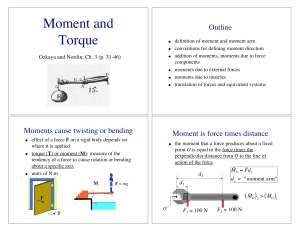
force
... You are driving a car with constant speed around a horizontal circular track. The net force acting on your car A) Points radially inward toward the center of the circular track B) Points radially outward, away from the center of the circular track C) Points forward in the same direction your car is ...
... You are driving a car with constant speed around a horizontal circular track. The net force acting on your car A) Points radially inward toward the center of the circular track B) Points radially outward, away from the center of the circular track C) Points forward in the same direction your car is ...
Lecture Notes 13: Steady Electric Currents, Magnetic Field, B
... For QCD (Quantum Chromo-Dynamics) – (i.e. the strong interactions / nuclear forces) there exist strong charges with associated so-called “chromo-electric” fields and “chromo-magnetic” fields! For gravity, gravitational charge = mass! There exist gravito-electric and gravito-magnetic fields. The “eve ...
... For QCD (Quantum Chromo-Dynamics) – (i.e. the strong interactions / nuclear forces) there exist strong charges with associated so-called “chromo-electric” fields and “chromo-magnetic” fields! For gravity, gravitational charge = mass! There exist gravito-electric and gravito-magnetic fields. The “eve ...
Syllabus 9749
... Systems and Interactions 1.1. Defining the systems under study (by specifying their boundaries and making explicit models of the systems) provides tools for understanding and testing ideas that are applicable throughout physics. 1.2. Objects can be treated as having no internal structure or an inter ...
... Systems and Interactions 1.1. Defining the systems under study (by specifying their boundaries and making explicit models of the systems) provides tools for understanding and testing ideas that are applicable throughout physics. 1.2. Objects can be treated as having no internal structure or an inter ...
8th Grade
... pairs are equal and opposite to each other. Why do these paired forces sometimes cause different motions if they are equal? ...
... pairs are equal and opposite to each other. Why do these paired forces sometimes cause different motions if they are equal? ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.