Micronutrient Cofactors
... Too much raw egg can cause vitamin B7 deficiency Avidin produced in egg whites binds with biotin with affinity ...
... Too much raw egg can cause vitamin B7 deficiency Avidin produced in egg whites binds with biotin with affinity ...
Chemistry Of Lichens Complete
... Introduction to Lichen Chemistry • Lichens produce a wide array of both primary (intracellular) and secondary (extracellular) compounds - Primary metabolites include amino acids, polyols, carotenoids, polysaccharides, and vitamins • Some, like the polysaccharide cell wall compounds lichenan and is ...
... Introduction to Lichen Chemistry • Lichens produce a wide array of both primary (intracellular) and secondary (extracellular) compounds - Primary metabolites include amino acids, polyols, carotenoids, polysaccharides, and vitamins • Some, like the polysaccharide cell wall compounds lichenan and is ...
1) Mesosomes 2) Vacuoles 3) Ribosomes 4) Lysosomes
... The secondary structure of protein refers to a. The alpha helix 2) The shape of the polypeptide 3) Amino acid sequence 4) Presence of other attachments to the polypeptide. Macromolecule chitin is 1) Nitrogen containing polysaccharide 2) Phosphorus containing polysaccharide 3) Sulphur polysaccharide ...
... The secondary structure of protein refers to a. The alpha helix 2) The shape of the polypeptide 3) Amino acid sequence 4) Presence of other attachments to the polypeptide. Macromolecule chitin is 1) Nitrogen containing polysaccharide 2) Phosphorus containing polysaccharide 3) Sulphur polysaccharide ...
printed handout sheets
... expression, and the selective responses to cytokines depend on specific DNA binding proteins which regulate gene expression. There may be literally thousands of these proteins, which are themselves expressed in a tissue selective fashion. We only have time to mention a few representative examples. P ...
... expression, and the selective responses to cytokines depend on specific DNA binding proteins which regulate gene expression. There may be literally thousands of these proteins, which are themselves expressed in a tissue selective fashion. We only have time to mention a few representative examples. P ...
(ATP). - WordPress.com
... NAD+ is produced and used to oxidize more glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (glycolysis), producing small amounts of ATP increased amount of lactate causes muscles to become tired and sore After exercise, a person breathes heavily to repay the oxygen debt and reform pyruvate in the liver. ...
... NAD+ is produced and used to oxidize more glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (glycolysis), producing small amounts of ATP increased amount of lactate causes muscles to become tired and sore After exercise, a person breathes heavily to repay the oxygen debt and reform pyruvate in the liver. ...
Document
... Addition of heparin makes it easier for thrombin to interact with antithrombin - positive allosteric effect. ...
... Addition of heparin makes it easier for thrombin to interact with antithrombin - positive allosteric effect. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. Which hormone is responsible for maintaining the level of serum calcium? Mention its role. 2. Write any two biological functions of Iron. 3. Why are humans unable to synthesis Vitamin C? 4. Give the structure of tocotrienol. 5. Why is HDL considered as good cholesterol? 6. What is physiological f ...
... 1. Which hormone is responsible for maintaining the level of serum calcium? Mention its role. 2. Write any two biological functions of Iron. 3. Why are humans unable to synthesis Vitamin C? 4. Give the structure of tocotrienol. 5. Why is HDL considered as good cholesterol? 6. What is physiological f ...
doc - STAO
... compare the biochemical compounds found in each food to those found in the others [PR, AI, C] C2.3 conduct a laboratory investigation of the process of photosynthesis to identify the products of the process, interpret the qualitative observations, and display them in an appropriate format [PR, AI,C] ...
... compare the biochemical compounds found in each food to those found in the others [PR, AI, C] C2.3 conduct a laboratory investigation of the process of photosynthesis to identify the products of the process, interpret the qualitative observations, and display them in an appropriate format [PR, AI,C] ...
Unit 13: Biochemistry and Biochemical Techniques
... The main focus of learning outcome 1 is for learners to understand the diverse, polymeric nature and shapes of biological macromolecules. For each class of biological molecules listed, learners should demonstrate structural diversity arising from differing combinations and sequences of a limited num ...
... The main focus of learning outcome 1 is for learners to understand the diverse, polymeric nature and shapes of biological macromolecules. For each class of biological molecules listed, learners should demonstrate structural diversity arising from differing combinations and sequences of a limited num ...
Chapter 8
... Pyrimidine nucleotides are hydrolyzed, yielding the building blocks of pyrimidine, ribose and phosphate. C and U are degraded to CO2, H2O and β alanine. T is degraded to CO2, H2O and β aminoisobutyric acid. ...
... Pyrimidine nucleotides are hydrolyzed, yielding the building blocks of pyrimidine, ribose and phosphate. C and U are degraded to CO2, H2O and β alanine. T is degraded to CO2, H2O and β aminoisobutyric acid. ...
Document
... Establish pipelines to import updates of annotation, and expert advice Display clusters or other statistictically-generated groupings of genes Visualisation of metabolite profiling data sets Combination of data-sets at different levels Statistical treatment of the responses of different BINS - rigor ...
... Establish pipelines to import updates of annotation, and expert advice Display clusters or other statistictically-generated groupings of genes Visualisation of metabolite profiling data sets Combination of data-sets at different levels Statistical treatment of the responses of different BINS - rigor ...
Chapter 22 (Part 1) - University of Nevada, Reno
... • Codon-anticodon pairing is the crucial feature of the "reading of the code" • But what accounts for "degeneracy": are there 61 different anticodons, or can you get by with fewer than 61, due to lack of specificity at the third position? • Crick's Wobble Hypothesis argues for the second possibility ...
... • Codon-anticodon pairing is the crucial feature of the "reading of the code" • But what accounts for "degeneracy": are there 61 different anticodons, or can you get by with fewer than 61, due to lack of specificity at the third position? • Crick's Wobble Hypothesis argues for the second possibility ...
H&C metabolism - Bryn Mawr College
... is indicative of a pro-inflammatory immune status. • Neopterin serves as a marker of cellular immune system activation (measured in body fluids: blood serum, cerebrospinal fluid or urine) . • Why is it formed? A result of activation of GTP cyclohydrolase I; so an excretory product of GTP metabolism. ...
... is indicative of a pro-inflammatory immune status. • Neopterin serves as a marker of cellular immune system activation (measured in body fluids: blood serum, cerebrospinal fluid or urine) . • Why is it formed? A result of activation of GTP cyclohydrolase I; so an excretory product of GTP metabolism. ...
2.1 The Nature of Matter
... C. proton. D. electron. 2. Two or more different atoms are combined in definite proportions in any A. symbol. B. isotope. C. element. D. compound. ...
... C. proton. D. electron. 2. Two or more different atoms are combined in definite proportions in any A. symbol. B. isotope. C. element. D. compound. ...
Microbiology
... It is found in a large number of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Gram-negative bacteria. The T2SSs of different species secrete a wide variety of folded exoproteins of different functions, shapes, sizes and quaternary structures. The T2SS secretion signal is still unknown, but it has been suggested tha ...
... It is found in a large number of pathogenic and nonpathogenic Gram-negative bacteria. The T2SSs of different species secrete a wide variety of folded exoproteins of different functions, shapes, sizes and quaternary structures. The T2SS secretion signal is still unknown, but it has been suggested tha ...
Document
... • Look at the slides that follow containing the list of reactions on which to focus. • Re-read the indicated pages where each reaction is described in Creighton. Look at related power point slides and examples discussed in class. • Put together a summary sheet with each reaction in as much detail as ...
... • Look at the slides that follow containing the list of reactions on which to focus. • Re-read the indicated pages where each reaction is described in Creighton. Look at related power point slides and examples discussed in class. • Put together a summary sheet with each reaction in as much detail as ...
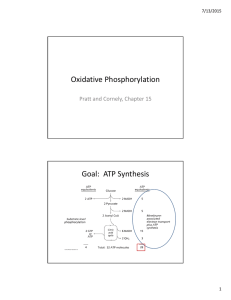
Oxidative Phosphorylation Goal: ATP Synthesis
... • NADH pumps 10 protons when 2 e‐ reduce ½ O2 – 4 protons in Complex I, 4 protons in Complex III, and 2 protons in Complex IV ...
... • NADH pumps 10 protons when 2 e‐ reduce ½ O2 – 4 protons in Complex I, 4 protons in Complex III, and 2 protons in Complex IV ...
Citric Acid Cycle Review Activity Goals
... the audio recording and find the inputs and outputs for the step that you are doing. Start at Step 1 where Acetyl CoA is fed into the system and is converted into citrate. Then work your way around taking care and keeping track of the required additions and expulsions from the system. Follow the sys ...
... the audio recording and find the inputs and outputs for the step that you are doing. Start at Step 1 where Acetyl CoA is fed into the system and is converted into citrate. Then work your way around taking care and keeping track of the required additions and expulsions from the system. Follow the sys ...
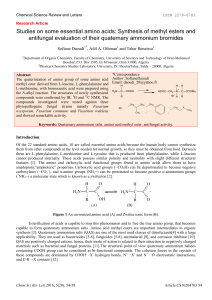
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
Human Physiology
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
Origin of Life | Principles of Biology from Nature Education
... From Organic Molecules to Self-Replicating Protocells How are plants and animals different from rocks and water? Living organisms reproduce themselves. Even the simplest bacteria produce copies of their single cells. How could this complicated process have evolved? Scientists generally agree on a ba ...
... From Organic Molecules to Self-Replicating Protocells How are plants and animals different from rocks and water? Living organisms reproduce themselves. Even the simplest bacteria produce copies of their single cells. How could this complicated process have evolved? Scientists generally agree on a ba ...
View
... Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids, and accounts for about 90% of the nitrogen-containing components of urine. One nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by free ammonia and the other nitrogen by aspartate. [Note: Glutamate is the immediate precursor of both ...
... Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids, and accounts for about 90% of the nitrogen-containing components of urine. One nitrogen of the urea molecule is supplied by free ammonia and the other nitrogen by aspartate. [Note: Glutamate is the immediate precursor of both ...
At the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games, David Davies won the silver
... the duration of a task. 1. Identify each of the energy systems A, B and C. (2 marks) 2. Explain how the differing energy sources of these systems are used during: * (i) a series of javelin throws; (2 marks) * (ii) a long-distance run of increasing intensity. (4 marks) ...
... the duration of a task. 1. Identify each of the energy systems A, B and C. (2 marks) 2. Explain how the differing energy sources of these systems are used during: * (i) a series of javelin throws; (2 marks) * (ii) a long-distance run of increasing intensity. (4 marks) ...
hydrocarbon chains
... acid chains -In animals, Cholesterol is the key regulator of membrane fluidity, (hydroxyl group : phospholipid head group, hydrocarbon tail : nonpolar core of the bilayer) -Cholesterol disrupts the interactions between fatty acid chain increasing the membrane fluidity. -Cholesterol forms specific co ...
... acid chains -In animals, Cholesterol is the key regulator of membrane fluidity, (hydroxyl group : phospholipid head group, hydrocarbon tail : nonpolar core of the bilayer) -Cholesterol disrupts the interactions between fatty acid chain increasing the membrane fluidity. -Cholesterol forms specific co ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.