2.4 How DNA Codes for Protein
... specific amino acid of the 20 possible. Note that “R” in this case is used for “residue” and not to denote the specific amino acid arginine. Figure 2.10 is a chemical schematic of an amino acid structure. The amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds where the carboxyl group gives up an OH an ...
... specific amino acid of the 20 possible. Note that “R” in this case is used for “residue” and not to denote the specific amino acid arginine. Figure 2.10 is a chemical schematic of an amino acid structure. The amino acids are joined together by peptide bonds where the carboxyl group gives up an OH an ...
Muscle cells generate force by shortening their length via chemical
... 2) Major fuels: Glycolysis in cytosol and fatty acid oxidation in mitochondria, both create NADH 3) Mitochondria use NADH to make ATP with oxygen required as electron acceptor 4) Mitochondria #1 ATP production site if O2 present 5) What happens when ATP demand surpasses the supply of oxygen require ...
... 2) Major fuels: Glycolysis in cytosol and fatty acid oxidation in mitochondria, both create NADH 3) Mitochondria use NADH to make ATP with oxygen required as electron acceptor 4) Mitochondria #1 ATP production site if O2 present 5) What happens when ATP demand surpasses the supply of oxygen require ...
Answer guide
... build-up of toxic waste products may be killing cells D – population size decreases due to lack of nutrients and a build-up of toxic waste products death rate is now greater than reproductive rate (ii) ...
... build-up of toxic waste products may be killing cells D – population size decreases due to lack of nutrients and a build-up of toxic waste products death rate is now greater than reproductive rate (ii) ...
Instructor Supplement: Ideas for Workshop Extension Activities Core
... These five proteins likely have very similar secondary and tertiary structures. These five proteins likely perform similar functions in the cell. The genes that encode these five proteins likely have a common evolutionary ancestor. A, B, and C are all correct. This is a remarkable coincidence, but y ...
... These five proteins likely have very similar secondary and tertiary structures. These five proteins likely perform similar functions in the cell. The genes that encode these five proteins likely have a common evolutionary ancestor. A, B, and C are all correct. This is a remarkable coincidence, but y ...
1. Lactose is a disaccharide found in milk. In the small intestine, it is
... The diagram shows the events that occur in the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids. These molecules enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine by diffusion. Once inside they are reassembled into triglycerides in organelle Q. The triglyceride molecules are formed into chylomicrons in ...
... The diagram shows the events that occur in the absorption of monoglycerides and fatty acids. These molecules enter the epithelial cells of the small intestine by diffusion. Once inside they are reassembled into triglycerides in organelle Q. The triglyceride molecules are formed into chylomicrons in ...
Lecture 16- Dr. Kumar
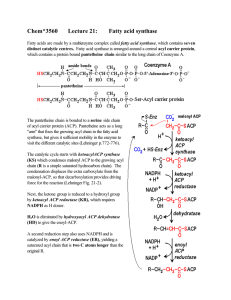
... • Know mechanism of intestinal absorption and clearance of triglycerides from blood • Know mechanism of action of drugs that prevent accumulation of plasma triglycerides • Know how carbon atoms of glucose are channeled into fatty acids • Know the rate limiting enzyme of fatty acid synthesis and how ...
... • Know mechanism of intestinal absorption and clearance of triglycerides from blood • Know mechanism of action of drugs that prevent accumulation of plasma triglycerides • Know how carbon atoms of glucose are channeled into fatty acids • Know the rate limiting enzyme of fatty acid synthesis and how ...
Syllabus of the International Chemistry Olympiad
... time, how the color of Delft blue pottery can be understood, how a bio-compatible polymer can be made from lactic acid, how modern spectroscopy is applied, how the structure of the natural product carvone can be unravelled, how aspects of green chemistry can be treated more quantitatively, how deter ...
... time, how the color of Delft blue pottery can be understood, how a bio-compatible polymer can be made from lactic acid, how modern spectroscopy is applied, how the structure of the natural product carvone can be unravelled, how aspects of green chemistry can be treated more quantitatively, how deter ...
Central Dogma of Genetics
... • This flow of information is unidirectional and irreversible. • The information carried within the DNA dictates the end product (protein) that will be synthesized. – This information is the genetic code. ...
... • This flow of information is unidirectional and irreversible. • The information carried within the DNA dictates the end product (protein) that will be synthesized. – This information is the genetic code. ...
1 2 , 3 4 5
... amino acid sequences may reval a homology that cannot be detected in present-day proteins. The employment of such ancestral sequences may be generally useful for detecting common ancestry not otherwise observable. ...
... amino acid sequences may reval a homology that cannot be detected in present-day proteins. The employment of such ancestral sequences may be generally useful for detecting common ancestry not otherwise observable. ...
k28 The hydrogen hypothesis for the first eukaryote - e
... Eubacteria, archaeabacteria, and eukaryotes (singular: eubacterium, archaeabacterium, and eukaryote) are three domains of life if no one of them evolved from the other. The same are referred to by Carl R. Woese, beginning in the 1970s, as bacteria, archaea, and eucarya (singular: bacterium, archaeon ...
... Eubacteria, archaeabacteria, and eukaryotes (singular: eubacterium, archaeabacterium, and eukaryote) are three domains of life if no one of them evolved from the other. The same are referred to by Carl R. Woese, beginning in the 1970s, as bacteria, archaea, and eucarya (singular: bacterium, archaeon ...
Animation Script for Translation
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
... 1. In translation, the cell uses an mRNA strand as a template to assemble proteins. The cell has just transcribed this mRNA strand from its DNA, and it now translates the mRNA’s nucleotide sequence into a chain of amino acids. This chain, called a polypeptide, forms the basic structure of a protein. ...
o C
... Elements are the simplest pure substances. An element cannot be changed into simpler substances by any chemical process. ...
... Elements are the simplest pure substances. An element cannot be changed into simpler substances by any chemical process. ...
Development of Biocatalysts for Production of Fine Chemicals
... work on a variety of substrates, they are used as Sumit- ...
... work on a variety of substrates, they are used as Sumit- ...
Amino acids used in Animal Nutrition
... How do Amino Acids build protein? How it works…… If during this process, there is an insufficient pool of just one of the required amino acids that the signal has called for… Then protein synthesis stops! ...
... How do Amino Acids build protein? How it works…… If during this process, there is an insufficient pool of just one of the required amino acids that the signal has called for… Then protein synthesis stops! ...
Coenzymes and Cofactors (PDF Available)
... acid–base catalysis, nucleophilic and electrophilic catalysis, and in a few instances radical initiation, but certainly do not account for all of the types of catalytic reactions of enzymes. For example, an important class of enzymatic reactions are redox reactions, and in general protein functional ...
... acid–base catalysis, nucleophilic and electrophilic catalysis, and in a few instances radical initiation, but certainly do not account for all of the types of catalytic reactions of enzymes. For example, an important class of enzymatic reactions are redox reactions, and in general protein functional ...
Chem ppt for lecture, part 2 File
... • Mixture of compounds that resist pH changes • Convert strong (completely dissociated) acids or bases into weak (slightly dissociated) ones • Carbonic acid-bicarbonate system ...
... • Mixture of compounds that resist pH changes • Convert strong (completely dissociated) acids or bases into weak (slightly dissociated) ones • Carbonic acid-bicarbonate system ...
U4L22 exercise - University of Sydney
... fatty acid oxidation can be used for ATP generation • Power output is lower when using only fatty acids • “Hitting the Wall” • Cannot sprint if there’s no glycogen ...
... fatty acid oxidation can be used for ATP generation • Power output is lower when using only fatty acids • “Hitting the Wall” • Cannot sprint if there’s no glycogen ...
Chapter 5
... with most muscles: the lactate is carried by the blood from the muscle cells to the liver, where it can be converted to glucose. Thus, although lactate is formed at high rates when muscles are overworked and become fatigued, it is not directly the cause of muscle fatigue. As oxygen availability cann ...
... with most muscles: the lactate is carried by the blood from the muscle cells to the liver, where it can be converted to glucose. Thus, although lactate is formed at high rates when muscles are overworked and become fatigued, it is not directly the cause of muscle fatigue. As oxygen availability cann ...
Bio251 07 HW2 1-26-0..
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
... The Oxygen atom attracts electrons much more forcefully than does a Hydrogen atom. In this way, oxygen is a strongly electronegative atom. As a result the O-H bond is said to be polarized, such that one of the atoms has a partial negative charge, and the other a partial positive charge. Molecules, s ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... and Mn2+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d5. Thus, the conversion of Mn3+ to Mn2+ will be a favourable reaction since 3d5 is a very stable configuration as it is half filled configuration. Hence, Eo value for Mn3+ / Mn2+ couple is positive. Cr3+ to Cr2+ undergoes a change in outer electro ...
... and Mn2+ has the outer electronic configuration of 3d5. Thus, the conversion of Mn3+ to Mn2+ will be a favourable reaction since 3d5 is a very stable configuration as it is half filled configuration. Hence, Eo value for Mn3+ / Mn2+ couple is positive. Cr3+ to Cr2+ undergoes a change in outer electro ...
Expanding the Genetic Code of Escherichia coli
... A unique transfer RNA (tRNA)/aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase pair has been generated that expands the number of genetically encoded amino acids in Escherichia coli. When introduced into E. coli, this pair leads to the in vivo incorporation of the synthetic amino acid O-methyl-L-tyrosine into protein in re ...
... A unique transfer RNA (tRNA)/aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase pair has been generated that expands the number of genetically encoded amino acids in Escherichia coli. When introduced into E. coli, this pair leads to the in vivo incorporation of the synthetic amino acid O-methyl-L-tyrosine into protein in re ...
Metabolomic Profiling Identifies Biomarkers Associated
... observational study in 10,000 Finnish men who live near the city of Kuopio.1 Cases and controls for this work are subsets from the METSIM study. Cases include 220 subjects who were not diabetic at baseline but were found to be diabetic at the 5 year follow up time point. Most cases exhibited some fo ...
... observational study in 10,000 Finnish men who live near the city of Kuopio.1 Cases and controls for this work are subsets from the METSIM study. Cases include 220 subjects who were not diabetic at baseline but were found to be diabetic at the 5 year follow up time point. Most cases exhibited some fo ...
Enzyme powerpoint
... most human enzymes = pH 6-8 depends on localized conditions pepsin (stomach) = pH 2-3 trypsin (small intestines) = pH 8 ...
... most human enzymes = pH 6-8 depends on localized conditions pepsin (stomach) = pH 2-3 trypsin (small intestines) = pH 8 ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.