The One-Dimensional Finite-Difference Time
... are far too complicated to ever solve by hand. Therefore, it is desirable to enlist the aid of computers when searching for solutions to quantum systems. One of the more common methods for numerically solving a time-dependent partial differential equation (PDE) is the finite-difference time-domain a ...
... are far too complicated to ever solve by hand. Therefore, it is desirable to enlist the aid of computers when searching for solutions to quantum systems. One of the more common methods for numerically solving a time-dependent partial differential equation (PDE) is the finite-difference time-domain a ...
Where is Fundamental Physics Heading?
... Qualitative question: explain the overall scales. • In particle physics: – Why is the scale of particle physics, so much longer than the Planck length (a factor of 1016)? • In cosmology: – Why is the observable Universe so much larger than the Planck length (a factor of 1060)? – Equivalently, why is ...
... Qualitative question: explain the overall scales. • In particle physics: – Why is the scale of particle physics, so much longer than the Planck length (a factor of 1016)? • In cosmology: – Why is the observable Universe so much larger than the Planck length (a factor of 1060)? – Equivalently, why is ...
Energy: A Physicist`s View - University of Colorado Boulder
... quarks and electrons as compose a rock or a river. ...
... quarks and electrons as compose a rock or a river. ...
the problem book
... Consider a rotating heteronuclear diatomic molecule constrained to move only in a plane (two dimensions). Assume that the molecule does not undergo translational motion. Indeed, it only has rotational kinetic energy about its center of mass. The quantized energy levels of a diatomic molecule in two ...
... Consider a rotating heteronuclear diatomic molecule constrained to move only in a plane (two dimensions). Assume that the molecule does not undergo translational motion. Indeed, it only has rotational kinetic energy about its center of mass. The quantized energy levels of a diatomic molecule in two ...
PH4025 - Physics of Electronic Devices
... Overview Materials with electronic band gap of up to ~3 eV, and resistivity ranging from 10-3 to 10-9 /cm, are known as semiconductors. Their electronic properties are strongly temperature dependent, and may be manipulated through the controlled addition of dopants. Through an understanding of the ...
... Overview Materials with electronic band gap of up to ~3 eV, and resistivity ranging from 10-3 to 10-9 /cm, are known as semiconductors. Their electronic properties are strongly temperature dependent, and may be manipulated through the controlled addition of dopants. Through an understanding of the ...
Chapter 6 and 7 Reading Guide Electronic Structure of Atoms and
... What is the shape of an s orbital? What is the difference between a 1s, 2s or 3s orbital? ...
... What is the shape of an s orbital? What is the difference between a 1s, 2s or 3s orbital? ...
Modeling Single Electron Transistor Sensitivity for Read
... Fermi Level of Source is lower then first unoccupied level of dot ...
... Fermi Level of Source is lower then first unoccupied level of dot ...
16 Sep 2012
... fields. Fields are all there is. Quantum physics, discovered last century, tells us these fields are "quantized." This means that every field comes in indivisible bundles or packets, called "quanta" (the plural of "quantum"), with each quantum carrying a certain amount of energy (energy just means t ...
... fields. Fields are all there is. Quantum physics, discovered last century, tells us these fields are "quantized." This means that every field comes in indivisible bundles or packets, called "quanta" (the plural of "quantum"), with each quantum carrying a certain amount of energy (energy just means t ...
Ambiguous model learning made unambiguous with 1/f priors
... The estimation of a model underlying the production of noisy data becomes highly nontrivial when there exists more than one equally plausible model that could be responsible for the output data. The viewing of ambiguous figures, such as the Necker cube [1], is a classical problem of this type in the ...
... The estimation of a model underlying the production of noisy data becomes highly nontrivial when there exists more than one equally plausible model that could be responsible for the output data. The viewing of ambiguous figures, such as the Necker cube [1], is a classical problem of this type in the ...
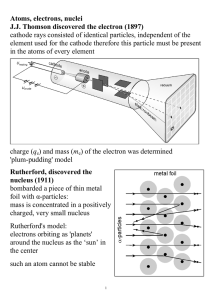
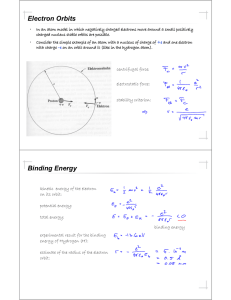
Electron Orbits
... Comment of Franck on their Experiment "It might interest you to know that when we made the experiments that we did not know Bohr's theory. We had neither read nor heard about it. We had not read it because we were negligent to read the literature well enough -- and you know how that happens. On the ...
... Comment of Franck on their Experiment "It might interest you to know that when we made the experiments that we did not know Bohr's theory. We had neither read nor heard about it. We had not read it because we were negligent to read the literature well enough -- and you know how that happens. On the ...
Undergraduate physical chemistry final examination topics 1
... 7. Chemical equilibrium in reactive systems. Equilibrium constant and related standard quantities of reactions. Temperature- and pressure dependence of the equilibrium constant. Calculation of the equilibrium constant on a canonical ensemble. 8. Transport phenomena. The general linear transport equa ...
... 7. Chemical equilibrium in reactive systems. Equilibrium constant and related standard quantities of reactions. Temperature- and pressure dependence of the equilibrium constant. Calculation of the equilibrium constant on a canonical ensemble. 8. Transport phenomena. The general linear transport equa ...
Optical Properties of Finite Systems: From Small Clusters to Million-Atom Nanostructures
... the system, have made semiconductor clusters promising materials for the development of new electronic and optical devices such as light emitting diodes and solar cells. In this talk we will present calculations of the optical properties of different systems ranging from small molecules to ~106 atom ...
... the system, have made semiconductor clusters promising materials for the development of new electronic and optical devices such as light emitting diodes and solar cells. In this talk we will present calculations of the optical properties of different systems ranging from small molecules to ~106 atom ...
Photoresponse of the GaAs/AlGaAs core
... Stationary and time-depended processes. I. I. Gerasimov In this work we research a photoresponse of the n-type GaAs/AlGaAs core-shell quantum wire array, grown by the vapor-liquid-crystal mechanism on p-type silicon substrate. Photovoltaic and photoconductivity spectra and temporal characteristics o ...
... Stationary and time-depended processes. I. I. Gerasimov In this work we research a photoresponse of the n-type GaAs/AlGaAs core-shell quantum wire array, grown by the vapor-liquid-crystal mechanism on p-type silicon substrate. Photovoltaic and photoconductivity spectra and temporal characteristics o ...
The Postulates of Quantum Mechanics
... Postulate IV (Precise measurements: eigenvalues/eigenfunctions) If Ψb is an eigenfunction of the operator Bˆ with eigenvalue b, then if we make a measurement of the physical observable represented by Bˆ for a system whose wavefunction is Ψb , we always obtain b as the result. Postulate V (Imprecise ...
... Postulate IV (Precise measurements: eigenvalues/eigenfunctions) If Ψb is an eigenfunction of the operator Bˆ with eigenvalue b, then if we make a measurement of the physical observable represented by Bˆ for a system whose wavefunction is Ψb , we always obtain b as the result. Postulate V (Imprecise ...
The world of Atoms - University of California, Irvine
... Theory that describes the physical properties of smallest particles (atoms, protons, electrons, photons) Max Planck "A scientific truth does not triumph by convincing its opponents and making them see the light, but rather because its opponents eventually die and a new generation grows up that is fa ...
... Theory that describes the physical properties of smallest particles (atoms, protons, electrons, photons) Max Planck "A scientific truth does not triumph by convincing its opponents and making them see the light, but rather because its opponents eventually die and a new generation grows up that is fa ...
Is There Room for God in the Cosmos?
... • Old goal of physics: explain it uniquely. • But the math hints that values of nature‟s fundamental constants are Plug & Play. • The “Standard Model” of particle physics has 19 settable parameters, one of mass (squared) and 18 dimensionless. • String Theory was purposed to explain them (and to marr ...
... • Old goal of physics: explain it uniquely. • But the math hints that values of nature‟s fundamental constants are Plug & Play. • The “Standard Model” of particle physics has 19 settable parameters, one of mass (squared) and 18 dimensionless. • String Theory was purposed to explain them (and to marr ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.