Quantum Correlations
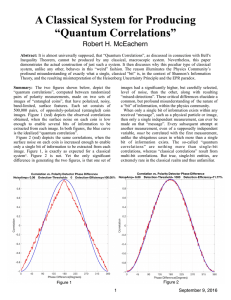
... information content of the measurements, results in the Classical Correlation curve reproducing the “Quantum Correlation” curve. ...
... information content of the measurements, results in the Classical Correlation curve reproducing the “Quantum Correlation” curve. ...
topics in atomic physics - University of Missouri
... pure Coulomb and Newtonian potentials, and thus hydrogen atoms and Keplerian orbits. We have therefore devoted a large portion of this book to the hydrogen atom in order to emphasize this distinctiveness. We attempt to stress the uniqueness of the attractive 1/r potential without delving into group ...
... pure Coulomb and Newtonian potentials, and thus hydrogen atoms and Keplerian orbits. We have therefore devoted a large portion of this book to the hydrogen atom in order to emphasize this distinctiveness. We attempt to stress the uniqueness of the attractive 1/r potential without delving into group ...
Electro-magnetic radiation (light)
... The problem with quantum mechanics • It s not hard to solve equations for the various wavefunctions if they are all alone (like H) • The problem is what happens in the presence of other electrons • The electron interaction problem • Electron interaction so complex, exact solutions are only poss ...
... The problem with quantum mechanics • It s not hard to solve equations for the various wavefunctions if they are all alone (like H) • The problem is what happens in the presence of other electrons • The electron interaction problem • Electron interaction so complex, exact solutions are only poss ...
\chapter{Introduction}
... To write a thesis on the vacuum is, from a naive point of view, to write a thesis on nothing at all. Classically one could define the vacuum as a box containing no matter or particles whatsoever or, more rigorously, a subspace $V$ of the $\mathbb{R}^3$ such that $N(V)=0$, where $N$ denotes the numbe ...
... To write a thesis on the vacuum is, from a naive point of view, to write a thesis on nothing at all. Classically one could define the vacuum as a box containing no matter or particles whatsoever or, more rigorously, a subspace $V$ of the $\mathbb{R}^3$ such that $N(V)=0$, where $N$ denotes the numbe ...
Chapter 41. One-Dimensional Quantum Mechanics
... state’ problems where the particle is trapped (localized in space), problems where the particle is trapped (localized in space) the energies will be found to be quantized upon solving the Schrodinger equation. In ‘unbound states’ where the particle is not trapped, the particle will travel as a tr ...
... state’ problems where the particle is trapped (localized in space), problems where the particle is trapped (localized in space) the energies will be found to be quantized upon solving the Schrodinger equation. In ‘unbound states’ where the particle is not trapped, the particle will travel as a tr ...
Here
... Entanglement: This is a strange state of being in which two particles are so deeply connected that they share the same existence, even when light years apart. Indeed, distance has no meaning for entangled particles. If the state of one is changed, the state of the other is instantly adjusted to be c ...
... Entanglement: This is a strange state of being in which two particles are so deeply connected that they share the same existence, even when light years apart. Indeed, distance has no meaning for entangled particles. If the state of one is changed, the state of the other is instantly adjusted to be c ...