Chapter 21: The Genetic Basis of Development
... in many diverse organisms is called a a. homeobox (431) 12. The gene ced-9 codes for a protein that inactivates the proteins of suicide genes found in the genome of C. elegans. For development to proceed normally, the ced-9 genes b. should be activated in all cells, but its product will be inactivat ...
... in many diverse organisms is called a a. homeobox (431) 12. The gene ced-9 codes for a protein that inactivates the proteins of suicide genes found in the genome of C. elegans. For development to proceed normally, the ced-9 genes b. should be activated in all cells, but its product will be inactivat ...
Identification of func
... With ~10 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occurring at >1% in humans, identifying the functionally important SNP can be likened to “finding a needle in a haystack”. It is thus not practical to investigate every SNP for their functionality or disease/drug response association. Our appro ...
... With ~10 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occurring at >1% in humans, identifying the functionally important SNP can be likened to “finding a needle in a haystack”. It is thus not practical to investigate every SNP for their functionality or disease/drug response association. Our appro ...
Evidence of Evolution by Natural Selection
... Living organisms are highly similar at the __________ level, suggesting that they have descended from a common ancestor, which carried the information to make these molecules. ...
... Living organisms are highly similar at the __________ level, suggesting that they have descended from a common ancestor, which carried the information to make these molecules. ...
Drosophila - mccombsscience
... Reddish-orange eyes and miniature wings almost always inherited together Observed this trend in many genes Grouped all the fly’s genes into four linkage groups Drosophila has four linkage groups and four pairs of chromosomes ...
... Reddish-orange eyes and miniature wings almost always inherited together Observed this trend in many genes Grouped all the fly’s genes into four linkage groups Drosophila has four linkage groups and four pairs of chromosomes ...
You and Your Genes Revision Lesson 1
... • Sex cells (sperm or egg) contain only 23 chromosomes. Every egg has an X, half of sperm have X, half Y. The Y chromosome has the instructions to make a male. • At fertilisation, if a Y sperm fertilises an egg, a male will develop. If an X sperm fertilises an egg a female will develop. ...
... • Sex cells (sperm or egg) contain only 23 chromosomes. Every egg has an X, half of sperm have X, half Y. The Y chromosome has the instructions to make a male. • At fertilisation, if a Y sperm fertilises an egg, a male will develop. If an X sperm fertilises an egg a female will develop. ...
Further Clarification of GENE LINKAGE When you did Gamete
... gametes formed during meiosis. These two possibilities are equally likely to form. ...
... gametes formed during meiosis. These two possibilities are equally likely to form. ...
How are we different? …at the RNA level.
... – HIV susceptibility, epithelial neoplasms (cancers), malaria, and Alzheimers, ...
... – HIV susceptibility, epithelial neoplasms (cancers), malaria, and Alzheimers, ...
Human Genetics
... Gene expression refers to whether a gene is turned on or off from being transcribed and translated into protein Tracking gene expression can reveal new information about diseases and show how diseases are related to each other ...
... Gene expression refers to whether a gene is turned on or off from being transcribed and translated into protein Tracking gene expression can reveal new information about diseases and show how diseases are related to each other ...
Clone
... from one organism to another, even if they are members of different species. Genetically modified organism (GMO): organism that has had genes transferred to it from another organism *also called transgenic organisms Genetic modification: process of transferring genes from one organism to another ex. ...
... from one organism to another, even if they are members of different species. Genetically modified organism (GMO): organism that has had genes transferred to it from another organism *also called transgenic organisms Genetic modification: process of transferring genes from one organism to another ex. ...
Cross over frequency and gene mapping Notes
... Crossing over – homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I, they may exchange pieces of chromosome Linked genes do not always stay together in gamete formation Crossing over results in new combinations of genes Crossing over occurs during meiosis and cause linked genes to separate. ...
... Crossing over – homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I, they may exchange pieces of chromosome Linked genes do not always stay together in gamete formation Crossing over results in new combinations of genes Crossing over occurs during meiosis and cause linked genes to separate. ...
epigenome
... genes allows cells to use the same genetic code in different ways. Fun fact: only 10-20% of genes are active in a differentiated cell ...
... genes allows cells to use the same genetic code in different ways. Fun fact: only 10-20% of genes are active in a differentiated cell ...
Genetics
... • Genotype: genetic make up of a trait; gene pair (2 letters that represent genes) • You receive 1 gene from each parent for a total of two genes per trait Ex: AA Bb tt ...
... • Genotype: genetic make up of a trait; gene pair (2 letters that represent genes) • You receive 1 gene from each parent for a total of two genes per trait Ex: AA Bb tt ...
Identifying essential genes in M. tuberculosis by random
... • Viable insertion within a gene gene is not essential • Essential genes: we will never see a viable insertion • Complication: Insertions in the very distal portion of an essential gene may not be sufficiently disruptive. Thus, we omit from consideration insertion sites within the last 20% and las ...
... • Viable insertion within a gene gene is not essential • Essential genes: we will never see a viable insertion • Complication: Insertions in the very distal portion of an essential gene may not be sufficiently disruptive. Thus, we omit from consideration insertion sites within the last 20% and las ...
Lecture 2
... The developing knowledge of genetics has led to much refinement of old ideas of Darwinian evolution and has also led to a number of entirely new insights into the evolutionary process. A key question for evolutionary biologists is: At what level does natural selection act? That is, does selection wo ...
... The developing knowledge of genetics has led to much refinement of old ideas of Darwinian evolution and has also led to a number of entirely new insights into the evolutionary process. A key question for evolutionary biologists is: At what level does natural selection act? That is, does selection wo ...
Genetic selection and variation
... Genes A gene can be described as a linear piece of DNA that includes a regulatory sequence that determines when the gene will be transcribed: An initiation sequence; Exons that are the coding region; Introns that are non coding regions and are spliced out of the gene during transcription; ...
... Genes A gene can be described as a linear piece of DNA that includes a regulatory sequence that determines when the gene will be transcribed: An initiation sequence; Exons that are the coding region; Introns that are non coding regions and are spliced out of the gene during transcription; ...
Molecular biology
... and their vital processes in living organisms • Genetics – study of the effect of genetic differences in organisms • Molecular biology – study of molecular emphasizing the process of replication, transcription and translation of genetic material ...
... and their vital processes in living organisms • Genetics – study of the effect of genetic differences in organisms • Molecular biology – study of molecular emphasizing the process of replication, transcription and translation of genetic material ...
epigenomics - IES Valldemossa
... Epigenetic treatment of mental illness is just around the corner. ...
... Epigenetic treatment of mental illness is just around the corner. ...
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
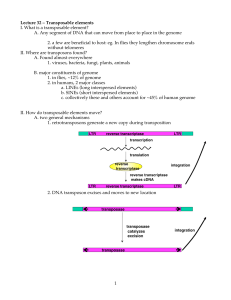
... A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome ...
... A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome ...
3. fused spleen and tumor cells.
... 3. fused spleen and tumor cells. 5. The existence of more than one form of a genetic trait. 8. An enzyme found in high concentrations in semen. 9. The liquid that separates from the blood when a clot is formed. 11. The absence of sperm. 13. The basic unit of heredity, consisting of a DNA segment loc ...
... 3. fused spleen and tumor cells. 5. The existence of more than one form of a genetic trait. 8. An enzyme found in high concentrations in semen. 9. The liquid that separates from the blood when a clot is formed. 11. The absence of sperm. 13. The basic unit of heredity, consisting of a DNA segment loc ...
TALK
... The Sargasso Sea SAR11 metagenome was substantially similar to the genomes from the two coastal isolates in conserved, core regions of the genome, but differed markedly in islands of genomic variability, and at the sites of gene indels. ...
... The Sargasso Sea SAR11 metagenome was substantially similar to the genomes from the two coastal isolates in conserved, core regions of the genome, but differed markedly in islands of genomic variability, and at the sites of gene indels. ...
Molecular Markers - Personal Web Pages
... reproducible positions, so the bands are another level of marker. Studies reveal that gene-rich and genepoor regions correspond to banding patterns within the genome. ...
... reproducible positions, so the bands are another level of marker. Studies reveal that gene-rich and genepoor regions correspond to banding patterns within the genome. ...
Horizontal Gene Transfer
... Viral DNA incorporated into recipient's DNA About 8% of human genome originates from viruses ...
... Viral DNA incorporated into recipient's DNA About 8% of human genome originates from viruses ...