Electrostatics Notetakers
... 1. There are two kinds of charge that exist in nature (_________________ charge and __________________ charge) and they have the property that __________ ___________________ one another, and ______________________________ one another. 2. The ___________________ between charges varies as the inverse ...
... 1. There are two kinds of charge that exist in nature (_________________ charge and __________________ charge) and they have the property that __________ ___________________ one another, and ______________________________ one another. 2. The ___________________ between charges varies as the inverse ...
Ball of Light Particle Model
... I assume some combinations of balls of light would be odd, figuratively—the resulting instability leading to decay. For example, a helium nucleus—a stable resonant harmonic frequency—is one ball of light that decays into 4 stable balls of light (2 neutrons and 2 protons—each also a stable resonant h ...
... I assume some combinations of balls of light would be odd, figuratively—the resulting instability leading to decay. For example, a helium nucleus—a stable resonant harmonic frequency—is one ball of light that decays into 4 stable balls of light (2 neutrons and 2 protons—each also a stable resonant h ...
Fundamental of Physics
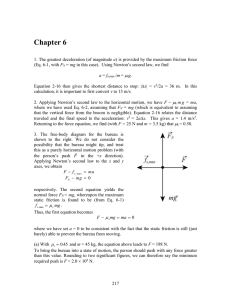
... cos s sin cos 15 0.50 sin 15 (b) The second law equations for the moving crate are T cos – f = ma FN + T sin – mg = 0. Now f =kFN, and the second equation gives FN = mg – Tsin, which yields f k (mg T sin ) . This expression is substituted for f in the first equation to obtain ...
... cos s sin cos 15 0.50 sin 15 (b) The second law equations for the moving crate are T cos – f = ma FN + T sin – mg = 0. Now f =kFN, and the second equation gives FN = mg – Tsin, which yields f k (mg T sin ) . This expression is substituted for f in the first equation to obtain ...
Ph 2001 Jan Key
... third the force experienced without the seatbelt. Sketch on the graph below how the force on the belted passenger might have varied with time. (2 marks) ...
... third the force experienced without the seatbelt. Sketch on the graph below how the force on the belted passenger might have varied with time. (2 marks) ...
Schutz A First Course in General Relativity(Second Edition).
... continuum physics in special relativity, study of tensor calculus in curvilinear coordinates in Euclidean and Minkowski spaces, geometry of curved manifolds, physics in a curved spacetime, and finally the field equations. The remaining four chapters study a few topics that I have chosen because of t ...
... continuum physics in special relativity, study of tensor calculus in curvilinear coordinates in Euclidean and Minkowski spaces, geometry of curved manifolds, physics in a curved spacetime, and finally the field equations. The remaining four chapters study a few topics that I have chosen because of t ...
Tangential force
... counterclockwise angular acceleration. <0 if the torque causes a clockwise angular acceleration. In a system of more than one torque, the sign of each torque is determined by the type of angular acceleration it alone would produce. The net torque acting on the system is the sum of each individual ...
... counterclockwise angular acceleration. <0 if the torque causes a clockwise angular acceleration. In a system of more than one torque, the sign of each torque is determined by the type of angular acceleration it alone would produce. The net torque acting on the system is the sum of each individual ...
Chapter 5: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 24. The weight of an object with mass m is calculated from the equation W = mg. 25. If an object is at rest, and remains at rest, it is not accelerating, and you can conclude that the vector sum of all the forces that act on it are zero. If the object is only momentarily at rest, such as at the top ...
... 24. The weight of an object with mass m is calculated from the equation W = mg. 25. If an object is at rest, and remains at rest, it is not accelerating, and you can conclude that the vector sum of all the forces that act on it are zero. If the object is only momentarily at rest, such as at the top ...
Applied Physics
... Schaum’s Easy Outline: Calculus Schaum’s Easy Outline: College Algebra Schaum’s Easy Outline: College Mathematics Schaum’s Easy Outline: Discrete Mathematics Schaum’s Easy Outline: Differential Equations Schaum’s Easy Outline: Elementary Algebra Schaum’s Easy Outline: Geometry Schaum’s Easy Outline: ...
... Schaum’s Easy Outline: Calculus Schaum’s Easy Outline: College Algebra Schaum’s Easy Outline: College Mathematics Schaum’s Easy Outline: Discrete Mathematics Schaum’s Easy Outline: Differential Equations Schaum’s Easy Outline: Elementary Algebra Schaum’s Easy Outline: Geometry Schaum’s Easy Outline: ...