What is a Gene? - GAURAV KUMAR PAL
... in cis and trans heterozygote, we can find if mutant alleles are present in same or two different genes. ...
... in cis and trans heterozygote, we can find if mutant alleles are present in same or two different genes. ...
Objectives 9 - U
... Biological fitness is a way of taking into account both survival to reproduction and reproduction itself to evaluate genotypes relative to one another with respect to transmitting genes to the next generation. Selection is complimentary to the fitness value (selection coefficient = s = 1 – f), and m ...
... Biological fitness is a way of taking into account both survival to reproduction and reproduction itself to evaluate genotypes relative to one another with respect to transmitting genes to the next generation. Selection is complimentary to the fitness value (selection coefficient = s = 1 – f), and m ...
Mutation and Genetic Variation - Cal State LA
... Anderssen et al. (1998) published the following model in Science to explain the observations of Cairns: (1) lac- frameshift mutation still produces 1% of b-gal enzyme encoded by wildtype lac+ allele (2) Cairns’ expt was done with the lac- mutation on a plasmid, which could increase the odds of gene ...
... Anderssen et al. (1998) published the following model in Science to explain the observations of Cairns: (1) lac- frameshift mutation still produces 1% of b-gal enzyme encoded by wildtype lac+ allele (2) Cairns’ expt was done with the lac- mutation on a plasmid, which could increase the odds of gene ...
Topic 4 Wearing Your Genes Genetics
... 3) Complete the Analyze questions (Pg. 41 #1, 4 & 6) on a separate sheet of paper, and attach it to you punnet square sheet. 4) Hand in when finished... Or complete for homework. ...
... 3) Complete the Analyze questions (Pg. 41 #1, 4 & 6) on a separate sheet of paper, and attach it to you punnet square sheet. 4) Hand in when finished... Or complete for homework. ...
Chapter 2 - Single–gene inheritance
... contained in the genetic make-up of an individual Genotype - the genetic make-up, latent or expressed. The sum of all genes present in an individual. P1 - the parental lines F1 - the first filial generation, the offspring resulting from a cross. F2/ F3 the second and third generations. ...
... contained in the genetic make-up of an individual Genotype - the genetic make-up, latent or expressed. The sum of all genes present in an individual. P1 - the parental lines F1 - the first filial generation, the offspring resulting from a cross. F2/ F3 the second and third generations. ...
1. Inheritance-general
... In different position in Neanderthal than in H. sapiens But: skin color is determined by multiple genes ...
... In different position in Neanderthal than in H. sapiens But: skin color is determined by multiple genes ...
/+ +/+ +/+ +/+ a +/ b - Molecular and Cell Biology
... p547: Fig. 15.5 (Penicillin) enrichment selection ...
... p547: Fig. 15.5 (Penicillin) enrichment selection ...
Document
... addition, translocations may move the duplicated genes to other chromosomes, so that the members of the gene family may be dispersed among several different chromosomes. Eventually, each member of a gene family will accumulate mutations, which may subtly alter their function. All the members of the ...
... addition, translocations may move the duplicated genes to other chromosomes, so that the members of the gene family may be dispersed among several different chromosomes. Eventually, each member of a gene family will accumulate mutations, which may subtly alter their function. All the members of the ...
Population Genetics The study of distribution of genes in
... • New hereditary variations arise by mutation, and the new gene is called a mutant. • The spontaneous mutation rate (u) varies for different loci: (u = n/2 N) (n = no. of cases with mutent gene / N = Total No. of births) Who have normal parents • The rate is easier to measure in dominant genes. Domi ...
... • New hereditary variations arise by mutation, and the new gene is called a mutant. • The spontaneous mutation rate (u) varies for different loci: (u = n/2 N) (n = no. of cases with mutent gene / N = Total No. of births) Who have normal parents • The rate is easier to measure in dominant genes. Domi ...
slides
... • Evolutionary computation (e.g., genetic algorithms) • Immune-system-inspired computer/network security • Ant-colony optimization • Swarm intelligence (e.g., decentralized robots) • Molecular (DNA) computation ...
... • Evolutionary computation (e.g., genetic algorithms) • Immune-system-inspired computer/network security • Ant-colony optimization • Swarm intelligence (e.g., decentralized robots) • Molecular (DNA) computation ...
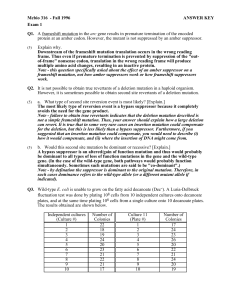
Mcbio 316 - Fall 1996 ANSWER KEY Exam 1 Q1. A frameshift
... screen or enrichment for mutants either. d. Why are there no colonies growing close to the mutagen in the figure? [Explain the reason.] High doses of mutagens are lethal because they may cause mutations in essential genes and because they often damage other cellular macromolecules as well as DNA. e. ...
... screen or enrichment for mutants either. d. Why are there no colonies growing close to the mutagen in the figure? [Explain the reason.] High doses of mutagens are lethal because they may cause mutations in essential genes and because they often damage other cellular macromolecules as well as DNA. e. ...
Scotland - Ovarian Cancer Action
... My maternal/paternal (select one) father/brother /uncle/grandfather/ (select one) was diagnosed with/breast cancer aged (insert age). There is a possibility that they carried a BRCA1/2 gene mutation, and if they did, there is a strong possibility that the gene will have been passed onto me. While th ...
... My maternal/paternal (select one) father/brother /uncle/grandfather/ (select one) was diagnosed with/breast cancer aged (insert age). There is a possibility that they carried a BRCA1/2 gene mutation, and if they did, there is a strong possibility that the gene will have been passed onto me. While th ...
Further Clarification of GENE LINKAGE When you did Gamete
... gametes formed during meiosis. These two possibilities are equally likely to form. ...
... gametes formed during meiosis. These two possibilities are equally likely to form. ...
AP Psychology - Coshocton High School
... • Homozygous – Possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent (both) / individuals express that phenotypic characteristic • Heterozygous – Possessing two different forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent (aka hybrid) • Dominant gene – gene expr ...
... • Homozygous – Possessing two identical forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent (both) / individuals express that phenotypic characteristic • Heterozygous – Possessing two different forms of a particular gene, one inherited from each parent (aka hybrid) • Dominant gene – gene expr ...
I Lecture and part of II lecture
... followed by a decimal point and a unique 4-digit variant number. For example, allelic variants in the factor IX gene (300746) are numbered 300746.0001 through 300746.0101. ...
... followed by a decimal point and a unique 4-digit variant number. For example, allelic variants in the factor IX gene (300746) are numbered 300746.0001 through 300746.0101. ...
Genetics Unit Test Review
... Genetics Unit Test Review Define the following terms by using your standard’s packet. If you cannot find your packet, there are plenty of extras in the extras tray on the front table. These are in order by standard 1. meiosis ...
... Genetics Unit Test Review Define the following terms by using your standard’s packet. If you cannot find your packet, there are plenty of extras in the extras tray on the front table. These are in order by standard 1. meiosis ...
Epistasis

Epistasis is a phenomenon that consists of the effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes' (genetic background). Similarly, epistatic mutations have different effects in combination than individually. It was originally a concept from genetics but is now used in biochemistry, population genetics, computational biology and evolutionary biology. It arises due to interactions, either between genes, or within them leading to non-additive effects. Epistasis has a large influence on the shape of evolutionary landscapes which leads to profound consequences for evolution and evolvability of traits.