Applied quantum mechanics 1 Applied Quantum Mechanics
... (d) Show that E kinetic = – E potential 2 (which is a result predicted by the virial theorem). (e) Show that the peak in radial probability occurs at r = a B Z . (f) Show that the expectation value r = 3a B 2Z . (g) Show that the expectation value of momentum p = 0 . Problem 11.3 T ...
... (d) Show that E kinetic = – E potential 2 (which is a result predicted by the virial theorem). (e) Show that the peak in radial probability occurs at r = a B Z . (f) Show that the expectation value r = 3a B 2Z . (g) Show that the expectation value of momentum p = 0 . Problem 11.3 T ...
Quantum gravity and consciousness, the most
... explained. The next related problem is a philosophical explanation of imagination of location [7, Sec. 6]. Therefore, because all processes in brain are located to the cell level, it should be found what causes “free will”. An alternative question is: “What is a difference between a philosophical zo ...
... explained. The next related problem is a philosophical explanation of imagination of location [7, Sec. 6]. Therefore, because all processes in brain are located to the cell level, it should be found what causes “free will”. An alternative question is: “What is a difference between a philosophical zo ...
Observable1 The term observable has become the - Philsci
... possibilities of assigning definite values to observables and to the possibilities of measurements in the quantum world. Indeed, observables A, B that do not commute do not share a complete system of eigenvectors, so that typically an eigenstate of (say) A will be a superposition of eigenstates of B ...
... possibilities of assigning definite values to observables and to the possibilities of measurements in the quantum world. Indeed, observables A, B that do not commute do not share a complete system of eigenvectors, so that typically an eigenstate of (say) A will be a superposition of eigenstates of B ...
1. Calculate the partition function of the hydrogen atom at room
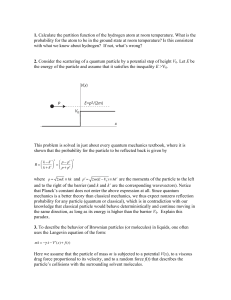
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
Quantum Information and Randomness - Max-Planck
... ontological questions such as ‘What is?’, Bohr may be interpreted as limiting physics to answering epistemological questions such as ‘What can be said?’ In 1935, Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen (EPR) published the seminal article5 ‘Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be ...
... ontological questions such as ‘What is?’, Bohr may be interpreted as limiting physics to answering epistemological questions such as ‘What can be said?’ In 1935, Einstein, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen (EPR) published the seminal article5 ‘Can quantum-mechanical description of physical reality be ...
Spin polarized transport in semiconductors – Challenges for
... Propagating surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are well-known to have both a subwavelength light confinement and long propagation lengths [1]. For this reason, their interaction with quantum emitters (QEs) has attracted great interest recently. The emergence of Strong Coupling (SC) when an ensemble o ...
... Propagating surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) are well-known to have both a subwavelength light confinement and long propagation lengths [1]. For this reason, their interaction with quantum emitters (QEs) has attracted great interest recently. The emergence of Strong Coupling (SC) when an ensemble o ...
A quantum thermal machine
... the coupling to the machine M. We can think of the time dependent Hamiltonian for the system as describing the system upon which the machine does work, periodically raising and lowering the energy difference between the two states. If the system starts in state |0> it remains there unless the therma ...
... the coupling to the machine M. We can think of the time dependent Hamiltonian for the system as describing the system upon which the machine does work, periodically raising and lowering the energy difference between the two states. If the system starts in state |0> it remains there unless the therma ...
Simulation of Quantum Computation with Wolfram
... Quantum computation and quantum information is a rapidly developing research area of modern science and technology. Quantum computers are to be able to perform certain computational tasks much more efficiently than classical computers. At the same time a realistic quantum computer is still not availab ...
... Quantum computation and quantum information is a rapidly developing research area of modern science and technology. Quantum computers are to be able to perform certain computational tasks much more efficiently than classical computers. At the same time a realistic quantum computer is still not availab ...
Non-linear gates enabling universal quantum computation
... much more efficient way than their classical counterpart. By harnessing the computational power of the quantum world, we can build quantum computers which store and process information at an unparalleled level [1, 2]. Among the various quantum systems available in Nature, quantum modes (infinite-dim ...
... much more efficient way than their classical counterpart. By harnessing the computational power of the quantum world, we can build quantum computers which store and process information at an unparalleled level [1, 2]. Among the various quantum systems available in Nature, quantum modes (infinite-dim ...