ECE692_1_1008
... The daunting task of solid state physics • Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation • The equations are only analytically solvable for a handful of special cases • One cannot solve the equations for more than two bodies! • Solid-state physics is about many-body problems There are 5 × 1022 ...
... The daunting task of solid state physics • Quantum mechanics gives us the fundamental equation • The equations are only analytically solvable for a handful of special cases • One cannot solve the equations for more than two bodies! • Solid-state physics is about many-body problems There are 5 × 1022 ...
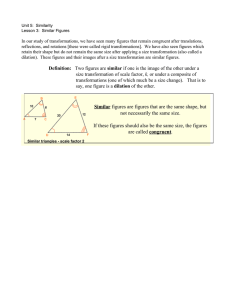
See 8.5 Transformations
... If we find that our data don't look very normal, we have a few options. 1) Use a different distribution. For example, Weibull distributions are often used to model lifetimes of machines. 2) There are "nonparametric methods" that don't rely on any assumption about the underlying distribution. These m ...
... If we find that our data don't look very normal, we have a few options. 1) Use a different distribution. For example, Weibull distributions are often used to model lifetimes of machines. 2) There are "nonparametric methods" that don't rely on any assumption about the underlying distribution. These m ...
An introduction to the concept of symmetry - Pierre
... Laws of physics would be the same if they were running backward in time Charge conjugation (C-Symmetry) Same laws of physics for particle and antiparticles Gauge transformation Laws of physics are invariant under changes of redundant degrees of freedom E.g.: Rising the voltage uniformly ...
... Laws of physics would be the same if they were running backward in time Charge conjugation (C-Symmetry) Same laws of physics for particle and antiparticles Gauge transformation Laws of physics are invariant under changes of redundant degrees of freedom E.g.: Rising the voltage uniformly ...
Atomic Term Symbols and Energy Splitting
... The term symbols determined for the ground and excited states of sodium can be used to label the transitions responsible for the sodium D-line emission, as shown in Figure 2. ...
... The term symbols determined for the ground and excited states of sodium can be used to label the transitions responsible for the sodium D-line emission, as shown in Figure 2. ...
URL - StealthSkater
... Still more details about M-matrix (06/18/2008) What goes wrong with string theories? (06/14/2008) Could a symplectic analog of conformal field theory be relevant for Quantum-TGD? (03/16/2008) Infinite primes and algebraic Brahman=Atman identity (07/05/2008) Configuration space gamma matrices as hyp ...
... Still more details about M-matrix (06/18/2008) What goes wrong with string theories? (06/14/2008) Could a symplectic analog of conformal field theory be relevant for Quantum-TGD? (03/16/2008) Infinite primes and algebraic Brahman=Atman identity (07/05/2008) Configuration space gamma matrices as hyp ...
NMR Studies on Magnetization Plateaus in Dimer Spin Systems
... A rich variety of quantum phase transitions can be induced in simple dimer-singlet spin systems by applying magnetic field strong enough to suppress the energy gap to triplet excitations. While the field-induced triplet bosons generally undergo Bose condensation, resulting in an antiferromagnetic or ...
... A rich variety of quantum phase transitions can be induced in simple dimer-singlet spin systems by applying magnetic field strong enough to suppress the energy gap to triplet excitations. While the field-induced triplet bosons generally undergo Bose condensation, resulting in an antiferromagnetic or ...
Generalising Unitary Time Evolution
... It is clear that something is to be gained from applying the quantum formalism to the description of systems not generally considered physical [1, 4, 14, 16, 23]. However, despite this initial promise, there are many elements of quantum theory that have yet to be properly applied within this framewo ...
... It is clear that something is to be gained from applying the quantum formalism to the description of systems not generally considered physical [1, 4, 14, 16, 23]. However, despite this initial promise, there are many elements of quantum theory that have yet to be properly applied within this framewo ...
Gravity and Quantum Mechanics
... infinite rate of scattering. The correct theory must cure this, but it is a very difficult problem. It turns out that one can fix it if particles are not points but strings, Planck energy ...
... infinite rate of scattering. The correct theory must cure this, but it is a very difficult problem. It turns out that one can fix it if particles are not points but strings, Planck energy ...
COMPLEXITY OF QUANTUM FIELD THEORIES 1. Introduction
... may attempt to study a quantum field theory. The one typically taught in QFT classes is that of perturbation theory, in which one considers a theory in which particles are essentially free; more precisely, they interact with each other only via weak interactions. This method has had tremendous succe ...
... may attempt to study a quantum field theory. The one typically taught in QFT classes is that of perturbation theory, in which one considers a theory in which particles are essentially free; more precisely, they interact with each other only via weak interactions. This method has had tremendous succe ...
January 2005
... Find µ(T, N ) for low temperatures kB T ~ω0 , including the leading behavior for non-zero temperatures. (Hint: finad an exact expression for µ(T, N0 ) at all temperatures and substitute the value of N0 (T, N ) in the temperature range of interest.) ...
... Find µ(T, N ) for low temperatures kB T ~ω0 , including the leading behavior for non-zero temperatures. (Hint: finad an exact expression for µ(T, N0 ) at all temperatures and substitute the value of N0 (T, N ) in the temperature range of interest.) ...
presentation source
... Relation between observations / experiences? Does it tell us what exists? What is a ‘system’? We agree that – cannot use naive models of particles or waves – assuming a ‘material world’ leads to problems, if ‘material’ means ‘solid’ or ‘fluid’ ...
... Relation between observations / experiences? Does it tell us what exists? What is a ‘system’? We agree that – cannot use naive models of particles or waves – assuming a ‘material world’ leads to problems, if ‘material’ means ‘solid’ or ‘fluid’ ...
Renormalization group

In theoretical physics, the renormalization group (RG) refers to a mathematical apparatus that allows systematic investigation of the changes of a physical system as viewed at different distance scales. In particle physics, it reflects the changes in the underlying force laws (codified in a quantum field theory) as the energy scale at which physical processes occur varies, energy/momentum and resolution distance scales being effectively conjugate under the uncertainty principle (cf. Compton wavelength).A change in scale is called a ""scale transformation"". The renormalization group is intimately related to ""scale invariance"" and ""conformal invariance"", symmetries in which a system appears the same at all scales (so-called self-similarity). (However, note that scale transformations are included in conformal transformations, in general: the latter including additional symmetry generators associated with special conformal transformations.)As the scale varies, it is as if one is changing the magnifying power of a notional microscope viewing the system. In so-called renormalizable theories, the system at one scale will generally be seen to consist of self-similar copies of itself when viewed at a smaller scale, with different parameters describing the components of the system. The components, or fundamental variables, may relate to atoms, elementary particles, atomic spins, etc. The parameters of the theory typically describe the interactions of the components. These may be variable ""couplings"" which measure the strength of various forces, or mass parameters themselves. The components themselves may appear to be composed of more of the self-same components as one goes to shorter distances.For example, in quantum electrodynamics (QED), an electron appears to be composed of electrons, positrons (anti-electrons) and photons, as one views it at higher resolution, at very short distances. The electron at such short distances has a slightly different electric charge than does the ""dressed electron"" seen at large distances, and this change, or ""running,"" in the value of the electric charge is determined by the renormalization group equation.