Potential Powerpoint
... Wg GMm rB rA Wg is the work that gravity does. This is the opposite of the work that we must do in order to move an object in a gravitational field. We are pushing against gravity we do positive work P04 - 8 ...
... Wg GMm rB rA Wg is the work that gravity does. This is the opposite of the work that we must do in order to move an object in a gravitational field. We are pushing against gravity we do positive work P04 - 8 ...
Harald Maurer – The Principle of Existence Edition
... is satisfied with such answers may put this book aside. Because this book tries to explain why the physicists had to discover their theories and what is really behind the phenomena. Will our theory be dynamite for arguments and discussions? Certainly not at once. In the eyes of the scientists, he w ...
... is satisfied with such answers may put this book aside. Because this book tries to explain why the physicists had to discover their theories and what is really behind the phenomena. Will our theory be dynamite for arguments and discussions? Certainly not at once. In the eyes of the scientists, he w ...
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL )
... Correct Response: D. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are the best source of information for properly storing and disposing of chemicals. MSDS documents are produced by the chemical manufacturer for each given chemical. They contain information about each chemical's characteristics, including know ...
... Correct Response: D. Material Safety Data Sheets (MSDS) are the best source of information for properly storing and disposing of chemicals. MSDS documents are produced by the chemical manufacturer for each given chemical. They contain information about each chemical's characteristics, including know ...
PHYSICS HOMEWORK #1 KINEMATICS DISPLACEMENT & VELOCITY
... 3. A car goes North a distance of 120 miles during a time period of 3.0 hours. What is the average speed of the car during this time interval? 4. The distance between Denver Colorado and Vail Colorado is 132 miles. With what average speed should you drive your car in order to travel this distance in ...
... 3. A car goes North a distance of 120 miles during a time period of 3.0 hours. What is the average speed of the car during this time interval? 4. The distance between Denver Colorado and Vail Colorado is 132 miles. With what average speed should you drive your car in order to travel this distance in ...
Conceptual Questions - Colorado Mesa University
... © Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
... © Copyright 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher. ...
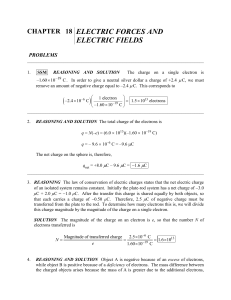
Ch 18 - SchemmScience.com
... unknown charges are both negative and have the same magnitude, as can be understood with the help of the free-body qA qB diagram for the 4.00 μC charge that is shown at the right. The diagram shows the attractive force F from each negative charge directed along the lines between the charges. Only wh ...
... unknown charges are both negative and have the same magnitude, as can be understood with the help of the free-body qA qB diagram for the 4.00 μC charge that is shown at the right. The diagram shows the attractive force F from each negative charge directed along the lines between the charges. Only wh ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.