... well as any other projects, upstream or downstream, that significantly affect salmon populations through their operations. For each stream, the State Board should consider criteria that would increase requirements for those agencies to provide reservoir releases and/or funding for habitat restoratio ...
Trophic interactions and behaviour Per B. Holliland
... copepodites (CIV–VI) of Acartia spp. and Eurytemora affinis, which also have the greatest contribution to its diet. Positive selection towards podonids was also likely. By contrast, evidence for extensive feeding on microzooplankton was weak and bosminids were not found to be an important prey. As t ...
... copepodites (CIV–VI) of Acartia spp. and Eurytemora affinis, which also have the greatest contribution to its diet. Positive selection towards podonids was also likely. By contrast, evidence for extensive feeding on microzooplankton was weak and bosminids were not found to be an important prey. As t ...
Phytoplankton chytridiomycosis: fungal parasites of phytoplankton
... propagules includes chytrids within the so-called group of zoosporic fungi, which are particularly adapted to the plankton lifestyle where they infect a wide variety of hosts, including fishes, eggs, zooplankton, algae, and other aquatic fungi but primarily freshwater phytoplankton. Related ecologic ...
... propagules includes chytrids within the so-called group of zoosporic fungi, which are particularly adapted to the plankton lifestyle where they infect a wide variety of hosts, including fishes, eggs, zooplankton, algae, and other aquatic fungi but primarily freshwater phytoplankton. Related ecologic ...
California red-legged frog - Baylands Ecosystem Habitat Goals Project
... routes, even crossing open pasture land and roads. In the San Francisco Bay Area, some populations are fragmented and isolated. The causes for population declines are many, and may include historical over-harvest for food, predation by non-native species, habitat alteration, pathogens and pollutants ...
... routes, even crossing open pasture land and roads. In the San Francisco Bay Area, some populations are fragmented and isolated. The causes for population declines are many, and may include historical over-harvest for food, predation by non-native species, habitat alteration, pathogens and pollutants ...
`Alkborough Managed Realignment` Measure analysis 30 in the
... the River Ouse and River Trent, is 440ha and is the largest managed realignment site on the Humber. The primary purpose of the site was to provide flood protection as the size of the site enables large capacity for water storage and reduces tidal levels throughout the upper estuary, thus delaying th ...
... the River Ouse and River Trent, is 440ha and is the largest managed realignment site on the Humber. The primary purpose of the site was to provide flood protection as the size of the site enables large capacity for water storage and reduces tidal levels throughout the upper estuary, thus delaying th ...
Trophic Cascades in Lakes:
... to aquatic consumers from both terrestrial and aquatic sources . However, terrestrial prey are available to top and mid-level predators and can therefore have a large effect on trophic cascades. In small lakes, fish consume significant quantities of terrestrial prey (Hodgson and Kitchell 1987, Hodgs ...
... to aquatic consumers from both terrestrial and aquatic sources . However, terrestrial prey are available to top and mid-level predators and can therefore have a large effect on trophic cascades. In small lakes, fish consume significant quantities of terrestrial prey (Hodgson and Kitchell 1987, Hodgs ...
UV radiation changes algal stoichiometry but does not have
... mortality in Calanus finmarchicus and cod eggs is a direct result of DNA damage (Browman et al., 2000; Browman and Vetter, 2002). However, direct effects are only part of the potential impact of UVR on trophic levels. Changes in the quantity and quality of many biologically important molecules such ...
... mortality in Calanus finmarchicus and cod eggs is a direct result of DNA damage (Browman et al., 2000; Browman and Vetter, 2002). However, direct effects are only part of the potential impact of UVR on trophic levels. Changes in the quantity and quality of many biologically important molecules such ...
Potential impacts of ocean acidification on the Puget Sound food web
... waters to the surface, while tributaries draining the surrounding lowlands and mountain ranges deposit low-pH, low alkalinity waters, further decreasing Puget Sound’s pH and buffering capacity. Biological activity and restrictions in water flow contribute to high pH variability observed in this and ...
... waters to the surface, while tributaries draining the surrounding lowlands and mountain ranges deposit low-pH, low alkalinity waters, further decreasing Puget Sound’s pH and buffering capacity. Biological activity and restrictions in water flow contribute to high pH variability observed in this and ...
Brasier, 1980
... Agglutinated wall: -----only feature for benthic---foraminifer builds its test wall by cementing together exogenous grains (e.g. sand grains, oolites, fine grains of calcite or sponge spicule) by carbonate mineralization. Wall is a simple layer that grades from fine grains inside to coarse grains ou ...
... Agglutinated wall: -----only feature for benthic---foraminifer builds its test wall by cementing together exogenous grains (e.g. sand grains, oolites, fine grains of calcite or sponge spicule) by carbonate mineralization. Wall is a simple layer that grades from fine grains inside to coarse grains ou ...
BONUS Briefing 8 BAZOOCA
... Jellyfish dynamics High densities of jellyfish can lead to problems for humans, such as clogged industrial cooling systems, destroyed trawling equipment and disturbed leisure activities. The predation impact by highly abundant jellyfish will reduce the populations of their zooplankton prey, includin ...
... Jellyfish dynamics High densities of jellyfish can lead to problems for humans, such as clogged industrial cooling systems, destroyed trawling equipment and disturbed leisure activities. The predation impact by highly abundant jellyfish will reduce the populations of their zooplankton prey, includin ...
Marine Ecology Progress Series 309:175
... Ecosim simulations. The consumption (Q) of a predator in the Ecosim simulations varies as a function of its biomass and the biomass of its prey and a parameter called ‘vulnerability’ (v) that conceptually represents a theoretical flow rate at which the prey biomass moves from a vulnerable state to a ...
... Ecosim simulations. The consumption (Q) of a predator in the Ecosim simulations varies as a function of its biomass and the biomass of its prey and a parameter called ‘vulnerability’ (v) that conceptually represents a theoretical flow rate at which the prey biomass moves from a vulnerable state to a ...
Harmful microalgal episodes in Greek coastal waters
... algae. During the present study, the majority of algal blooms were observed in Thermaikos and Amvrakikos Bays. It is generally accepted that one of the most important factors promoting the development of algal blooms in coastal waters is the nutrient supply from terrestrial sources (Cadée, 1986; Rad ...
... algae. During the present study, the majority of algal blooms were observed in Thermaikos and Amvrakikos Bays. It is generally accepted that one of the most important factors promoting the development of algal blooms in coastal waters is the nutrient supply from terrestrial sources (Cadée, 1986; Rad ...
Which factors regulate seagrass growth and distribution?
... marina and P. oceanica, respectively. The importance of grazing for the distribution of seagrasses is in general considered relatively low in European waters, but investigations suggest that grazing on fresh leaves is more important in the fast growing species Z. marina, Z. noltii and C. nodosa than ...
... marina and P. oceanica, respectively. The importance of grazing for the distribution of seagrasses is in general considered relatively low in European waters, but investigations suggest that grazing on fresh leaves is more important in the fast growing species Z. marina, Z. noltii and C. nodosa than ...
HARMFUL ALGAE NEWS - University of Liverpool
... (turbulence, shear, advection) and biological behaviour (migration, physiological adaptation) holds the key to understanding vertical distributions, bloom dynamics, and patterns of toxicity.” Thus questions like those asked in the late nineteenth century by some of the pioneers of marine science con ...
... (turbulence, shear, advection) and biological behaviour (migration, physiological adaptation) holds the key to understanding vertical distributions, bloom dynamics, and patterns of toxicity.” Thus questions like those asked in the late nineteenth century by some of the pioneers of marine science con ...
Terrestrial predators and abiotic conditions affect hatching survival
... inputs due to predator and abiotic factors would have a positive effect on primary productivity (Fig. 6a). However, at these low densities, zooplankton density decreases which will have a negative effect on primary productivity. Theory predicts that our patterns could result from either population l ...
... inputs due to predator and abiotic factors would have a positive effect on primary productivity (Fig. 6a). However, at these low densities, zooplankton density decreases which will have a negative effect on primary productivity. Theory predicts that our patterns could result from either population l ...
Annotated Bibliography Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst.
... -It is a credible source because it examines both sides of the argument. It gives benefits and negative effects for both aspects. Schaefer Center for Public Policy. Poll on Maryland's Evironmental Laws. 14 Dec. 1992. Raw data. University of Baltimore, Baltimore. -This is a relevant source because it ...
... -It is a credible source because it examines both sides of the argument. It gives benefits and negative effects for both aspects. Schaefer Center for Public Policy. Poll on Maryland's Evironmental Laws. 14 Dec. 1992. Raw data. University of Baltimore, Baltimore. -This is a relevant source because it ...
Behavior of Plankton and Patch Formation in Pelagic Ecosystems
... and pelagic systems ... [based on asymmetries in the] ... temporal and spatial patterns of nutrient cycling ... On land, the material [and ultimately limiting] resource is water ... passed up the food pyramid but ... not recycled ... because of evaporation." In aquatic systems water is never limitin ...
... and pelagic systems ... [based on asymmetries in the] ... temporal and spatial patterns of nutrient cycling ... On land, the material [and ultimately limiting] resource is water ... passed up the food pyramid but ... not recycled ... because of evaporation." In aquatic systems water is never limitin ...
Caribbean and Pacific Coastal marine system
... system is exploited only by subsistence fishing. Even if certain reef-fish are overharvested, alternative species might be taken. Conversely, excess nutrient input is likely to have a greater effect on ecosystems that are normally exposed to low levels of nutrient input. Eutrophication via sewage ma ...
... system is exploited only by subsistence fishing. Even if certain reef-fish are overharvested, alternative species might be taken. Conversely, excess nutrient input is likely to have a greater effect on ecosystems that are normally exposed to low levels of nutrient input. Eutrophication via sewage ma ...
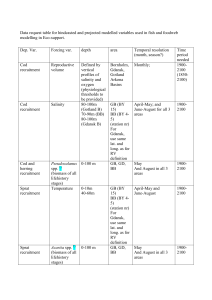
Revised Water Quality Control Plan Appendix K
... populations migrating through the Delta. Flow conditions that reasonably contribute toward maintaining viable native migratory San Joaquin River fish populations include, but may not be limited to, flows that mimic the natural hydrographic conditions to which native fish species are adapted, includi ...
... populations migrating through the Delta. Flow conditions that reasonably contribute toward maintaining viable native migratory San Joaquin River fish populations include, but may not be limited to, flows that mimic the natural hydrographic conditions to which native fish species are adapted, includi ...
Data request table for hindcasted and projected modelled
... For models only generating a generic zooplankton, not specified to species, biomass of total zooplankton replaces request for Pseudocalanus, Acartia and Temora projections. ...
... For models only generating a generic zooplankton, not specified to species, biomass of total zooplankton replaces request for Pseudocalanus, Acartia and Temora projections. ...
Influence of diet on copepod survival in the laboratory
... copepods were fed either good-quality food (Rhodomonas sp.) or nutritionally poor food (Dunaliella sp., Amphidinium sp., Chrysochromulina polylepis and Synechococcus sp.) in high (> 300 µg C l–1) or low (<100 µg C l–1) concentrations and survival was monitored. Both copepod species had low mortality ...
... copepods were fed either good-quality food (Rhodomonas sp.) or nutritionally poor food (Dunaliella sp., Amphidinium sp., Chrysochromulina polylepis and Synechococcus sp.) in high (> 300 µg C l–1) or low (<100 µg C l–1) concentrations and survival was monitored. Both copepod species had low mortality ...
Food selection and habitat preferences in deep-sea fishes
... values it is poorer (lighter) in 13C. For 8 13C analyses, tissue from animals (about 10 g) and samples from fresh animals were washed in distilled water and dry frozen (-20 °C) for several days. The tissue samples from fishes were: muscles from the predorsal region (without skin), the liver, and fin ...
... values it is poorer (lighter) in 13C. For 8 13C analyses, tissue from animals (about 10 g) and samples from fresh animals were washed in distilled water and dry frozen (-20 °C) for several days. The tissue samples from fishes were: muscles from the predorsal region (without skin), the liver, and fin ...
CHARACTERIZATION OF ENVIRONMENTAL PARAMETERS AND
... The rocky intertidal has an array of species found in the different zones. The intertidal is typically broken up into three parts: high, middle and low. The zones can be differentiated by either measuring the physical height from mean low water level or by identifying the key species (typically alga ...
... The rocky intertidal has an array of species found in the different zones. The intertidal is typically broken up into three parts: high, middle and low. The zones can be differentiated by either measuring the physical height from mean low water level or by identifying the key species (typically alga ...
Deep pelagic biology - School of Ocean and Earth Science and
... The physical and chemical properties of the oceanic water column show considerable variability within the upper kilometer but at greater depths they remain relatively constant. Conditions in the horizontal plane are spatially homogeneous and have been very stable over time. Patterns of seasonal and ...
... The physical and chemical properties of the oceanic water column show considerable variability within the upper kilometer but at greater depths they remain relatively constant. Conditions in the horizontal plane are spatially homogeneous and have been very stable over time. Patterns of seasonal and ...
clam fact sheet - World Animal Foundation
... subphylum. Crustaceans include lobsters, crabs and shrimp. Crustaceans are really more related to insects than to clams. Some shellfish or mollusks only have one shell, such as snails. Clams have two shells so they are known as bivalve mollusks. The shells are held together with a hinge. Other bival ...
... subphylum. Crustaceans include lobsters, crabs and shrimp. Crustaceans are really more related to insects than to clams. Some shellfish or mollusks only have one shell, such as snails. Clams have two shells so they are known as bivalve mollusks. The shells are held together with a hinge. Other bival ...
Ecology of the San Francisco Estuary

The San Francisco Estuary together with the Sacramento-San Joaquin River Delta represents a highly altered ecosystem. The region has been heavily re-engineered to accommodate the needs of water delivery, shipping, agriculture, and most recently, suburban development. These needs have wrought direct changes in the movement of water and the nature of the landscape, and indirect changes from the introduction of non-native species. New species have altered the architecture of the food web as surely as levees have altered the landscape of islands and channels that form the complex system known as the Delta.This article deals particularly with the ecology of the low salinity zone (LSZ) of the estuary. Reconstructing a historic food web for the LSZ is difficult for a number of reasons. First, there is no clear record of the species that historically have occupied the estuary. Second, the San Francisco Estuary and Delta have been in geologic and hydrologic transition for most of their 10,000 year history, and so describing the ""natural"" condition of the estuary is much like ""hitting a moving target"". Climate change, hydrologic engineering, shifting water needs, and newly introduced species will continue to alter the food web configuration of the estuary. This model provides a snapshot of the current state, with notes about recent changes or species introductions that have altered the configuration of the food web. Understanding the dynamics of the current food web may prove useful for restoration efforts to improve the functioning and species diversity of the estuary.