B. Multiple Choice Questions
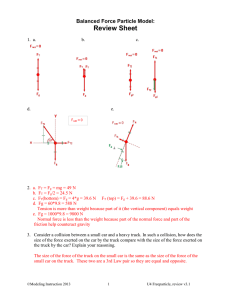
... 1. Why is a moving 80 kg steel ball difficult to stop in a weightless condition? A.) It isn't really weightless. B.) There is no friction in a weightless situation. C.) The ball is unable to accelerate D.) The 80 kg. ball has a lot of inertia. 2. What objects are affected by the law of inertia? A.) ...
... 1. Why is a moving 80 kg steel ball difficult to stop in a weightless condition? A.) It isn't really weightless. B.) There is no friction in a weightless situation. C.) The ball is unable to accelerate D.) The 80 kg. ball has a lot of inertia. 2. What objects are affected by the law of inertia? A.) ...
magnet experiment to measuring space propulsion heim
... a completely different type of propulsion, denoted gravitophoton field propulsion. The gravitophoton force, would accelerate a material body without the need of propellant. Gravitophoton particles are generated in pairs from the vacuum itself by the effect of vacuum polarization (virtual electrons), ...
... a completely different type of propulsion, denoted gravitophoton field propulsion. The gravitophoton force, would accelerate a material body without the need of propellant. Gravitophoton particles are generated in pairs from the vacuum itself by the effect of vacuum polarization (virtual electrons), ...
Physics 211 Lab #2 – Forces
... change in motion, not motion itself. In addition, he carefully distinguished between individual forces and the net force acting on an object. He said that if the Net Force acting on an object was zero, then the object would continue to move with constant velocity. Constant velocity includes two impo ...
... change in motion, not motion itself. In addition, he carefully distinguished between individual forces and the net force acting on an object. He said that if the Net Force acting on an object was zero, then the object would continue to move with constant velocity. Constant velocity includes two impo ...
Lect 3 Force Production
... gravity - measured in kilograms (kg) Weight: force due to gravity - is mass x gravity (9.81m/s²) Force: a pushing a pulling action that causes a change of state (rest/motion) of a body - is proportional to mass x acceleration - is measured in Newtons (N) where 1N is the force that will produce an ac ...
... gravity - measured in kilograms (kg) Weight: force due to gravity - is mass x gravity (9.81m/s²) Force: a pushing a pulling action that causes a change of state (rest/motion) of a body - is proportional to mass x acceleration - is measured in Newtons (N) where 1N is the force that will produce an ac ...
Raising and Lowering
... negative velocity. Draw a motion diagram for the box. Is the net force on the box, up, down or zero? Draw a force diagram for the box. Acceleration is positive, e.g. velocity might change from -10 to -5, an increase of +5. The net force = mass x acceleration which is upwards since acceleration is ...
... negative velocity. Draw a motion diagram for the box. Is the net force on the box, up, down or zero? Draw a force diagram for the box. Acceleration is positive, e.g. velocity might change from -10 to -5, an increase of +5. The net force = mass x acceleration which is upwards since acceleration is ...
Weightlessness

Weightlessness, or an absence of 'weight', is an absence of stress and strain resulting from externally applied mechanical contact-forces, typically normal forces from floors, seats, beds, scales, and the like. Counterintuitively, a uniform gravitational field does not by itself cause stress or strain, and a body in free fall in such an environment experiences no g-force acceleration and feels weightless. This is also termed ""zero-g"" where the term is more correctly understood as meaning ""zero g-force.""When bodies are acted upon by non-gravitational forces, as in a centrifuge, a rotating space station, or within a space ship with rockets firing, a sensation of weight is produced, as the contact forces from the moving structure act to overcome the body's inertia. In such cases, a sensation of weight, in the sense of a state of stress can occur, even if the gravitational field was zero. In such cases, g-forces are felt, and bodies are not weightless.When the gravitational field is non-uniform, a body in free fall suffers tidal effects and is not stress-free. Near a black hole, such tidal effects can be very strong. In the case of the Earth, the effects are minor, especially on objects of relatively small dimension (such as the human body or a spacecraft) and the overall sensation of weightlessness in these cases is preserved. This condition is known as microgravity and it prevails in orbiting spacecraft.