Course pack - MSU Department of Physics and Astronomy
... But even a superficial look can teach you a lot about the inescapable unity between the physical and biological worlds. At a minimum you should learn how physical laws constrain organisms, and with luck this new understanding will change the way you think about life. 1.2 Three examples to set the st ...
... But even a superficial look can teach you a lot about the inescapable unity between the physical and biological worlds. At a minimum you should learn how physical laws constrain organisms, and with luck this new understanding will change the way you think about life. 1.2 Three examples to set the st ...
Procedure for analysis
... 3-Dimensional – if the support reaction all intersec a common axis 2-Dimensional – the axis is perpendicular to the plane of the forces When all the reactive forces are concurrent at the point, the body is improperly constraint. Improper constraining leads to instability occurs when the reactive for ...
... 3-Dimensional – if the support reaction all intersec a common axis 2-Dimensional – the axis is perpendicular to the plane of the forces When all the reactive forces are concurrent at the point, the body is improperly constraint. Improper constraining leads to instability occurs when the reactive for ...
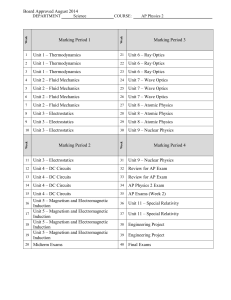
Marking Period 1 Marking Period 3 Unit 1 – Thermodynamics 21
... The AP Physics 1: Algebra-based and AP Physics 2: Algebra-based concepts are articulated together in one concept outline, providing the full scope of conceptual understandings a student should acquire by the end of an introductory sequence in college-level algebra-based physics. The key concepts and ...
... The AP Physics 1: Algebra-based and AP Physics 2: Algebra-based concepts are articulated together in one concept outline, providing the full scope of conceptual understandings a student should acquire by the end of an introductory sequence in college-level algebra-based physics. The key concepts and ...
Ch 18 - SchemmScience.com
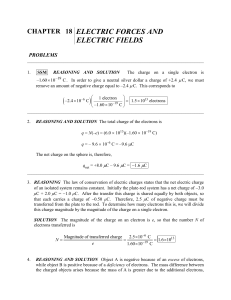
... be determined using Coulomb’s law to express the electrostatic force that each 30.0º F cos 30.0º unknown charge exerts on the 4.00 μC charge. In applying this law, we will use F the fact that the net force points downward in the drawing. This tells us that the F sin 30.0º unknown charges are both ne ...
... be determined using Coulomb’s law to express the electrostatic force that each 30.0º F cos 30.0º unknown charge exerts on the 4.00 μC charge. In applying this law, we will use F the fact that the net force points downward in the drawing. This tells us that the F sin 30.0º unknown charges are both ne ...
Physics Marking Key - SCSA - School Curriculum and Standards
... The Standard Model categorises all particles as being matter (fermions) or force carriers (gauge bosons). The gauge bosons are exchange particles that are responsible for the interactions between matter involving three of the four fundamental forces. Describe how exchange particles prevent you from ...
... The Standard Model categorises all particles as being matter (fermions) or force carriers (gauge bosons). The gauge bosons are exchange particles that are responsible for the interactions between matter involving three of the four fundamental forces. Describe how exchange particles prevent you from ...
3 EQUILIBRIUM - Chulalongkorn University: Faculties and
... • Establish the x, y axes in any suitable orientation. • Draw an outlined shape of the body. • Show all the forces and couple moments acting on the body. • Label all the loadings and specify their directions relative to the x, y axes. The sense of a force or couple moment having an unknown magnitude ...
... • Establish the x, y axes in any suitable orientation. • Draw an outlined shape of the body. • Show all the forces and couple moments acting on the body. • Label all the loadings and specify their directions relative to the x, y axes. The sense of a force or couple moment having an unknown magnitude ...