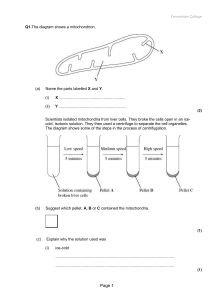
Genes & Inheritance Series: Set 3 Copyright © 2005 Version: 2.0
... This process releases energy, including heat to keep us warm. Examples include: Digestion of food: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are broken down into their constituent parts for absorption. Cellular respiration: glucose molecules are broken down to release energy (as ATP). ...
... This process releases energy, including heat to keep us warm. Examples include: Digestion of food: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are broken down into their constituent parts for absorption. Cellular respiration: glucose molecules are broken down to release energy (as ATP). ...
U4L23 starvation - The University of Sydney
... • BUT liver can do b-oxidation on FA even if there is no need for ATP – In the liver, CoA can be regenerated in a pathway other than the Krebs cycle ...
... • BUT liver can do b-oxidation on FA even if there is no need for ATP – In the liver, CoA can be regenerated in a pathway other than the Krebs cycle ...
Proteomic Mapping of Mitochondria in Living Cells
... detect this labeling (fig. S2), and HRP is inactive when expressed in the mammalian cytosol (5). We recently introduced engineered ascorbate peroxidase (APEX) as a genetic tag for electron microscopy (EM) (5). Unlike HRP, APEX is active within all cellular compartments. In addition to catalyzing the ...
... detect this labeling (fig. S2), and HRP is inactive when expressed in the mammalian cytosol (5). We recently introduced engineered ascorbate peroxidase (APEX) as a genetic tag for electron microscopy (EM) (5). Unlike HRP, APEX is active within all cellular compartments. In addition to catalyzing the ...
enzymes - Yengage
... Amino acids far away in the primary structure contribute to the formation of active site amino acids at the active sites – *serine *aspartate *histidine *cysteine *Lysine *arginine *glutamate *tyrosine ...
... Amino acids far away in the primary structure contribute to the formation of active site amino acids at the active sites – *serine *aspartate *histidine *cysteine *Lysine *arginine *glutamate *tyrosine ...
Sequence Motif Identification and Protein Family - IME-USP
... transitions associated to each context. Given a context, its associated probability transition gives the distribution of occurrence of the next symbol immediately after the context. In a PST the set of contexts has the suffix property: looking from the present to the past no context is a suffix of anoth ...
... transitions associated to each context. Given a context, its associated probability transition gives the distribution of occurrence of the next symbol immediately after the context. In a PST the set of contexts has the suffix property: looking from the present to the past no context is a suffix of anoth ...
Magnesium: Mineral Link to Energy
... and is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules (glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids). In the course of the citric acid cycle, Acetyl CoA is completely oxidized to form carbon dioxide. The first four reactions of the citric acid cycle are catalyzed by isocitrate ...
... and is the final common pathway for the oxidation of fuel molecules (glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids). In the course of the citric acid cycle, Acetyl CoA is completely oxidized to form carbon dioxide. The first four reactions of the citric acid cycle are catalyzed by isocitrate ...
Chapter 26:Biomolecules: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... Most enzymes are specific for substrates while enzymes involved in digestion such as papain attack many substrates ...
... Most enzymes are specific for substrates while enzymes involved in digestion such as papain attack many substrates ...
Brief Introduction of Patent Prosecution Issues in Biotech Field
... Claim: A nucleic acid (polypeptide) comprising a nucleotide (amino acid) sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO:1. Rejection: “comprising” lacks support because additional nucleotides (amino acids) added to any of the terminals of SEQ ID NO:1 will change the activity of the nucleic acid (polypeptide) wi ...
... Claim: A nucleic acid (polypeptide) comprising a nucleotide (amino acid) sequence as set forth in SEQ ID NO:1. Rejection: “comprising” lacks support because additional nucleotides (amino acids) added to any of the terminals of SEQ ID NO:1 will change the activity of the nucleic acid (polypeptide) wi ...
Energy Substrate Metabolism in - Journal of Clinical Investigation
... in 24 hr and 7.5% in 48 hr. By comparison with the much greater per cent decreases in the rates of oleic acid-1-'C oxidation after storage of the platelets, the small changes in specific radioactivity of the fatty acid pool were considered negligible. Changes in the specific activity of the fatty ac ...
... in 24 hr and 7.5% in 48 hr. By comparison with the much greater per cent decreases in the rates of oleic acid-1-'C oxidation after storage of the platelets, the small changes in specific radioactivity of the fatty acid pool were considered negligible. Changes in the specific activity of the fatty ac ...
RespirationQuestions.doc - KS3, GCSE and A
... is sufficient oxygen, this pyruvate is fully broken down. Name two substances formed from the pyruvate. ...
... is sufficient oxygen, this pyruvate is fully broken down. Name two substances formed from the pyruvate. ...
Isoprenoid metabolism: cholesterol and the others
... detergents work: hydrophobic molecules such as fats do not want to face aqueous environment (for entropic reasons) and therefore clump together in an attempt to minimise the surface area exposed to water. Detergents prevent that and keep hydrophobic droplets very small and dispersed. Bile acids are ...
... detergents work: hydrophobic molecules such as fats do not want to face aqueous environment (for entropic reasons) and therefore clump together in an attempt to minimise the surface area exposed to water. Detergents prevent that and keep hydrophobic droplets very small and dispersed. Bile acids are ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter 6 PowerPoint Lectures for
... 6.10 Cells use three main kinds of food molecules to make ATP • Carbohydrates - digested down into • Proteins - digested down into • Fats ...
... 6.10 Cells use three main kinds of food molecules to make ATP • Carbohydrates - digested down into • Proteins - digested down into • Fats ...
Structure of chicken calcitonin predicted by partial nucleotide
... shows important differences in its amino acid sequence. Based on structure, three groups of calcitonins can be distinguished: (i) human and murine [1,2] (Primate and Rodentia); (n) bovine, porcine and ovine [3-51 (Artiodactyls); (iii) salmon and eel [6,7] (Teleosteans). They all share in common 9 am ...
... shows important differences in its amino acid sequence. Based on structure, three groups of calcitonins can be distinguished: (i) human and murine [1,2] (Primate and Rodentia); (n) bovine, porcine and ovine [3-51 (Artiodactyls); (iii) salmon and eel [6,7] (Teleosteans). They all share in common 9 am ...
respiration in plants
... In plants the problem of definition is slightly different because 1. Breathing movements are not performed. The gaseous exchange is often marked by photosynthesis in the day time. Oxygen need not be utilised. 2. CO2 may not be released in some cases. For these reasons plant physiologists use the t ...
... In plants the problem of definition is slightly different because 1. Breathing movements are not performed. The gaseous exchange is often marked by photosynthesis in the day time. Oxygen need not be utilised. 2. CO2 may not be released in some cases. For these reasons plant physiologists use the t ...
Basic Agricultural Chemistry - Macmillan Education South Africa
... down, a molecule is the smallest particle of a substance which can exist independently and still display the properties of that substance. Some elements (such as hydrogen) consist of molecules made up of two atoms (H2), while others (such as helium) consist of molecules of single atoms (He). An atom ...
... down, a molecule is the smallest particle of a substance which can exist independently and still display the properties of that substance. Some elements (such as hydrogen) consist of molecules made up of two atoms (H2), while others (such as helium) consist of molecules of single atoms (He). An atom ...
Effect of ovarian hormones on mitochondrial enzyme activity in the
... with E2 stimulated fatty acid oxidation during prolonged exercise, whereas treatment with E2 and progesterone (Prog) in combination inhibited this oxidative effect (11). The mechanisms underlying these effects remain poorly understood; however, insight into these functional differences might be gain ...
... with E2 stimulated fatty acid oxidation during prolonged exercise, whereas treatment with E2 and progesterone (Prog) in combination inhibited this oxidative effect (11). The mechanisms underlying these effects remain poorly understood; however, insight into these functional differences might be gain ...
Relative Reactivity of Amino Acids with Chlorine
... Values of kapp are also compared in Table 1 at pH 7. Within this limited data set, proline had the slowest reaction rate with HOCl. There is also a 2-fold difference in the estimated values of the rate constants for the reaction of HOCl with glycine and alanine. In view of the small subset of amino ...
... Values of kapp are also compared in Table 1 at pH 7. Within this limited data set, proline had the slowest reaction rate with HOCl. There is also a 2-fold difference in the estimated values of the rate constants for the reaction of HOCl with glycine and alanine. In view of the small subset of amino ...
Chapter 4 - Open Science Online
... This produces immune activation by NFKB induction, oncogene activation, glutamate excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration, release of monoamines into synaptic junction and schizophrenia. The depletion of ATP can also affect the gut blood barrier producing an acute phase response and leaky gut syndrome. ...
... This produces immune activation by NFKB induction, oncogene activation, glutamate excitotoxicity and neurodegeneration, release of monoamines into synaptic junction and schizophrenia. The depletion of ATP can also affect the gut blood barrier producing an acute phase response and leaky gut syndrome. ...
Pairwise alignment
... Pairwise alignment result of human beta globin and myoglobin: the score is a sum of match, mismatch, gap creation, and gap extension scores ...
... Pairwise alignment result of human beta globin and myoglobin: the score is a sum of match, mismatch, gap creation, and gap extension scores ...
Advanced continuous cultivation methods for systems microbiology
... enabling the control of environmental parameters (e.g. temperature, pH) and substrate feeding rates (for both fluids and gases) together with culture outflow is available. The first application of such a system was the development of the chemostat continuous cultivation method 65 years ago allowing ...
... enabling the control of environmental parameters (e.g. temperature, pH) and substrate feeding rates (for both fluids and gases) together with culture outflow is available. The first application of such a system was the development of the chemostat continuous cultivation method 65 years ago allowing ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Mixture of compounds that resist pH changes • Convert strong (completely dissociated) acids or bases into weak (slightly dissociated) ones • Carbonic acid-bicarbonate system ...
... • Mixture of compounds that resist pH changes • Convert strong (completely dissociated) acids or bases into weak (slightly dissociated) ones • Carbonic acid-bicarbonate system ...
Modeling allosteric regulation of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis in
... allosteric sites distinct from the active site. Under physiological conditions, substrate concentrations near their KM facilitate the rapid adjustments of reaction rates. In some cases, there are mechanisms of homotropic cooperativity in which the affinity of interdependent catalytic sites is altered ...
... allosteric sites distinct from the active site. Under physiological conditions, substrate concentrations near their KM facilitate the rapid adjustments of reaction rates. In some cases, there are mechanisms of homotropic cooperativity in which the affinity of interdependent catalytic sites is altered ...
1 Tirmania pinoyi: chemical composition, in vitro antioxidant and
... 20% of the dry weight in desert truffles, is significantly higher than in most vegetables and other fungi and, therefore, the consumption of these truffles is recommended (Murcia et al., 2003). Desert truffles (Tirmania pinoyi, T. nivea, Terfezia claveryi, Picoa juniperi) comprise a vast unexploited ...
... 20% of the dry weight in desert truffles, is significantly higher than in most vegetables and other fungi and, therefore, the consumption of these truffles is recommended (Murcia et al., 2003). Desert truffles (Tirmania pinoyi, T. nivea, Terfezia claveryi, Picoa juniperi) comprise a vast unexploited ...
Metabolism

Metabolism (from Greek: μεταβολή metabolē, ""change"") is the set of life-sustaining chemical transformations within the cells of living organisms. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. The word metabolism can also refer to all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transport of substances into and between different cells, in which case the set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary metabolism or intermediate metabolism.Metabolism is usually divided into two categories: catabolism, the breaking down of organic matter by way of cellular respiration, and anabolism, the building up of components of cells such as proteins and nucleic acids. Usually, breaking down releases energy and building up consumes energy.The chemical reactions of metabolism are organized into metabolic pathways, in which one chemical is transformed through a series of steps into another chemical, by a sequence of enzymes. Enzymes are crucial to metabolism because they allow organisms to drive desirable reactions that require energy that will not occur by themselves, by coupling them to spontaneous reactions that release energy. Enzymes act as catalysts that allow the reactions to proceed more rapidly. Enzymes also allow the regulation of metabolic pathways in response to changes in the cell's environment or to signals from other cells.The metabolic system of a particular organism determines which substances it will find nutritious and which poisonous. For example, some prokaryotes use hydrogen sulfide as a nutrient, yet this gas is poisonous to animals. The speed of metabolism, the metabolic rate, influences how much food an organism will require, and also affects how it is able to obtain that food.A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways and components between even vastly different species. For example, the set of carboxylic acids that are best known as the intermediates in the citric acid cycle are present in all known organisms, being found in species as diverse as the unicellular bacterium Escherichia coli and huge multicellular organisms like elephants. These striking similarities in metabolic pathways are likely due to their early appearance in evolutionary history, and their retention because of their efficacy.