CHAPTER 27
... Serum analysis works on antigen-antibody reactions. The more alike the serums of two different species the less will be the precipitation between them. Since each serum protein is the product of a gene, this indicates the similarities between the genes coding for the proteins. ...
... Serum analysis works on antigen-antibody reactions. The more alike the serums of two different species the less will be the precipitation between them. Since each serum protein is the product of a gene, this indicates the similarities between the genes coding for the proteins. ...
Clinical Next Generation Sequencing (From Bench to Clinitions)
... Target Exome Sequencing With targeted sequencing, a subset of genes or regions of the genome are isolated and sequenced. Targeted approaches using next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to focus time, expenses, and data analysis on specific areas of interest. Such targeted analysis can ...
... Target Exome Sequencing With targeted sequencing, a subset of genes or regions of the genome are isolated and sequenced. Targeted approaches using next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to focus time, expenses, and data analysis on specific areas of interest. Such targeted analysis can ...
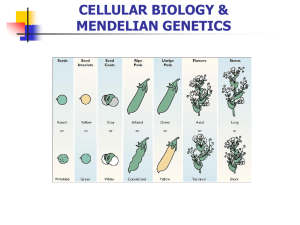
Biology 212 General Genetics
... Parental types = 497 + 472 = 969/1000 = 96.9% non-recombinant Recombinant types = 19 + 12 = 31/1000 = 3.1% recombinant types Construct a linkage map of the two genes ...
... Parental types = 497 + 472 = 969/1000 = 96.9% non-recombinant Recombinant types = 19 + 12 = 31/1000 = 3.1% recombinant types Construct a linkage map of the two genes ...
Sea Slug Steals Photosynthesis Genes From Algae
... to rely on sunshine for its nutrition. So if something happens to their food source, they have a way of not starving to death until they find more algae to eat." Chloroplast are plant organelles that contain chlorophyll, the green photosynthetic pigment. Researchers have known since the 1970s that t ...
... to rely on sunshine for its nutrition. So if something happens to their food source, they have a way of not starving to death until they find more algae to eat." Chloroplast are plant organelles that contain chlorophyll, the green photosynthetic pigment. Researchers have known since the 1970s that t ...
Introduction to Epigenetics - BITS Embryo
... • Tight control for maintaining gene silencing (vertebrate genes are less “leaky” compared to bacterial) • Transcriptional silencing of transposons (‘genome ...
... • Tight control for maintaining gene silencing (vertebrate genes are less “leaky” compared to bacterial) • Transcriptional silencing of transposons (‘genome ...
09. Paramecium Species Reading C
... partner, and cunningly hunt for food, all of which allow it to thrive in unsalted waters worldwide. The myth of the simple Paramecium was shattered in 2006 when scientists sequenced its genome. They discovered almost 40,000 genes-about twice as many as in a human cell. They also found evidence of ep ...
... partner, and cunningly hunt for food, all of which allow it to thrive in unsalted waters worldwide. The myth of the simple Paramecium was shattered in 2006 when scientists sequenced its genome. They discovered almost 40,000 genes-about twice as many as in a human cell. They also found evidence of ep ...
Human Genetics and Molecular Biology Review Packet
... 7) How does the structure of DNA predict its function as the source of an organism’s genetic information? a) How does the structure of the double helix predict how it is copied? b) What did scientists infer about the information that must be contained in the DNA sequence? 8) Some of the energy in su ...
... 7) How does the structure of DNA predict its function as the source of an organism’s genetic information? a) How does the structure of the double helix predict how it is copied? b) What did scientists infer about the information that must be contained in the DNA sequence? 8) Some of the energy in su ...
Protein-coding genes in eukaryotic DNA
... Why are the number of protein-coding genes about the same for worms, flies, plants, and humans? This has been called the N-value paradox (number of genes) or the G value paradox (number of genes). ...
... Why are the number of protein-coding genes about the same for worms, flies, plants, and humans? This has been called the N-value paradox (number of genes) or the G value paradox (number of genes). ...
Genetics - World of Teaching
... genes from a parent to the child. Example : Marfan Syndrome (Individual is tall, has long arms and legs) ...
... genes from a parent to the child. Example : Marfan Syndrome (Individual is tall, has long arms and legs) ...
Chapter 10: Genes and Chromosomes
... Several important human genes are located on the X chromosome o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ ...
... Several important human genes are located on the X chromosome o ___________________________________ o ___________________________________ ...
ppt - Barley World
... the transformed cells to grow while the growth of the nontransformed cells is inhibited. Examples include 1. Antibiotic resistance 2. Herbicide resistance “Among the most widely used antibiotic resistance genes as selectable markers are neomycin phosphotransferase II (nptII) and hygromycin phosphotr ...
... the transformed cells to grow while the growth of the nontransformed cells is inhibited. Examples include 1. Antibiotic resistance 2. Herbicide resistance “Among the most widely used antibiotic resistance genes as selectable markers are neomycin phosphotransferase II (nptII) and hygromycin phosphotr ...
Inheritance of Sex and Sex-Linked or Influenced Traits
... Another form of epigenetics Gene from specific parent is silenced in each generation using attached methyl groups Methyl group are removed during meiosis and replaced once new embryo forms Most seem to control early ...
... Another form of epigenetics Gene from specific parent is silenced in each generation using attached methyl groups Methyl group are removed during meiosis and replaced once new embryo forms Most seem to control early ...
Exploring Mendelian Genetics
... Thomas Hunt Morgan wanted to test Mendel’s principles on organisms other than plants ...
... Thomas Hunt Morgan wanted to test Mendel’s principles on organisms other than plants ...
LEQ: How do genes assort independently?
... From that he came up with the Law of Independent Assortment: Each pair of alleles segregates independently from other pairs of alleles during gamete formation ...
... From that he came up with the Law of Independent Assortment: Each pair of alleles segregates independently from other pairs of alleles during gamete formation ...
Lecture: Mendelian Genetics
... Chromosomes = made up of a protein core and strands of DNA in the nucleus of a cell (46 chromosomes make up 1 human cell) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) = Molecule that carries the genetic code, ladder with rungs made of base pairs ...
... Chromosomes = made up of a protein core and strands of DNA in the nucleus of a cell (46 chromosomes make up 1 human cell) DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) = Molecule that carries the genetic code, ladder with rungs made of base pairs ...
Honors BIOLOGY
... The farther apart two genes are on a chromosome, the more likely a break will occur between them due to crossing-over. In fact, if two genes are more than a half-chromosome length away from each other, they will cross over so frequently (50%) that they appear to be on different chromosomes. That is, ...
... The farther apart two genes are on a chromosome, the more likely a break will occur between them due to crossing-over. In fact, if two genes are more than a half-chromosome length away from each other, they will cross over so frequently (50%) that they appear to be on different chromosomes. That is, ...
Genetic nomenclature for Trypanosoma and Leishmania
... 6. Choosing names for genes Gene names are groups of three to six letters without any interruptions, if possible an abbreviation of the name of encoded protein or RNA. Ultimately it will be necessary to generate and maintain standardised lists of known genes and their names in salivarian trypanosome ...
... 6. Choosing names for genes Gene names are groups of three to six letters without any interruptions, if possible an abbreviation of the name of encoded protein or RNA. Ultimately it will be necessary to generate and maintain standardised lists of known genes and their names in salivarian trypanosome ...
File
... DNA was first discovered in 1869, but scientists didn’t really know much about it. After analyzing cells of may different organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals, scientists found DNA in all of them. In 1944 Avery confirmed that DNA was the material of inheritance. ...
... DNA was first discovered in 1869, but scientists didn’t really know much about it. After analyzing cells of may different organisms, from bacteria to plants and animals, scientists found DNA in all of them. In 1944 Avery confirmed that DNA was the material of inheritance. ...
Genetics: The Science of Heredity
... The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies the type of protein produced A group of three bases codes for one specific amino acid Ex: ...
... The order of the nitrogen bases along a gene forms a genetic code that specifies the type of protein produced A group of three bases codes for one specific amino acid Ex: ...
CHAPTER 1
... had been based on extrapolations from gene-rich areas as opposed to a composite of gene-rich and gene-poor areas. • The order of almost all (99.9%) nucleotide bases are exactly the same in all people. •The functions are unknown for over 50% of discovered genes. ...
... had been based on extrapolations from gene-rich areas as opposed to a composite of gene-rich and gene-poor areas. • The order of almost all (99.9%) nucleotide bases are exactly the same in all people. •The functions are unknown for over 50% of discovered genes. ...
Relating Mendelism to Chromosomes
... 8. Describe the independent assortment of chromosomes during Meiosis I. Explain how independent assortment of chromosomes produces genetic recombination of unlinked genes. 9. Distinguish between parental and recombinant phenotypes. 10. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. Explain ho ...
... 8. Describe the independent assortment of chromosomes during Meiosis I. Explain how independent assortment of chromosomes produces genetic recombination of unlinked genes. 9. Distinguish between parental and recombinant phenotypes. 10. Explain why linked genes do not assort independently. Explain ho ...
New Genes for New Environments Facilities
... Enabling evaluation of the world’s best candidate GM traits from both public and private research organisations under Western Australian conditions in a highly contained and safe testing environment. The aim of the New Genes for New Environment facilities is to accelerate the development of higher y ...
... Enabling evaluation of the world’s best candidate GM traits from both public and private research organisations under Western Australian conditions in a highly contained and safe testing environment. The aim of the New Genes for New Environment facilities is to accelerate the development of higher y ...