The Quantum Universe for Educators PHYS 597 410, Spring 2014
... Quantum theories underpin our modern world: without quantum mechanics, modern electronic devices such as computers and cell phones, most modern medical imaging and technology, most development in materials science, the World Wide Web, and many other things would not exist. It is the most accurately ...
... Quantum theories underpin our modern world: without quantum mechanics, modern electronic devices such as computers and cell phones, most modern medical imaging and technology, most development in materials science, the World Wide Web, and many other things would not exist. It is the most accurately ...
2010 midterm exam - MIT OpenCourseWare
... a) (15 points) In the following figures you can see for a given potential profile a set of eigenfunctions (left column) and a set of possible total energy values (right column) describing different scenarios of scattering for a particle incoming from the left side (here I plot the real part of the e ...
... a) (15 points) In the following figures you can see for a given potential profile a set of eigenfunctions (left column) and a set of possible total energy values (right column) describing different scenarios of scattering for a particle incoming from the left side (here I plot the real part of the e ...
slides
... I found it particularly beautiful in the presentation of the complex structure that you have left all modellmässig considerations to one side. The model-idea now finds itself in a difficult, fundamental [prinzipiellen] crisis, which I believe will end with a further radical sharpening of the opposit ...
... I found it particularly beautiful in the presentation of the complex structure that you have left all modellmässig considerations to one side. The model-idea now finds itself in a difficult, fundamental [prinzipiellen] crisis, which I believe will end with a further radical sharpening of the opposit ...
Weak measurements [1] Pre and Post selection in strong measurements
... We call the state |Ψi the ”pre-selected state” which is the state we prepare the system at and we call the state hΦ| the ”post-selected state” which is the state the system is at the end of the process. These two measurements are strong measurements. We notice that similarly to eq. (1) formalism the ...
... We call the state |Ψi the ”pre-selected state” which is the state we prepare the system at and we call the state hΦ| the ”post-selected state” which is the state the system is at the end of the process. These two measurements are strong measurements. We notice that similarly to eq. (1) formalism the ...
Concept of the Gibbsian ensemble
... Transition from classical to quantum statistics In classical mechanics a state of a system is determined by knowledge of position, q, and momentum, p. Dynamic evolution given by : trajectory in -space ...
... Transition from classical to quantum statistics In classical mechanics a state of a system is determined by knowledge of position, q, and momentum, p. Dynamic evolution given by : trajectory in -space ...
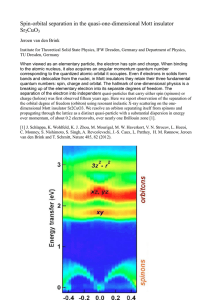
Spin-orbital separation in the quasi-one
... When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott i ...
... When viewed as an elementary particle, the electron has spin and charge. When binding to the atomic nucleus, it also acquires an angular momentum quantum number corresponding to the quantized atomic orbital it occupies. Even if electrons in solids form bands and delocalize from the nuclei, in Mott i ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... and others. This theory came to be known as quantum mechanics. In 1927, Werner Heisenberg developed his uncertainty principle, which states that you cannot know both the momentum and position of a particle at the same time with absolute certainty. The uncertainty principle gives us a limit to our kn ...
... and others. This theory came to be known as quantum mechanics. In 1927, Werner Heisenberg developed his uncertainty principle, which states that you cannot know both the momentum and position of a particle at the same time with absolute certainty. The uncertainty principle gives us a limit to our kn ...
Lecture 4
... What does that mean? There might be a deeper „classical“ theory that allows to eliminate the probabilistic predictions of quantum mechanics by referring to „hidden parameters“ The state 1/21/2 (|00i+|11i) on two spatially separated qubits exhibits „spooky actions at a distance“: when measured it beh ...
... What does that mean? There might be a deeper „classical“ theory that allows to eliminate the probabilistic predictions of quantum mechanics by referring to „hidden parameters“ The state 1/21/2 (|00i+|11i) on two spatially separated qubits exhibits „spooky actions at a distance“: when measured it beh ...
When to use Quantum Probabilities in Quantum - gaips - INESC-ID
... In quantum probability theory, events are characterized by a superposition state, which is represented by a state vector comprising the occurrence of all events. The probability of an event is given by the squared magnitude of the projection of this superposition state into the desired subspace. Thi ...
... In quantum probability theory, events are characterized by a superposition state, which is represented by a state vector comprising the occurrence of all events. The probability of an event is given by the squared magnitude of the projection of this superposition state into the desired subspace. Thi ...
poster
... • Interactive lectures on the foundations of quantum mechanics engage students in questions of classical and quantum reality: • Clicker questions stimulate student discussion, where the answers can sometimes be a matter of interpretation. • Make realist expectations explicit and help students deve ...
... • Interactive lectures on the foundations of quantum mechanics engage students in questions of classical and quantum reality: • Clicker questions stimulate student discussion, where the answers can sometimes be a matter of interpretation. • Make realist expectations explicit and help students deve ...



![Weak measurements [1] Pre and Post selection in strong measurements](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008913441_1-7a0f5f5a1778eb5da686e2de8a47882f-300x300.png)