Physics - Separate Science
... There are two fissionable substances in common use in nuclear reactors: uranium-235 and plutonium-239 – the nucleus must first absorb a neutron for fission to occur Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one – this is how energy is released in stars Stars form when enoug ...
... There are two fissionable substances in common use in nuclear reactors: uranium-235 and plutonium-239 – the nucleus must first absorb a neutron for fission to occur Nuclear fusion is the joining of two atomic nuclei to form a larger one – this is how energy is released in stars Stars form when enoug ...
ForcesandMotion new
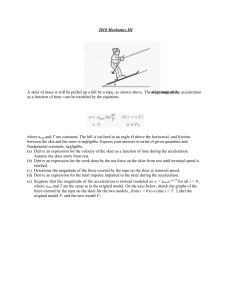
... The study of the relation between a force and the acceleration it causes as discovered by Isaac Newton It does not apply to some situations Very fast moving bodies Ex: Bodies traveling near the speed of light Must replace with Einstein’s theory of relativity Interacting bodies on the sca ...
... The study of the relation between a force and the acceleration it causes as discovered by Isaac Newton It does not apply to some situations Very fast moving bodies Ex: Bodies traveling near the speed of light Must replace with Einstein’s theory of relativity Interacting bodies on the sca ...
Net Force
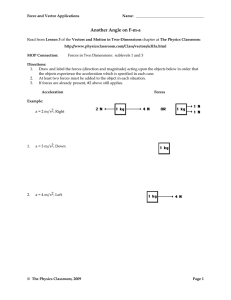
... 1. The amount of matter in an object is called its weight. 2. The combination of all the forces on an object is called the net force. 3. Inertia is the reluctance any material object has to change in its state of motion. 4. Objects move only when a force is exerted. 5. The acceleration of an object ...
... 1. The amount of matter in an object is called its weight. 2. The combination of all the forces on an object is called the net force. 3. Inertia is the reluctance any material object has to change in its state of motion. 4. Objects move only when a force is exerted. 5. The acceleration of an object ...
Mrs. Burns: 2012185859 Day 1 Physics consist of a variety of topics
... causes friction from the spark timer as it went through. Air resistance is also possible for the cause of error. However since the mass was dense and air resistance does not really affect dense materials, air resistance would be considered tribule and would not take into account in this case. Since ...
... causes friction from the spark timer as it went through. Air resistance is also possible for the cause of error. However since the mass was dense and air resistance does not really affect dense materials, air resistance would be considered tribule and would not take into account in this case. Since ...
Solutions
... atoms are around 10 m, so this r r assumption isn’t looking too good as the y atoms are actually larger than the spacing between their centers- meaning the electron clouds overlap. But, we’re saved x Cl by something we’ll see a short while-e when we’re outside of spherically symmetric charge distrib ...
... atoms are around 10 m, so this r r assumption isn’t looking too good as the y atoms are actually larger than the spacing between their centers- meaning the electron clouds overlap. But, we’re saved x Cl by something we’ll see a short while-e when we’re outside of spherically symmetric charge distrib ...
6 Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation
... Introduction to Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation Many motions, such as the arc of a bird’s flight or Earth’s path around the Sun, are curved. Recall that Newton’s first law tells us that motion is along a straight line at constant speed unless there is a net external force. We will therefore ...
... Introduction to Uniform Circular Motion and Gravitation Many motions, such as the arc of a bird’s flight or Earth’s path around the Sun, are curved. Recall that Newton’s first law tells us that motion is along a straight line at constant speed unless there is a net external force. We will therefore ...
Document
... out” of their preferred motion state. Many forces can act on an object at rest, but unless the forces are unbalanced, the object will not move. The same can be said for objects moving at a constant velocity. Now for the one million dollar question. What happens to an object IF an unbalanced, externa ...
... out” of their preferred motion state. Many forces can act on an object at rest, but unless the forces are unbalanced, the object will not move. The same can be said for objects moving at a constant velocity. Now for the one million dollar question. What happens to an object IF an unbalanced, externa ...
Secondary: 5E Date: 17/06/2013
... A technician wants to measure the mass of an particle. He connects two parallel metal plates to an EHT power supply. The plates are 0.5 cm apart. particles are emitted horizontally from one side of the plates and a detector is placed on the other side as shown. The technician expects that the we ...
... A technician wants to measure the mass of an particle. He connects two parallel metal plates to an EHT power supply. The plates are 0.5 cm apart. particles are emitted horizontally from one side of the plates and a detector is placed on the other side as shown. The technician expects that the we ...
Physics 207: Lecture 2 Notes
... attractive, long-range force between any two objects. When two objects with masses m1 and m2 are separated by distance r, each object “pulls” on the other with a force given by Newton’s law of gravity, as follows: ...
... attractive, long-range force between any two objects. When two objects with masses m1 and m2 are separated by distance r, each object “pulls” on the other with a force given by Newton’s law of gravity, as follows: ...
15.4 outline phy sci
... ____________________________________________ as the force you apply. Just as with a first class lever, how ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________. If you want to move a very large load with a small applied force, you must put the load __________ ...
... ____________________________________________ as the force you apply. Just as with a first class lever, how ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________. If you want to move a very large load with a small applied force, you must put the load __________ ...