An Ancient Method of Finding and Extending Direction
... a precise star measuring system. I believe, however, the means used for orienting the pyramids was actually based on the movements of the sun. Many ancient cultures have made use of the sun's movements by measuring its shadows with an instrument called a gnomon, a pole placed vertically on the groun ...
... a precise star measuring system. I believe, however, the means used for orienting the pyramids was actually based on the movements of the sun. Many ancient cultures have made use of the sun's movements by measuring its shadows with an instrument called a gnomon, a pole placed vertically on the groun ...
Further VLBA Observations of SiO Masers toward Mira
... The compressed total intensity images for each epoch and transition with superposed polarization “E” vectors are shown in Figures 1 – 3. (Expanded views of these figures with and without polarization vectors are avaliable in electronic form.) The fitted ring diameters and width are shown in Table 2 ...
... The compressed total intensity images for each epoch and transition with superposed polarization “E” vectors are shown in Figures 1 – 3. (Expanded views of these figures with and without polarization vectors are avaliable in electronic form.) The fitted ring diameters and width are shown in Table 2 ...
The Sun
... studied by monitoring waves caused by eathquakes Convection is source of waves in Sun On Sun’s surface, the waves appear as up and down oscillations of the gases, observed as Doppler shifts of ...
... studied by monitoring waves caused by eathquakes Convection is source of waves in Sun On Sun’s surface, the waves appear as up and down oscillations of the gases, observed as Doppler shifts of ...
Elastic electron scattering by lead atom in the energy range from 10
... employing a complex optical potential approach. The potential Vopt (r,k) was constructed using only two parameters, namely the spherical dipole polarizability (αd ) and the ionization potential energy of the ground state of the target atom. After generating the full optical potential of the scatteri ...
... employing a complex optical potential approach. The potential Vopt (r,k) was constructed using only two parameters, namely the spherical dipole polarizability (αd ) and the ionization potential energy of the ground state of the target atom. After generating the full optical potential of the scatteri ...
egg nebula - IOPscience
... of the 2 mm extinction, text(2 mm), from k1 to K1. The radius of this boundary, which is presumably intrinsically circular but appears elliptical because it is seen nearly edge-on, is about 40. The minor-to-major axis ratio of the cocoon implies that its symmetry axis is inclined by 107–207 to the s ...
... of the 2 mm extinction, text(2 mm), from k1 to K1. The radius of this boundary, which is presumably intrinsically circular but appears elliptical because it is seen nearly edge-on, is about 40. The minor-to-major axis ratio of the cocoon implies that its symmetry axis is inclined by 107–207 to the s ...
8 The Sun - Journigan-wiki
... The Sun’s Atmosphere You’d think with the density of the gases decreasing, that the temperature would decrease too, but just the opposite occurs. Because they are more easily heated at higher altitudes, the gases burn with great intensity. The temperature immediately above the photosphere has an av ...
... The Sun’s Atmosphere You’d think with the density of the gases decreasing, that the temperature would decrease too, but just the opposite occurs. Because they are more easily heated at higher altitudes, the gases burn with great intensity. The temperature immediately above the photosphere has an av ...
Chapter 5
... phase angle α equal to 0◦ (i.e. seen from the middle of the planet, the angle between the star and the observer equals 0◦ ), the total reflected flux πF equals the planet’s geometric albedo AG (see e.g. Stam et al. 2004). We will indicate the hence normalized total flux by πFn and the associated lin ...
... phase angle α equal to 0◦ (i.e. seen from the middle of the planet, the angle between the star and the observer equals 0◦ ), the total reflected flux πF equals the planet’s geometric albedo AG (see e.g. Stam et al. 2004). We will indicate the hence normalized total flux by πFn and the associated lin ...
The Science Case for SPICA Far
... Planck’s beam size is 5´, which will average over a lot of cloud structure even within our Galaxy. However, with Planck observations, we will have, for the first-time, the “magnetic context” for any subsequent measurement. Polarimetry will continue with ground-based telescopes. Two particularly powe ...
... Planck’s beam size is 5´, which will average over a lot of cloud structure even within our Galaxy. However, with Planck observations, we will have, for the first-time, the “magnetic context” for any subsequent measurement. Polarimetry will continue with ground-based telescopes. Two particularly powe ...
Parallax — How Far Is It?
... they differ in brightness, but we cannot easily tell how far away stars are. Astronomers can take advantage of the Earth’s motion around the Sun to help measure distances to stars by using parallax, a process similar to the way surveyors measure distances on Earth. Parallax is the apparent change in ...
... they differ in brightness, but we cannot easily tell how far away stars are. Astronomers can take advantage of the Earth’s motion around the Sun to help measure distances to stars by using parallax, a process similar to the way surveyors measure distances on Earth. Parallax is the apparent change in ...
T Tauri stars Optical lucky imaging polarimetry of HL and XZ Tau
... The idea that stars are formed out of interstellar clouds have been present for several centuries. The initial idea, that the Sun and Planets formed out of a rotating cloud or disk of material was called the Nebular Hypothesis, which was formulated by Emanuel Swedenborg in 1734. It sprung from the r ...
... The idea that stars are formed out of interstellar clouds have been present for several centuries. The initial idea, that the Sun and Planets formed out of a rotating cloud or disk of material was called the Nebular Hypothesis, which was formulated by Emanuel Swedenborg in 1734. It sprung from the r ...
Probing atmospheric electric fields in thunderstorms through radio
... This changes both the magnitude and the polarization of the radiation which follows F. During shower development the air shower particles loose energy. The parallel component of the atmospheric electric field partially compensates this energy loss. Therefore the total number of particles within a gi ...
... This changes both the magnitude and the polarization of the radiation which follows F. During shower development the air shower particles loose energy. The parallel component of the atmospheric electric field partially compensates this energy loss. Therefore the total number of particles within a gi ...
Soft X-Ray Polarimetry
... years, starting with a very simple design 18 emulating an experiment performed using the Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer 23 . Several missions have been proposed to NASA programs based on this approach. One example was the Polarimeter for Low Energy X-ray Astrophysical Sources (PLEXAS) that was propose ...
... years, starting with a very simple design 18 emulating an experiment performed using the Extreme Ultraviolet Explorer 23 . Several missions have been proposed to NASA programs based on this approach. One example was the Polarimeter for Low Energy X-ray Astrophysical Sources (PLEXAS) that was propose ...
Multi-band Dual-Polarization Lens-coupled Planar
... This effect can be mitigated by doing a polarization calibration of the entire experiment for each frequency band. The second effect is depolarization, or signal loss, if there is significant polarization rotation within one frequency band. For our current design, a ±5o polarization rotation, the de ...
... This effect can be mitigated by doing a polarization calibration of the entire experiment for each frequency band. The second effect is depolarization, or signal loss, if there is significant polarization rotation within one frequency band. For our current design, a ±5o polarization rotation, the de ...
Rotation of the Sun - University of California, Berkeley
... roughly equal amounts, which is white light. If the Sun were yellow, then white T-shirts would look yellow in the mid-day sunshine. When you observe the Sun safely, by projecting its image through a pinhole camera or a telescope, you see that it is white. Don’t stare directly at the Sun! The UV radi ...
... roughly equal amounts, which is white light. If the Sun were yellow, then white T-shirts would look yellow in the mid-day sunshine. When you observe the Sun safely, by projecting its image through a pinhole camera or a telescope, you see that it is white. Don’t stare directly at the Sun! The UV radi ...
arXiv: 1106.2158
... theory. A priori, Einf could lie anywhere between the TeV scale of current accelerator data and the Planck scale (1019 GeV), and over most of this range the inflationary B-mode signal will be undetectable amidst the background from gravitational lensing of E-modes. If inflation is associated with th ...
... theory. A priori, Einf could lie anywhere between the TeV scale of current accelerator data and the Planck scale (1019 GeV), and over most of this range the inflationary B-mode signal will be undetectable amidst the background from gravitational lensing of E-modes. If inflation is associated with th ...
The Celestial Sphere If you look out from an empty field into a dark
... sphere very like the one at the top of this section. A celestial sphere forms the basis for the application of many coordinate systems. For example, the horizon and the celestial meridian together form the reference circles for giving the position of stars in altitude and azimuth, making it easier f ...
... sphere very like the one at the top of this section. A celestial sphere forms the basis for the application of many coordinate systems. For example, the horizon and the celestial meridian together form the reference circles for giving the position of stars in altitude and azimuth, making it easier f ...
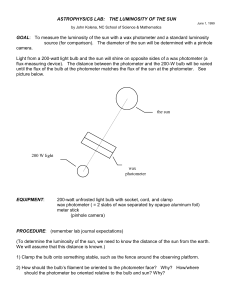
ASTROPHYSICS LAB: THE LUMINOSITY OF THE SUN
... 2) Using the average value of your group's measured distances (of balanced solar and bulb flux), calculate the luminosity of the sun. 3) Give one good reason that would explain why your calculated value of the solar luminosity could be higher than the accepted value. Explain clearly why your calcula ...
... 2) Using the average value of your group's measured distances (of balanced solar and bulb flux), calculate the luminosity of the sun. 3) Give one good reason that would explain why your calculated value of the solar luminosity could be higher than the accepted value. Explain clearly why your calcula ...
Zeeman observations: Measuring magnetic fields in the atomic and
... energies. Observationally, the resulting atomic and molecular transitions are partially circularly polarized. The circular polarized emission depends on the magnetic field strength along the line-of-sight and on the magnetic dipole moment. Only H I and molecules with an unpaired electron in the oute ...
... energies. Observationally, the resulting atomic and molecular transitions are partially circularly polarized. The circular polarized emission depends on the magnetic field strength along the line-of-sight and on the magnetic dipole moment. Only H I and molecules with an unpaired electron in the oute ...
The Sun powerpoint
... The intensity of the magnetic fields cause solar flares (jets of hot gases that explode off the sun) and prominences (loops of gas off the sun) which are solar storms. Sunspots and solar storms cause intense auroras, ionized light that generally form above the magnetic poles of the Earth. They can a ...
... The intensity of the magnetic fields cause solar flares (jets of hot gases that explode off the sun) and prominences (loops of gas off the sun) which are solar storms. Sunspots and solar storms cause intense auroras, ionized light that generally form above the magnetic poles of the Earth. They can a ...
History of IGM (C. Carilli)
... 0.4 Gyr after the big bang • Coeval formation of SMBH + stars in earliest galaxies – break-down of M-s at high z? • Cosmic Stromgren sphere of 4.7 Mpc => ‘witnessing process of reionization’ ...
... 0.4 Gyr after the big bang • Coeval formation of SMBH + stars in earliest galaxies – break-down of M-s at high z? • Cosmic Stromgren sphere of 4.7 Mpc => ‘witnessing process of reionization’ ...
VLTI
... Dense equatorial wind disk-like structure able to shield the disk material to allow molecules and dust to be formed near the hot central star (Kraus & Lamers 2003). ...
... Dense equatorial wind disk-like structure able to shield the disk material to allow molecules and dust to be formed near the hot central star (Kraus & Lamers 2003). ...
Lecture 6: Continuum Opacity and Stellar Atmospheres
... Note on Mie Scattering: Dust in the interstellar medium has a typical size of about 0.1 microns, or 1,000 angstroms. This is the size of a wavelength of ultraviolet light. More than a century ago, the physicist Mie (pronounced “Me”) developed a classical theory of scattering that applies to small s ...
... Note on Mie Scattering: Dust in the interstellar medium has a typical size of about 0.1 microns, or 1,000 angstroms. This is the size of a wavelength of ultraviolet light. More than a century ago, the physicist Mie (pronounced “Me”) developed a classical theory of scattering that applies to small s ...
Episode 5: Constellations of the zodiac
... Universe. It is not designed to be a popular account of the development of astronomy as a scientific discipline and its impact on our understanding of the cosmos. Since the treatment is not rigorous, many details are not included. The script has to be developed along the outline suggested using simp ...
... Universe. It is not designed to be a popular account of the development of astronomy as a scientific discipline and its impact on our understanding of the cosmos. Since the treatment is not rigorous, many details are not included. The script has to be developed along the outline suggested using simp ...
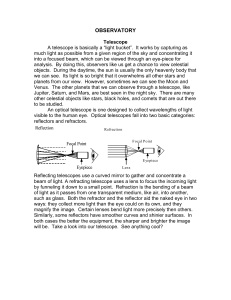
observatory - Science Presenters Central
... Look at the edge of the sun. Can you see the fuzzy result of those solar gases? The other filter we use is a Mylar filter, which reduces the sun’s apparent brightness. This makes it easier to view sunspots, the darkened areas where the surface of the sun is cooler. Each body in space has its own coo ...
... Look at the edge of the sun. Can you see the fuzzy result of those solar gases? The other filter we use is a Mylar filter, which reduces the sun’s apparent brightness. This makes it easier to view sunspots, the darkened areas where the surface of the sun is cooler. Each body in space has its own coo ...
Investigation of the Earth Ionosphere using the Radio Emission of
... (7) Due to limited resources of the computer, in both ranges (20 MHz and 30 MHz), the bandwidths were chosen to be relatively small and equal to 4.8 kHz; (8) To simplify the solution of the direct and inverse problems, we used the analytical form for the representation of model signals (Marple 1999) ...
... (7) Due to limited resources of the computer, in both ranges (20 MHz and 30 MHz), the bandwidths were chosen to be relatively small and equal to 4.8 kHz; (8) To simplify the solution of the direct and inverse problems, we used the analytical form for the representation of model signals (Marple 1999) ...
Rayleigh sky model

The Rayleigh sky model describes the observed polarization pattern of the daytime sky. Within the atmosphere Rayleigh scattering of light from air molecules, water, dust, and aerosols causes the sky's light to have a defined polarization pattern. The same elastic scattering processes cause the sky to be blue. The polarization is characterized at each wavelength by its degree of polarization, and orientation (the e-vector angle, or scattering angle).The polarization pattern of the sky is dependent on the celestial position of the sun. While all scattered light is polarized to some extent, light is highly polarized at a scattering angle of 90° from the light source. In most cases the light source is the sun, but the moon creates the same pattern as well. The degree of polarization first increases with increasing distance from the sun, and then decreases toward the anti-sun. Thus, the maximum degree of polarization occurs in a circular band 90° from the sun. In this band, degrees of polarization near 80% are typically reached.When the sun is located at the zenith, the band of maximal polarization wraps around the horizon. Light from the sky is polarized horizontally along the horizon. During twilight at either the Vernal or Autumnal equinox, the band of maximal polarization is defined by the North-Zenith-South plane, or meridian. In particular, the polarization is vertical at the horizon in the North and South, where the meridian meets the horizon. The polarization at twilight at an equinox is represented by the figure to the right. The red band represents the circle in the North-Zenith-South plane where the sky is highly polarized. The cardinal directions N, E, S, W are shown at 12-o'clock, 9 o'clock, 6 o'clock and 3 o'clock (counter-clockwise around the celestial sphere since the observer is looking up at the sky).Note that because the polarization pattern is dependent on the sun, it changes not only throughout the day but throughout the year. When the sun sets toward the South, in the winter, the North-Zenith-South plane is offset, with ""effective"" North actually located somewhat toward the West. Thus if the sun sets at an azimuth of 255° (15° South of West) the polarization pattern will be at its maximum along the horizon at an azimuth of 345° (15° West of North) and 165° (15° East of South).During a single day, the pattern rotates with the changing position of the sun. At twilight it typically appears about 45 minutes before local sunrise and disappears 45 minutes after local sunset. Once established it is very stable, showing change only in its rotation. It can easily be seen on any given day using polarized sunglasses.Many animals use the polarization patterns of the sky at twilight and throughout the day as a navigation tool. Because it is determined purely by the position of the sun, it is easily used as a compass for animal orientation. By orienting themselves with respect to the polarization patterns, animals can locate the sun and thus determine the cardinal directions.