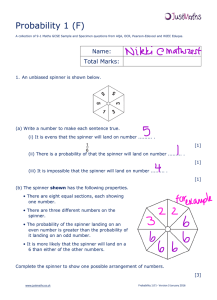
Probability 1 (F)
... assessment materials and whilst every effort has been made to ensure there are no errors, any that do appear are mine and not the exam board s (similarly any errors I have corrected from the originals are also my corrections and not theirs!). Please also note that the layout in terms of fonts, answe ...
... assessment materials and whilst every effort has been made to ensure there are no errors, any that do appear are mine and not the exam board s (similarly any errors I have corrected from the originals are also my corrections and not theirs!). Please also note that the layout in terms of fonts, answe ...
First Return Probabilities - University of California, Berkeley
... Proof. We begin by noting that the expression f2n 22n is equal to the number of 2n-paths that only touch the origin at the endpoints, that is the on cartesian coordiantes (0, 0) and (2n, 0). Similarly, u2n 22n is equal to the total number of 2npaths that end at the origin. The collection of these 2n ...
... Proof. We begin by noting that the expression f2n 22n is equal to the number of 2n-paths that only touch the origin at the endpoints, that is the on cartesian coordiantes (0, 0) and (2n, 0). Similarly, u2n 22n is equal to the total number of 2npaths that end at the origin. The collection of these 2n ...
Study Materials
... in many fields as Genetic engineering , Insurance and Medical sciences. There are three possible states of expectation namely (I)certainty (II)impossibility (III)uncertainty The probability theory describes certainty by 1, impossibility by 0 and the various grades of uncertainties by co-efficient ra ...
... in many fields as Genetic engineering , Insurance and Medical sciences. There are three possible states of expectation namely (I)certainty (II)impossibility (III)uncertainty The probability theory describes certainty by 1, impossibility by 0 and the various grades of uncertainties by co-efficient ra ...
The Principle of Common Cause and Indeterminism: A Review
... 6 There is a certain amount of confusion in the literature regarding the terminology and a clarifying note is perhaps in order. In some cases the expression ‘Reichenbach’s Principle of the Common Cause’ is used to refer just to the four probabilistic relations, i.e. Reichenbach’s characterisation of ...
... 6 There is a certain amount of confusion in the literature regarding the terminology and a clarifying note is perhaps in order. In some cases the expression ‘Reichenbach’s Principle of the Common Cause’ is used to refer just to the four probabilistic relations, i.e. Reichenbach’s characterisation of ...
6 The Basic Rules of Probability
... irrational, because so many of us come up with the wrong probability orderings. But perhaps people are merely careless! Perhaps most of us do not attend closely to the exact wording of the question, "Which of statements (aHf) are more probable, that is have the highest probability." Instead we think ...
... irrational, because so many of us come up with the wrong probability orderings. But perhaps people are merely careless! Perhaps most of us do not attend closely to the exact wording of the question, "Which of statements (aHf) are more probable, that is have the highest probability." Instead we think ...
Lesson 6: Probability Rules
... Example 2: Formula for Conditional Probability When a room is randomly selected in a downtown hotel, the probability that the room has a king-sized bed is 0.62, the probability that the room has a view of the town square is 0.43, and the probability that it has a king-sized bed and a view of the tow ...
... Example 2: Formula for Conditional Probability When a room is randomly selected in a downtown hotel, the probability that the room has a king-sized bed is 0.62, the probability that the room has a view of the town square is 0.43, and the probability that it has a king-sized bed and a view of the tow ...
Ballot theorems for random walks with finite variance
... symmetric simple random walk suggests that the partial sums stay positive until this time with probability of order O(n−(3/4)·(1/2) ) = O(n−3/8 ). In order that the partial sums stay positive, it is also essentially necessary that the √ “subrandom walk” consisting of the partial sums of only element ...
... symmetric simple random walk suggests that the partial sums stay positive until this time with probability of order O(n−(3/4)·(1/2) ) = O(n−3/8 ). In order that the partial sums stay positive, it is also essentially necessary that the √ “subrandom walk” consisting of the partial sums of only element ...
CHAPTER 13 DECISION THEORY { HISTORICAL
... parameter. Probability theory determined only the robot's state of knowledge about the parameter; it did not tell us what estimate it should in fact make. We noted at that time that taking the mean value over the posterior pdf was the same as making that decision which minimizes the expected square ...
... parameter. Probability theory determined only the robot's state of knowledge about the parameter; it did not tell us what estimate it should in fact make. We noted at that time that taking the mean value over the posterior pdf was the same as making that decision which minimizes the expected square ...
Determine whether the events are independent or dependent. Then
... 2. Yana has 4 black socks, 6 blue socks, and 8 white socks in his drawer. If he selects three socks at random with no replacement, what is the probability that he will first select a blue sock, then a black sock, and then another blue sock? SOLUTION: Since the socks are being selected with out rep ...
... 2. Yana has 4 black socks, 6 blue socks, and 8 white socks in his drawer. If he selects three socks at random with no replacement, what is the probability that he will first select a blue sock, then a black sock, and then another blue sock? SOLUTION: Since the socks are being selected with out rep ...
Interpreting Probability - Assets - Cambridge
... causes to be inferred from known effects. The method was championed from the late eighteenth century by Laplace as a universal model of rationality. He applied this ‘doctrine of chances’ widely. In the courtroom, for example, the probability that the accused was guilty could be calculated from the k ...
... causes to be inferred from known effects. The method was championed from the late eighteenth century by Laplace as a universal model of rationality. He applied this ‘doctrine of chances’ widely. In the courtroom, for example, the probability that the accused was guilty could be calculated from the k ...
A power point presentation - Einstein Institute of Mathematics @ The
... Highly entangled systems as required in quantum computers (will lead to) come along with very strong error synchronization (that we do not often encounter), which in turn implies that such highly entangled states are unrealistic. ...
... Highly entangled systems as required in quantum computers (will lead to) come along with very strong error synchronization (that we do not often encounter), which in turn implies that such highly entangled states are unrealistic. ...
Document
... H(p) = NS(π), where H(p) is the entropy measure based on the probability distribution p and NS(π) nonspecificity measure based on the possibility ...
... H(p) = NS(π), where H(p) is the entropy measure based on the probability distribution p and NS(π) nonspecificity measure based on the possibility ...