Static Electricity NAME_________________________ Guided
... 39. A physics teacher rubs a glass object and a felt cloth together and the glass becomes positively charged. Which of the following statements are true? Circle all that apply. a. The glass gained protons during the rubbing process. b. The felt became charged negatively during this rubbing process. ...
... 39. A physics teacher rubs a glass object and a felt cloth together and the glass becomes positively charged. Which of the following statements are true? Circle all that apply. a. The glass gained protons during the rubbing process. b. The felt became charged negatively during this rubbing process. ...
MS-Word - Rex Research
... depends in some way on the motion of the rest; and at the same time these connexions must be capable of a certain kind of elastic yielding, since the communication of motion is not instantaneous, but occupies time. The medium is therefore capable of receiving and storing up two kinds of energy, name ...
... depends in some way on the motion of the rest; and at the same time these connexions must be capable of a certain kind of elastic yielding, since the communication of motion is not instantaneous, but occupies time. The medium is therefore capable of receiving and storing up two kinds of energy, name ...
Entanglement and the black hole information paradox
... 5.4 Einsteins equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.4.1 The Schwarzschild solution . . . . . . 6 Black holes 6.1 Event horizon . . . . . . . 6.2 The equivalence principle . 6.3 Diagram representations of 6.4 No-hair theorem . . . . . . 6.5 Hawking radiation . . . . ...
... 5.4 Einsteins equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5.4.1 The Schwarzschild solution . . . . . . 6 Black holes 6.1 Event horizon . . . . . . . 6.2 The equivalence principle . 6.3 Diagram representations of 6.4 No-hair theorem . . . . . . 6.5 Hawking radiation . . . . ...
Chapters 2, 3, and 4
... Gravity is the force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses. Gravity can effect the position of an object or the direction of an object. Property of NASA Chapter 4 Section 4 ...
... Gravity is the force of attraction between objects that is due to their masses. Gravity can effect the position of an object or the direction of an object. Property of NASA Chapter 4 Section 4 ...
Assessment
... _____ 2. A child with a mass of 23 kg rides a bike with a mass of 5.5 kg at a velocity of 4.5 m/s to the south. Compare the momentum of the child with the momentum of the bike. a. Both the child and the bike have the same momentum. b. The bike has a greater momentum than the child. c. The child has ...
... _____ 2. A child with a mass of 23 kg rides a bike with a mass of 5.5 kg at a velocity of 4.5 m/s to the south. Compare the momentum of the child with the momentum of the bike. a. Both the child and the bike have the same momentum. b. The bike has a greater momentum than the child. c. The child has ...
Solutions
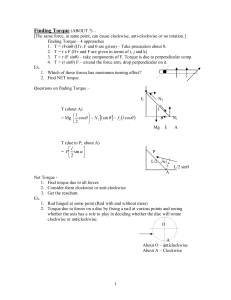
... 2 Kg – Wt to be applied at one end to open it. The force that must be applied at a point 0.5 m distant from the hinges for opening the gate is a) 0.5 Kg – Wt b) 2 Kg – Wt c) 4.5 Kg – Wt d) 8 Kg – Wt Vikasana - CET 2012 ...
... 2 Kg – Wt to be applied at one end to open it. The force that must be applied at a point 0.5 m distant from the hinges for opening the gate is a) 0.5 Kg – Wt b) 2 Kg – Wt c) 4.5 Kg – Wt d) 8 Kg – Wt Vikasana - CET 2012 ...
Lecture Chapter 15
... important to note that the charge on the rod remains constant (negative). The charge on the sphere is now positive as it lost electrons to Earth. Compared to the amount of free electrons already in Earth, the earth has gained an insignificant amount of charge and therefore the charge on the earth st ...
... important to note that the charge on the rod remains constant (negative). The charge on the sphere is now positive as it lost electrons to Earth. Compared to the amount of free electrons already in Earth, the earth has gained an insignificant amount of charge and therefore the charge on the earth st ...
Simple Machines Lever Wheel and Axel Pulley
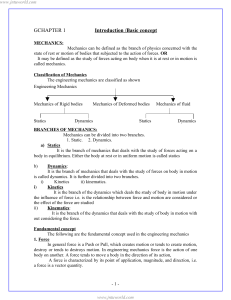
... A condition where there are no net external forces acting upon a particle or rigid body. As a result the body remains at rest or continues at a constant velocity. Note: “no net external forces” doesn’t mean “no forces”… it just means if forces exist they are cancelling each other out. So, the “net r ...
... A condition where there are no net external forces acting upon a particle or rigid body. As a result the body remains at rest or continues at a constant velocity. Note: “no net external forces” doesn’t mean “no forces”… it just means if forces exist they are cancelling each other out. So, the “net r ...