Chapter 1 Review Key
... shapes and sizes in molecules. Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds, forming structures of various strengths. 70. A dehydration reaction removes a water molecule to join two smaller molecules into one larger one (also called condensation). A hydrolysis reaction adds a water molecule to sp ...
... shapes and sizes in molecules. Carbon can form single, double, or triple bonds, forming structures of various strengths. 70. A dehydration reaction removes a water molecule to join two smaller molecules into one larger one (also called condensation). A hydrolysis reaction adds a water molecule to sp ...
Biochemistry Note
... Macromolecules – Large organic molecules that contain dozens of carbon atoms and many functional groups. There are four major groups of biologically important macromolecules: ...
... Macromolecules – Large organic molecules that contain dozens of carbon atoms and many functional groups. There are four major groups of biologically important macromolecules: ...
100
... kreb’s cycle, this many ATP have been synthesized due to substrate level phosphorylation ...
... kreb’s cycle, this many ATP have been synthesized due to substrate level phosphorylation ...
2.4 Chemical Reactions
... reactions, as shown in FIGURE 2.21. Cellular respiration, the process that uses glucose and oxygen to provide usable energy for cells, is also exothermic. Cellular respiration releases not only usable energy for your cells but also heat that keeps your body warm. An endothermic chemical reaction abs ...
... reactions, as shown in FIGURE 2.21. Cellular respiration, the process that uses glucose and oxygen to provide usable energy for cells, is also exothermic. Cellular respiration releases not only usable energy for your cells but also heat that keeps your body warm. An endothermic chemical reaction abs ...
Lactic acid fermentation
... then be used to drive processes requiring energy, including biosynthesis, locomotion or transportation of molecules across cell membranes… etc. ...
... then be used to drive processes requiring energy, including biosynthesis, locomotion or transportation of molecules across cell membranes… etc. ...
respiration - Mrs. Towers` Website
... 14. If you hold your breathe a) you could die of suffocation b) rising oxygen concentration will stimulate the breathing center c) accumulated carbon dioxide will force resumption of breathing d) increased nitrogen concentration will have a toxic effect 15. Impulses from the fully inflated lungs to ...
... 14. If you hold your breathe a) you could die of suffocation b) rising oxygen concentration will stimulate the breathing center c) accumulated carbon dioxide will force resumption of breathing d) increased nitrogen concentration will have a toxic effect 15. Impulses from the fully inflated lungs to ...
Selective toxicity of antibiotics
... All microorganisms require elemental oxygen to build their biochemical components, but not all of them require atmospheric oxygen. Most heterotrophic bacteria obtain oxygen from the same molecule that serves as a carbon source (CH2O). Autotrophs obtain oxygen from CO2. Most aerobic bacteria have an ...
... All microorganisms require elemental oxygen to build their biochemical components, but not all of them require atmospheric oxygen. Most heterotrophic bacteria obtain oxygen from the same molecule that serves as a carbon source (CH2O). Autotrophs obtain oxygen from CO2. Most aerobic bacteria have an ...
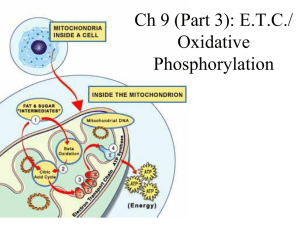
Ch 9: E.T.C./ Oxidative Phosphorylation
... they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
... they accept and donate electrons • each successive group is more electronegative than the group before it, so the electrons are “pulled downhill” towards OXYGEN (the final electron carrier!) ...
You can keep your lungs healthy anytime!
... • Keep oxygen concentration high and carbon dioxide concentration low in alveoli. • To get rid of waste carbon dioxide made by cells. ...
... • Keep oxygen concentration high and carbon dioxide concentration low in alveoli. • To get rid of waste carbon dioxide made by cells. ...
C454_lect1 - University of Wisconsin
... Key reactions are reiterated throughout metabolism. Metabolic processes are regulated in ...
... Key reactions are reiterated throughout metabolism. Metabolic processes are regulated in ...
Across 6. the process of breathing in. Oxygen is moved into the
... 9. the preferred entrance for outside air into the respiratory system. The hairs that line the wall are part of the air-cleaning system 10. smallest subdivision of the bronchi 13. the strong wall of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. By moving downward, it creates suct ...
... 9. the preferred entrance for outside air into the respiratory system. The hairs that line the wall are part of the air-cleaning system 10. smallest subdivision of the bronchi 13. the strong wall of muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity. By moving downward, it creates suct ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint - Ms. McQuades Biology Connection
... • Consumers are organisms that get their energy by eating other living or once-living resources. • Consumers are also called heterotrophs because they feed off of ...
... • Consumers are organisms that get their energy by eating other living or once-living resources. • Consumers are also called heterotrophs because they feed off of ...
Homeostasis, Levels of Organization of Living Things, Skeletal
... 3. Skeletal System : Explain each of the 5 jobs of the skeleton system? 1. Protects organs (ribs protect heart and lungs, skull protects brain, vertebrae protect spinal cord) 2. Bones store minerals such as calcium, potassium and iron 3. Allow movement of body, and supports shape of body (muscles pu ...
... 3. Skeletal System : Explain each of the 5 jobs of the skeleton system? 1. Protects organs (ribs protect heart and lungs, skull protects brain, vertebrae protect spinal cord) 2. Bones store minerals such as calcium, potassium and iron 3. Allow movement of body, and supports shape of body (muscles pu ...
Chapter 2) Understanding Aquaponics
... The small animal in the diagram above produces waste (faeces and urine) which is largely made up of ammonia (NH₃). Other decaying organic matter found in nature (like dead plants or dead animals) is also broken down by fungus and different bacteria groups into ammonia (NH₃). This ammonia is then con ...
... The small animal in the diagram above produces waste (faeces and urine) which is largely made up of ammonia (NH₃). Other decaying organic matter found in nature (like dead plants or dead animals) is also broken down by fungus and different bacteria groups into ammonia (NH₃). This ammonia is then con ...
here
... Read Chapter 9 in Campbell & Reece. Answer the following questions. Glycolysis & Krebs Cycle HW 1. Contrast glycolysis with cell respiration, citing such factors as locale, oxygen use, energy yields, and type of phosphorylation used. 2. Briefly describe the two means by which ADP is phosphorylated. ...
... Read Chapter 9 in Campbell & Reece. Answer the following questions. Glycolysis & Krebs Cycle HW 1. Contrast glycolysis with cell respiration, citing such factors as locale, oxygen use, energy yields, and type of phosphorylation used. 2. Briefly describe the two means by which ADP is phosphorylated. ...
3-CoralStrFn1
... • Many corals have different growth forms - can vary with local environment - light, depth etc. • Local environment affects distribution of the ...
... • Many corals have different growth forms - can vary with local environment - light, depth etc. • Local environment affects distribution of the ...
Circulatory and Respiratory System Review
... How does your respiration rate change when you increase physical activity levels? During physical activity your respiration rate will increase because there is an increased need for oxygen in the blood. ...
... How does your respiration rate change when you increase physical activity levels? During physical activity your respiration rate will increase because there is an increased need for oxygen in the blood. ...
No Slide Title
... Light Water is semi-transparent to sunlight; sunlight will pass through water and gradually be absorbed and scattered until, at some depth, there is total darkness. The depth of the photic zone at any given location depends on how rapidly light is absorbed and scattered at that spot. This can chan ...
... Light Water is semi-transparent to sunlight; sunlight will pass through water and gradually be absorbed and scattered until, at some depth, there is total darkness. The depth of the photic zone at any given location depends on how rapidly light is absorbed and scattered at that spot. This can chan ...
Bio302 Biochemistry II
... Question 19. (5 points) Explain why less ATP is made from the reoxidation of FADH2 as compared to NADH. ...
... Question 19. (5 points) Explain why less ATP is made from the reoxidation of FADH2 as compared to NADH. ...
Regents Biology Homework Packet Unit 4: Biochemistry
... Organic Catalysts are molecules that __________________ the rates of reactions. Most enzyme names end in –ase. Enzymes lower the energy needed to start a chemical reaction. (activation energy) It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take ...
... Organic Catalysts are molecules that __________________ the rates of reactions. Most enzyme names end in –ase. Enzymes lower the energy needed to start a chemical reaction. (activation energy) It is thought that, in order for an enzyme to affect the rate of a reaction, the following events must take ...
Chapter 14- RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a
... Chapter 14‐ RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic food substances present in the cells. The food substances like Carbohydrates, proteins, fats which are used for oxidation dur ...
... Chapter 14‐ RESPIRATION IN PLANTS Living cells require a continuous supply of energy for maintaining various life activities. This energy is obtained by oxidizing the organic food substances present in the cells. The food substances like Carbohydrates, proteins, fats which are used for oxidation dur ...
Mission 2 Workbook - NC State University
... process by which a plant produces food using water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight ...
... process by which a plant produces food using water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight ...
NADH - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... Other Types of Photosynthesis • In hot climates, Stomata closes CO2 decreases O2 increases O2 combines with RuBP leads to the production of CO2 photorespiration • C4 plants solving the problem of photorespiration - Fix CO2 to PEP ( a C3 molecule), which results in a C4 molecule called oxa ...
... Other Types of Photosynthesis • In hot climates, Stomata closes CO2 decreases O2 increases O2 combines with RuBP leads to the production of CO2 photorespiration • C4 plants solving the problem of photorespiration - Fix CO2 to PEP ( a C3 molecule), which results in a C4 molecule called oxa ...
chapter-02
... a) The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain. b) The secondary structure, which can take the form of an alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet, is maintained by hydrogen bonds between amino acids in different regions of the original polypeptide strand. c) T ...
... a) The primary structure is the sequence of amino acids that make up the polypeptide chain. b) The secondary structure, which can take the form of an alpha-helix or a beta-pleated sheet, is maintained by hydrogen bonds between amino acids in different regions of the original polypeptide strand. c) T ...
Photosynthesis

Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy, normally from the Sun, into chemical energy that can be later released to fuel the organisms' activities. This chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name photosynthesis, from the Greek φῶς, phōs, ""light"", and σύνθεσις, synthesis, ""putting together"". In most cases, oxygen is also released as a waste product. Most plants, most algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels and supplies all of the organic compounds and most of the energy necessary for life on Earth.Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centres that contain green chlorophyll pigments. In plants, these proteins are held inside organelles called chloroplasts, which are most abundant in leaf cells, while in bacteria they are embedded in the plasma membrane. In these light-dependent reactions, some energy is used to strip electrons from suitable substances, such as water, producing oxygen gas. Furthermore, two further compounds are generated: reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the ""energy currency"" of cells.In plants, algae and cyanobacteria, sugars are produced by a subsequent sequence of light-independent reactions called the Calvin cycle, but some bacteria use different mechanisms, such as the reverse Krebs cycle. In the Calvin cycle, atmospheric carbon dioxide is incorporated into already existing organic carbon compounds, such as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). Using the ATP and NADPH produced by the light-dependent reactions, the resulting compounds are then reduced and removed to form further carbohydrates, such as glucose.The first photosynthetic organisms probably evolved early in the evolutionary history of life and most likely used reducing agents, such as hydrogen or hydrogen sulfide, as sources of electrons, rather than water. Cyanobacteria appeared later; the excess oxygen they produced contributed to the oxygen catastrophe, which rendered the evolution of complex life possible. Today, the average rate of energy capture by photosynthesis globally is approximately 130 terawatts, which is about three times the current power consumption of human civilization.Photosynthetic organisms also convert around 100–115 thousand million metric tonnes of carbon into biomass per year.