
Horizontal Kinematics - The Woodlands High School
... 10. How fast must a bullet be shot to reach a height of 250 m? 11. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 8.9 m/s2. If balls on Mars and the Earth are thrown upward simultaneously with a speed of 10m/s, which would return to the ground first and by how much time would it beat the other ball? [th ...
... 10. How fast must a bullet be shot to reach a height of 250 m? 11. The acceleration due to gravity on Mars is 8.9 m/s2. If balls on Mars and the Earth are thrown upward simultaneously with a speed of 10m/s, which would return to the ground first and by how much time would it beat the other ball? [th ...
Homework Problems
... intuitively wrong only because we tend to forget the role of friction forces.) Objects made of matter can exert forces on each other, causing changes in their motion. A more massive object changes its motion more slowly in response to a given force. 2 Conservation Laws Newton’s matter-and-forces pic ...
... intuitively wrong only because we tend to forget the role of friction forces.) Objects made of matter can exert forces on each other, causing changes in their motion. A more massive object changes its motion more slowly in response to a given force. 2 Conservation Laws Newton’s matter-and-forces pic ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
Lecture 2 - Purdue Physics
... What is relative strength of the electric force compared with the force of gravity for two electrons? ...
... What is relative strength of the electric force compared with the force of gravity for two electrons? ...
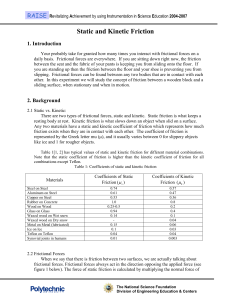
Static and Kinetic Friction
... daily basis. Frictional forces are everywhere. If you are sitting down right now, the friction between the seat and the fabric of your pants is keeping you from sliding onto the floor. If you are standing up then the friction between the floor and your shoe is preventing you from slipping. Frictiona ...
... daily basis. Frictional forces are everywhere. If you are sitting down right now, the friction between the seat and the fabric of your pants is keeping you from sliding onto the floor. If you are standing up then the friction between the floor and your shoe is preventing you from slipping. Frictiona ...
FE1 MOTION
... (Draw your own diagrams. They should show the path of the object together with arrows to represent velocity and acceleration at some instant.) When the ball is thrown vertically upwards, the acceleration is 9.8 m.s-2 downwards along the same vertical line, and the problem is one-dimensional. When th ...
... (Draw your own diagrams. They should show the path of the object together with arrows to represent velocity and acceleration at some instant.) When the ball is thrown vertically upwards, the acceleration is 9.8 m.s-2 downwards along the same vertical line, and the problem is one-dimensional. When th ...
L11_torque
... What upward force must the far support provide to support the weight of the truck? Hint: Several ways will work: • canceling forces on the truck • canceling torques about the near support ...
... What upward force must the far support provide to support the weight of the truck? Hint: Several ways will work: • canceling forces on the truck • canceling torques about the near support ...
Exam Review
... 59. Uranus orbits the Sun (MS = 1.99 1030 kg) with a mean radius of 2.87 1012 m. How long does it take Uranus to complete one orbit? Give your answer in Earth years. 60. How fast must a satellite leave Earth’s surface to reach an orbit with an altitude of 895 km? ...
... 59. Uranus orbits the Sun (MS = 1.99 1030 kg) with a mean radius of 2.87 1012 m. How long does it take Uranus to complete one orbit? Give your answer in Earth years. 60. How fast must a satellite leave Earth’s surface to reach an orbit with an altitude of 895 km? ...
P2 04 Terminal Velocity
... stretch of road with the same force as before. It takes them 18 seconds to get the second car up to a speed of 3 metres per second. What does this tell you about the mass of the second car? (You can ignore forces of friction.) ...
... stretch of road with the same force as before. It takes them 18 seconds to get the second car up to a speed of 3 metres per second. What does this tell you about the mass of the second car? (You can ignore forces of friction.) ...
AP Physics Review - stoweschools.com
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
... Weight = Force due to Gravity = product of mass and acceleration due to gravity Universal Gravitational Force is directly proportional to the universal gravitational constant, the mass of one object, the mass of another object and inversely proportional to the distance between the center of the obje ...
Physics Chapter 12
... Electric charges exert forces that can attract and repel each other even when they are not in direct contact. What causes the force? We don’t see anything between the charges that could be responsible for it. Yet this kind of force is already familiar to you. The force of gravity was explained in te ...
... Electric charges exert forces that can attract and repel each other even when they are not in direct contact. What causes the force? We don’t see anything between the charges that could be responsible for it. Yet this kind of force is already familiar to you. The force of gravity was explained in te ...











![oahspe`s cosmogony [1882] - to Oahspe Study and Confirmation](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009410841_1-f1816b5b5415180517f6b926d8156e1d-300x300.png)









