Amino Acids
... Polarity. The nonpolar amino acids are alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, and valine. Six of the polar amino acids are uncharged: these are asparagine, cysteine, glutamine, serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Five polar amino acids are charged; these ...
... Polarity. The nonpolar amino acids are alanine, glycine, isoleucine, leucine, methionine, phenylalanine, proline, tryptophan, and valine. Six of the polar amino acids are uncharged: these are asparagine, cysteine, glutamine, serine, threonine, and tyrosine. Five polar amino acids are charged; these ...
Flux Balance Analysis of Photoautotrophic
... Maximum Uptake Rates. To perform simulations of growth, it is necessary to add constraints for maximum nutrient and light uptake rates. The maximum growth rate of photoautotrophically cultivated Synechocystis was measured to be 0.085 ( 0.015 h-l from four separate experiments. This value is consiste ...
... Maximum Uptake Rates. To perform simulations of growth, it is necessary to add constraints for maximum nutrient and light uptake rates. The maximum growth rate of photoautotrophically cultivated Synechocystis was measured to be 0.085 ( 0.015 h-l from four separate experiments. This value is consiste ...
Reaction Engineering - Aalborg Universitet
... 2) Semi-continuous: fed batch-gradual addition of concentrated nutrients so that the culture volume and product amount are increased (e.g. industrial production of baker’s yeast); Perfusion-addition of medium to the culture and withdrawal of an equal volume of used cell-free medium (e.g. animal cell ...
... 2) Semi-continuous: fed batch-gradual addition of concentrated nutrients so that the culture volume and product amount are increased (e.g. industrial production of baker’s yeast); Perfusion-addition of medium to the culture and withdrawal of an equal volume of used cell-free medium (e.g. animal cell ...
AUG
... The ribosome has two sites for binding charged tRNA mRNA is associated with small (30S) subunit ...
... The ribosome has two sites for binding charged tRNA mRNA is associated with small (30S) subunit ...
Nutr-4-Prot
... High quality protein: Meat, Egg, Fish Poultry, Milk, Soybean Suppl. Ratio in diet:40-50% Protein in Energy:15-20% ...
... High quality protein: Meat, Egg, Fish Poultry, Milk, Soybean Suppl. Ratio in diet:40-50% Protein in Energy:15-20% ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... be used to do work; the rest is dissipated as heat. One catabolic process, fermentation, is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen. However, the most prevalent and efficient catabolic pathway is aerobic respiration, in which oxygen is consumed as a ...
... be used to do work; the rest is dissipated as heat. One catabolic process, fermentation, is a partial degradation of sugars or other organic fuel that occurs without the use of oxygen. However, the most prevalent and efficient catabolic pathway is aerobic respiration, in which oxygen is consumed as a ...
18.3 Amino Acids - Haverford Alchemy
... • Protein molecules in solution can be separated from each other by taking advantage of their net charges. • In the electric field between two electrodes, a positively charged particle moves toward the negative electrode and a negatively charged particle moves toward the positive electrode. This mov ...
... • Protein molecules in solution can be separated from each other by taking advantage of their net charges. • In the electric field between two electrodes, a positively charged particle moves toward the negative electrode and a negatively charged particle moves toward the positive electrode. This mov ...
CLINICALLY RELEVANT OF CYTOCHROME P450 FAMILY
... group of heme-containing enzymes involved in the metabolism of many drugs, steroids and carcinogens1. In particular, these isoenzymes are responsible for catalyzing the oxygenation of a broad number and variety of endogenous and xenobiotic substrates. CYP450-catalyzed reactions can be divided into f ...
... group of heme-containing enzymes involved in the metabolism of many drugs, steroids and carcinogens1. In particular, these isoenzymes are responsible for catalyzing the oxygenation of a broad number and variety of endogenous and xenobiotic substrates. CYP450-catalyzed reactions can be divided into f ...
Direct measurement of CO2 flux and its isotopic composition
... On geological timescales, oxidative weathering of sedimentary rocks can result in important emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) to the atmosphere, and consume atmospheric O2. The main processes are the oxidation of rock-derived organic carbon, and the weathering of carbonate minerals by sulfuric acid ...
... On geological timescales, oxidative weathering of sedimentary rocks can result in important emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) to the atmosphere, and consume atmospheric O2. The main processes are the oxidation of rock-derived organic carbon, and the weathering of carbonate minerals by sulfuric acid ...
... Sonesson M, Eliasson L, Matsson L. (2003) Minor salivary gland secretion in children and adults. Arch Oral Biol. 48: 535-539. Sonesson M, Wickström C, Kinnby B, Ericson D, Matsson L. (2008) Mucins MUC5B and MUC7 in minor salivary gland secretion of children and adults. Arch Oral Biol. 53: 523-527. ...
Adipocyte metabolic pathways regulated by diet control
... (Spradling 1993). GSCs and their progeny grow and divide faster on yeast-rich relative to -poor diets, ...
... (Spradling 1993). GSCs and their progeny grow and divide faster on yeast-rich relative to -poor diets, ...
Ch 8 Lecture Notes
... Sample Exercise 8.7 – Prediction the Mass of a Precipitate Barium sulfate is used to enhance Xray imaging of the upper and lower GI tract. In upper GI imaging, patients drink a suspension of solid barium sulfate in H 2O. The compound is not toxic because of its limited solubility. To make pure bari ...
... Sample Exercise 8.7 – Prediction the Mass of a Precipitate Barium sulfate is used to enhance Xray imaging of the upper and lower GI tract. In upper GI imaging, patients drink a suspension of solid barium sulfate in H 2O. The compound is not toxic because of its limited solubility. To make pure bari ...
13. Condensed azines. Quinoline. Isoquinoline. Acridine. Diazines
... and morphine. The isoquinoline ring in these natural compound derives from the aromatic amino acid tyrosine. Isoquinoline is a colourless hygroscopic liquid at room temperature with a penetrating, unpleasant odour. Impure samples can appear brownish, as is typical for nitrogen heterocycles. It cryst ...
... and morphine. The isoquinoline ring in these natural compound derives from the aromatic amino acid tyrosine. Isoquinoline is a colourless hygroscopic liquid at room temperature with a penetrating, unpleasant odour. Impure samples can appear brownish, as is typical for nitrogen heterocycles. It cryst ...
2. CYCLIC AMINOACIDS 2.1. Aromatic
... Play important roles in all biological processes Elementary composition: C 51-55%, O 21-23%, N 15-18%, H 6-7%, S 0.3-2.5% Structure - they are – high-molecular (the mass of single-chain protein is 10-50 kilodaltons (350 dal-1000 kdal); multichain protein complexes >200 kdal. – N containing organic c ...
... Play important roles in all biological processes Elementary composition: C 51-55%, O 21-23%, N 15-18%, H 6-7%, S 0.3-2.5% Structure - they are – high-molecular (the mass of single-chain protein is 10-50 kilodaltons (350 dal-1000 kdal); multichain protein complexes >200 kdal. – N containing organic c ...
T06 Fermentations 2014
... A chemostat is used to produce microbial biomass for the purpose of recombinant protein production. Lactate (CH3-CHOH-COOH) from dairy wastewater is used as the substrate. The yield coefficient of the recombinant strain is 0.3 g of cells per g of lactate degraded. When interrupting the air flow the ...
... A chemostat is used to produce microbial biomass for the purpose of recombinant protein production. Lactate (CH3-CHOH-COOH) from dairy wastewater is used as the substrate. The yield coefficient of the recombinant strain is 0.3 g of cells per g of lactate degraded. When interrupting the air flow the ...
Glossary - ChristopherKing.name
... prostaglandins that aid in digestion. Therefore, aspirin is a poor choice for pain and inflammation management for those with ulcers or other digestion problems. Recent advances in targeting specific prostaglandin-synthesizing enzymes have led to the development of Celebrex, which is marketed as an ...
... prostaglandins that aid in digestion. Therefore, aspirin is a poor choice for pain and inflammation management for those with ulcers or other digestion problems. Recent advances in targeting specific prostaglandin-synthesizing enzymes have led to the development of Celebrex, which is marketed as an ...
GraphPAC: Graph Theoretical Identification of Mutated Amino Acid
... amino acids on the very left should have no effect on the reordering position of the amino acids on the right. In order to run the clustering methodology we will describe below, 3 types of data are required. First, you need the amino acid sequence of the protein. Second, you need the protein tertiar ...
... amino acids on the very left should have no effect on the reordering position of the amino acids on the right. In order to run the clustering methodology we will describe below, 3 types of data are required. First, you need the amino acid sequence of the protein. Second, you need the protein tertiar ...
Measurement of Enzymes and Their Clinical Significance
... • IUB standardized these as international units (IU) – IU: the amount of enzyme that will convert one micromole of substrate per minute in an assay system – Expressed as units per liter or U/L – Conditions: pH, temperature, substrate,activators ...
... • IUB standardized these as international units (IU) – IU: the amount of enzyme that will convert one micromole of substrate per minute in an assay system – Expressed as units per liter or U/L – Conditions: pH, temperature, substrate,activators ...
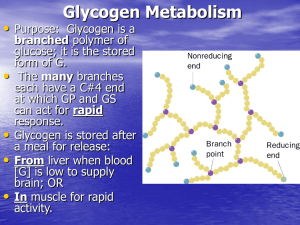
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... in this rxn, but kg is reduced to glutamate at the same time so there’s not a net AA oxidation The amino group transferred to kg (---> glu) is toxic when released as NH3, this ammonia is detoxified by conversion to urea in the urea cycle (NH3 can be excreted). Net oxidation occurs by coupling of ...
... in this rxn, but kg is reduced to glutamate at the same time so there’s not a net AA oxidation The amino group transferred to kg (---> glu) is toxic when released as NH3, this ammonia is detoxified by conversion to urea in the urea cycle (NH3 can be excreted). Net oxidation occurs by coupling of ...
Block 1 Unit 2 Objectives Bone Tissue Objectives List and describe
... 1. The three types of muscle tissue are Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth. Skeletal muscle causes movement/stature of the body. They act on bone tissue to exert a force in a direction. They are striated muscle tissue in that the myofibrils are organized and inline with one another. They are multinuclea ...
... 1. The three types of muscle tissue are Skeletal, Cardiac, and Smooth. Skeletal muscle causes movement/stature of the body. They act on bone tissue to exert a force in a direction. They are striated muscle tissue in that the myofibrils are organized and inline with one another. They are multinuclea ...
Slayt 1 - Cumhuriyet University
... • Secretion by GH, IGF-I, thyroid hormones • Chemistr S S y: Ala-Gly-Cys-Lys-Asn-Phe-Phe-Trp-Lys-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Cys A single peptide of 14 amino acids A 28-amino acid form is found in the gut ...
... • Secretion by GH, IGF-I, thyroid hormones • Chemistr S S y: Ala-Gly-Cys-Lys-Asn-Phe-Phe-Trp-Lys-Thr-Phe-Thr-Ser-Cys A single peptide of 14 amino acids A 28-amino acid form is found in the gut ...
Acid-Base Balance
... Acidosis or acidemia – arterial pH drops below 7.35 (physiological acidosis) ...
... Acidosis or acidemia – arterial pH drops below 7.35 (physiological acidosis) ...
Nucleotide
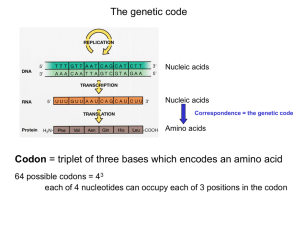
... DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides that is ultimately expressed in the form of proteins—it accomplishes such a remarkable feat via three major mechanisms: (1) DNA Replication—a process by which DNA copies or “replicas” itself, or simply produces two identical ...
... DNA carries genetic information in the form of its sequence of nucleotides that is ultimately expressed in the form of proteins—it accomplishes such a remarkable feat via three major mechanisms: (1) DNA Replication—a process by which DNA copies or “replicas” itself, or simply produces two identical ...
Metabolic flux analysis of Escherichia coli in glucose
... specific rates of glucose, ammonium and oxygen uptake and the specific carbon dioxide evolution rate increased linearly with the dilution rate up to 0?3 h”1. At dilution rates between 0?3 h”1 and 0?4 h”1, a strong deviation from the linear increase to lower specific oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide ...
... specific rates of glucose, ammonium and oxygen uptake and the specific carbon dioxide evolution rate increased linearly with the dilution rate up to 0?3 h”1. At dilution rates between 0?3 h”1 and 0?4 h”1, a strong deviation from the linear increase to lower specific oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide ...
L12 - flat - Biology Courses Server
... Energetics - ATP to AMP; equivalent to 2 ATPs to charge tRNA ...
... Energetics - ATP to AMP; equivalent to 2 ATPs to charge tRNA ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.