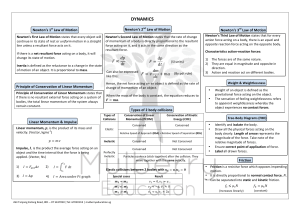
dynamics - Mulberry Education Centre
... Newton’s First Law of Motion states that every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a resultant force acts on it. If there is a net resultant ...
... Newton’s First Law of Motion states that every object will continue in its state of rest or uniform motion in a straight line unless a resultant force acts on it. If there is a net resultant ...
Newton`s Third LAw
... A 2 ton car, going 60 m.p.h. hits a 5 ton truck, going 20 m.p.h.. The force of impact is greatest on which vehicle, the car or the truck? Force on each is equal (by Newton’s 3rd Law). The change in velocity (the acceleration) is greatest for which vehicle? For the car, which has less mass. By what p ...
... A 2 ton car, going 60 m.p.h. hits a 5 ton truck, going 20 m.p.h.. The force of impact is greatest on which vehicle, the car or the truck? Force on each is equal (by Newton’s 3rd Law). The change in velocity (the acceleration) is greatest for which vehicle? For the car, which has less mass. By what p ...
Name: Newton`s First Law of Motion: The Law of Inertia “An object at
... _______________ and in the _______________ direction unless some _______________ force acts on it. ...
... _______________ and in the _______________ direction unless some _______________ force acts on it. ...
Name
... 1. A net force F accelerates a mass m with an acceleration of a. If the same net force is applied to mass 2m, then the acceleration will be a. 4a b. 2a c. a/2 d. a/4 2. A 20-ton truck collides with a 1500 lb car and causes a lot of damage to the car. Since a lot of damage is done on the car, a. the ...
... 1. A net force F accelerates a mass m with an acceleration of a. If the same net force is applied to mass 2m, then the acceleration will be a. 4a b. 2a c. a/2 d. a/4 2. A 20-ton truck collides with a 1500 lb car and causes a lot of damage to the car. Since a lot of damage is done on the car, a. the ...
1st Law An object will not change its speed or direction unless an
... When two or more motions are required, athletes must execute movements continuously in sequence. For example, if a javelin thrower hesitates or stops at the end of the approach just prior to the throw, the advantage of the the approach is lost. Athletes can increase mass and/or velocity to realize p ...
... When two or more motions are required, athletes must execute movements continuously in sequence. For example, if a javelin thrower hesitates or stops at the end of the approach just prior to the throw, the advantage of the the approach is lost. Athletes can increase mass and/or velocity to realize p ...
PPT
... know to push back harder when I push with increasing force? At the most basic level the object placed upon a surface is repelled by electromagnetism. The outer most electrons that comprise the object are electrically repelled by the electrons that comprise the surface. The electrons offer a stronger ...
... know to push back harder when I push with increasing force? At the most basic level the object placed upon a surface is repelled by electromagnetism. The outer most electrons that comprise the object are electrically repelled by the electrons that comprise the surface. The electrons offer a stronger ...
Unit 3 - Forces
... Newton’s First Law - In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
... Newton’s First Law - In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
Monday, Oct. 6, 2008
... observations for a long time. The data people collected, however, have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportio ...
... observations for a long time. The data people collected, however, have not been explained until Newton has discovered the law of gravitation. Every particle in the Universe attracts every other particle with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportio ...
Atwood Lab #5 - Jay Mathy Science Wiki
... Newton's first law of motion states that objects at rest remain at rest unless an unbalanced force is applied. The second law of motion describes what happens if the resultant force is different from zero. If the acceleration is constant, the body is said to be moving with uniformly accelerated moti ...
... Newton's first law of motion states that objects at rest remain at rest unless an unbalanced force is applied. The second law of motion describes what happens if the resultant force is different from zero. If the acceleration is constant, the body is said to be moving with uniformly accelerated moti ...
Powerpoint
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...