Circular Motion
... Linear speed is the distance moved per unit of time. A point on the outer edge of a merry-go-round moves a greater distance in one complete rotation that a point near the center. The linear speed is greater on the outer edge of rotating objects than it is closer to its axis. The speed of something m ...
... Linear speed is the distance moved per unit of time. A point on the outer edge of a merry-go-round moves a greater distance in one complete rotation that a point near the center. The linear speed is greater on the outer edge of rotating objects than it is closer to its axis. The speed of something m ...
force and laws of motion
... 20.A car of mass 1000kg moving with a velocity of 45km/h collides with a tree and comes to a stop in 5s.Waht will be the force exerted by the car on the tree? 21.A force of 0.6 N acting on a body increases its velocity from 5m/s to 6m/s in 2s. Calculate the mass of the body. 22.For how much time sho ...
... 20.A car of mass 1000kg moving with a velocity of 45km/h collides with a tree and comes to a stop in 5s.Waht will be the force exerted by the car on the tree? 21.A force of 0.6 N acting on a body increases its velocity from 5m/s to 6m/s in 2s. Calculate the mass of the body. 22.For how much time sho ...
Chapter 5: Force and Motion
... In equilibrium, all forces cancel out leaving zero net force. Objects that are standing still are in equilibrium because their acceleration is zero. Objects that are moving at constant speed and direction are also in equilibrium. A static problem usually means there is no motion. ...
... In equilibrium, all forces cancel out leaving zero net force. Objects that are standing still are in equilibrium because their acceleration is zero. Objects that are moving at constant speed and direction are also in equilibrium. A static problem usually means there is no motion. ...
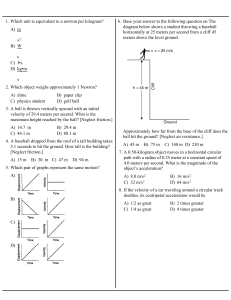
1.Which unit is equivalent to a newton per kilogram?
... noted. It appeared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there was another force on the planet that was not included in the calculation. Assuming that this force was exerted by an unobserved planet, two scientists working independently calculated ...
... noted. It appeared that the sum of the forces on Uranus did not equal its mass times its acceleration, unless there was another force on the planet that was not included in the calculation. Assuming that this force was exerted by an unobserved planet, two scientists working independently calculated ...
science curriculum framework
... Whether observing airplanes, baseballs, planets, or people, the motion of all bodies is governed by the same basic rules. At the middle level, qualitative descriptions of the relationship between forces and motion will provide the foundation for quantitative applications of Newton’s Laws. ...
... Whether observing airplanes, baseballs, planets, or people, the motion of all bodies is governed by the same basic rules. At the middle level, qualitative descriptions of the relationship between forces and motion will provide the foundation for quantitative applications of Newton’s Laws. ...
Lecture 13
... An object exerts no force on the bathroom scales as the scales are also being accelerated toward the centre of the earth at the same rate as the object. ...
... An object exerts no force on the bathroom scales as the scales are also being accelerated toward the centre of the earth at the same rate as the object. ...












![PhysRozz Midterm 2012 [via06-07] Version 18](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014722455_1-33f5b15b25beb94441904fea997b655c-300x300.png)