Ch33 - Wells College
... • the line of action of F is also shown • any component of the force ║ to r will do nothing to help turn the nut • this component is F cos f, where f is the angle between F and r tailtail • the component of the force ┴ to r is what really does the job • this component is F sin f • notice that the mo ...
... • the line of action of F is also shown • any component of the force ║ to r will do nothing to help turn the nut • this component is F cos f, where f is the angle between F and r tailtail • the component of the force ┴ to r is what really does the job • this component is F sin f • notice that the mo ...
A-level Mathematics Question paper Mechanics 1B January 2013
... Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work that you do not want to be marked. ...
... Do all rough work in this book. Cross through any work that you do not want to be marked. ...
document
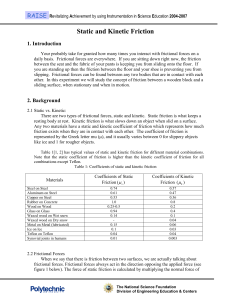
... There is a limit to how large the static friction force can be. Once your force is greater than this maximum static friction, the couch begins moving and kinetic friction begins to act on it instead of static friction ...
... There is a limit to how large the static friction force can be. Once your force is greater than this maximum static friction, the couch begins moving and kinetic friction begins to act on it instead of static friction ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE THEORY OF BLACK HOLES∗
... behavior of material particles, fields or other substances near or inside a black hole. What is more, astronomers have now identified numerous objects in the heavens that completely match the detailed descriptions theoreticians have derived. These objects cannot be interpreted as anything else but ...
... behavior of material particles, fields or other substances near or inside a black hole. What is more, astronomers have now identified numerous objects in the heavens that completely match the detailed descriptions theoreticians have derived. These objects cannot be interpreted as anything else but ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.